Boiling Point Trends
advertisement
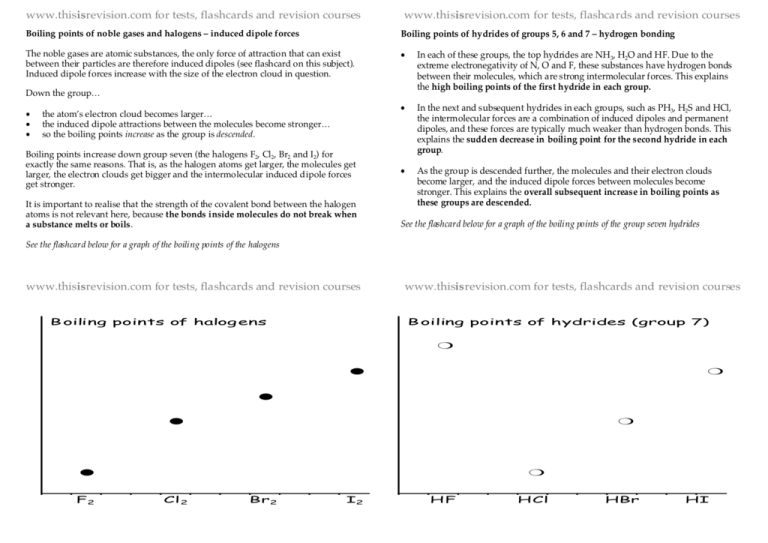
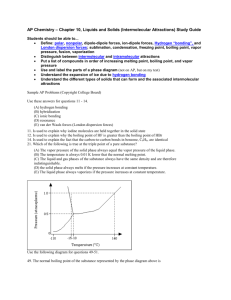
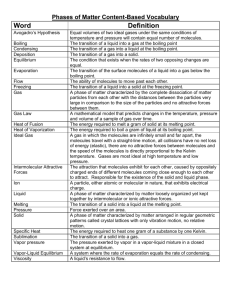
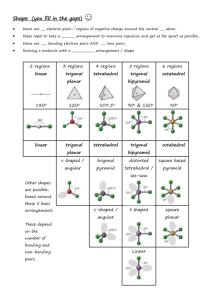
www.thisisrevision.com for tests, flashcards and revision courses www.thisisrevision.com for tests, flashcards and revision courses Boiling points of noble gases and halogens – induced dipole forces Boiling points of hydrides of groups 5, 6 and 7 – hydrogen bonding The noble gases are atomic substances, the only force of attraction that can exist between their particles are therefore induced dipoles (see flashcard on this subject). Induced dipole forces increase with the size of the electron cloud in question. • In each of these groups, the top hydrides are NH3, H2O and HF. Due to the extreme electronegativity of N, O and F, these substances have hydrogen bonds between their molecules, which are strong intermolecular forces. This explains the high boiling points of the first hydride in each group. • In the next and subsequent hydrides in each groups, such as PH3, H2S and HCl, the intermolecular forces are a combination of induced dipoles and permanent dipoles, and these forces are typically much weaker than hydrogen bonds. This explains the sudden decrease in boiling point for the second hydride in each group. • As the group is descended further, the molecules and their electron clouds become larger, and the induced dipole forces between molecules become stronger. This explains the overall subsequent increase in boiling points as these groups are descended. Down the group… • • • the atom’s electron cloud becomes larger… the induced dipole attractions between the molecules become stronger… so the boiling points increase as the group is descended. Boiling points increase down group seven (the halogens F2, Cl2, Br2 and I2) for exactly the same reasons. That is, as the halogen atoms get larger, the molecules get larger, the electron clouds get bigger and the intermolecular induced dipole forces get stronger. It is important to realise that the strength of the covalent bond between the halogen atoms is not relevant here, because the bonds inside molecules do not break when a substance melts or boils. See the flashcard below for a graph of the boiling points of the group seven hydrides See the flashcard below for a graph of the boiling points of the halogens www.thisisrevision.com for tests, flashcards and revision courses B oiling points of halog ens www.thisisrevision.com for tests, flashcards and revision courses B oiling points of hydrides (group 7) ❍ ● ❍ ● ● ❍ ● F2 ❍ Cl 2 Br2 I2 HF HCl HBr HI