Common Ions
advertisement
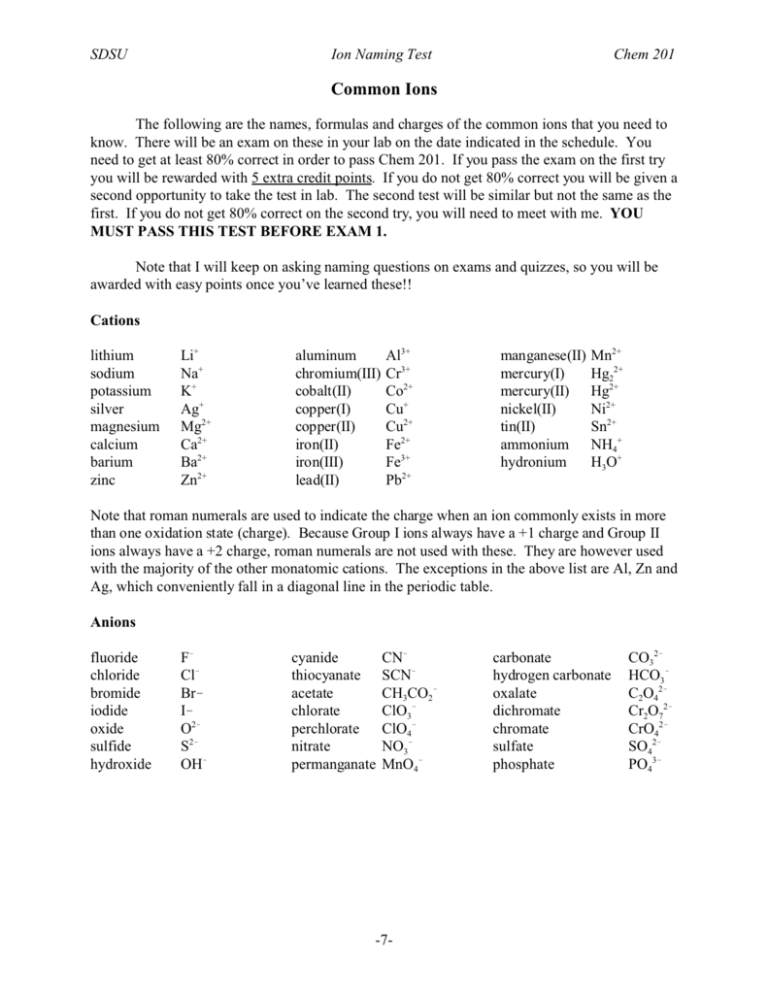
SDSU Ion Naming Test Chem 201 Common Ions The following are the names, formulas and charges of the common ions that you need to know. There will be an exam on these in your lab on the date indicated in the schedule. You need to get at least 80% correct in order to pass Chem 201. If you pass the exam on the first try you will be rewarded with 5 extra credit points. If you do not get 80% correct you will be given a second opportunity to take the test in lab. The second test will be similar but not the same as the first. If you do not get 80% correct on the second try, you will need to meet with me. YOU MUST PASS THIS TEST BEFORE EXAM 1. Note that I will keep on asking naming questions on exams and quizzes, so you will be awarded with easy points once you’ve learned these!! Cations lithium sodium potassium silver magnesium calcium barium zinc Li+ Na+ K+ Ag+ Mg2+ Ca2+ Ba2+ Zn2+ aluminum chromium(III) cobalt(II) copper(I) copper(II) iron(II) iron(III) lead(II) Al3+ Cr3+ Co2+ Cu+ Cu2+ Fe2+ Fe3+ Pb2+ manganese(II) mercury(I) mercury(II) nickel(II) tin(II) ammonium hydronium Mn2+ Hg22+ Hg2+ Ni2+ Sn2+ NH4+ H3O+ Note that roman numerals are used to indicate the charge when an ion commonly exists in more than one oxidation state (charge). Because Group I ions always have a +1 charge and Group II ions always have a +2 charge, roman numerals are not used with these. They are however used with the majority of the other monatomic cations. The exceptions in the above list are Al, Zn and Ag, which conveniently fall in a diagonal line in the periodic table. Anions fluoride chloride bromide iodide oxide sulfide hydroxide F! Cl! Br! I! O2! S2! OH! cyanide thiocyanate acetate chlorate perchlorate nitrate permanganate CN! SCN! CH3CO2! ClO3! ClO4! NO3! MnO4! -7- carbonate hydrogen carbonate oxalate dichromate chromate sulfate phosphate CO32! HCO3! C2O42! Cr2O72! CrO42! SO42! PO43! SDSU Ion Naming Test Chem 201 Naming Rules The cation is named first, then the anion. No prefixes are used to indicate the number of each, since if you know the ion charges you can determine how many of each will be in the chemical formula. The overall charge has to be zero, so each ion in the formula is multiplied by the smallest integer that will give an overall charge of zero. Example: aluminum chloride aluminum = Al3+ chloride = Cl! Since chloride is !1, three chlorides are needed to cancel the +3 of aluminum. The formula is AlCl3. Example: iron(III) sulfate iron(III) = Fe3+ sulfate = SO42! Since iron(III) is +3 and sulfate is !2, both ions have to be multiplied by integers in order to cancel the charges. The smallest integers would be 2 for iron(III) (to give a total +6) and 3 for sulfate (to give a total !6). The formula is Fe2(SO4)3. Note that parentheses are placed around a polyatomic ion when more than one is used. -8- SDSU Ion Naming Test Chem 201 Practice Exam Name the following ionic compounds: 1. BaBr2 2. NaNO3 3. NH4 [CH3 CO2 ] 4. CuSO4 5. Fe2 O3 6. ZnCl2 7. Na2 Cr2 O7 8. Cr(OH)3 9. KClO3 10. LiHCO3 Give the correct molecular formula for the following: 1. sodium perchlorate 2. calcium phosphate 3. copper(I) nitrate 4. mercury(II) iodide 5. potassium permanganate 6. zinc sulfide 7. lead(II) sulfate 8. lithium dichromate 9. manganese(II) fluoride 10. barium acetate answers: barium bromide, sodium nitrate, ammonium acetate, copper(II) sulfate, iron(III) oxide, zinc chloride, sodium dichromate, chromium(III) hyd roxid e, potassium chlora te, lithium hyd rogen carb onate, NaClO 4, Ca3(PO 4) 2, CuNO3, HgI 2, KM nO 4, ZnS, PbSO 4, Li2Cr 2O 7, MnF 2, Ba(CH 3CO 2) 2. -9- -10-











