Digestive System Enzymes and Hormone Chart
advertisement
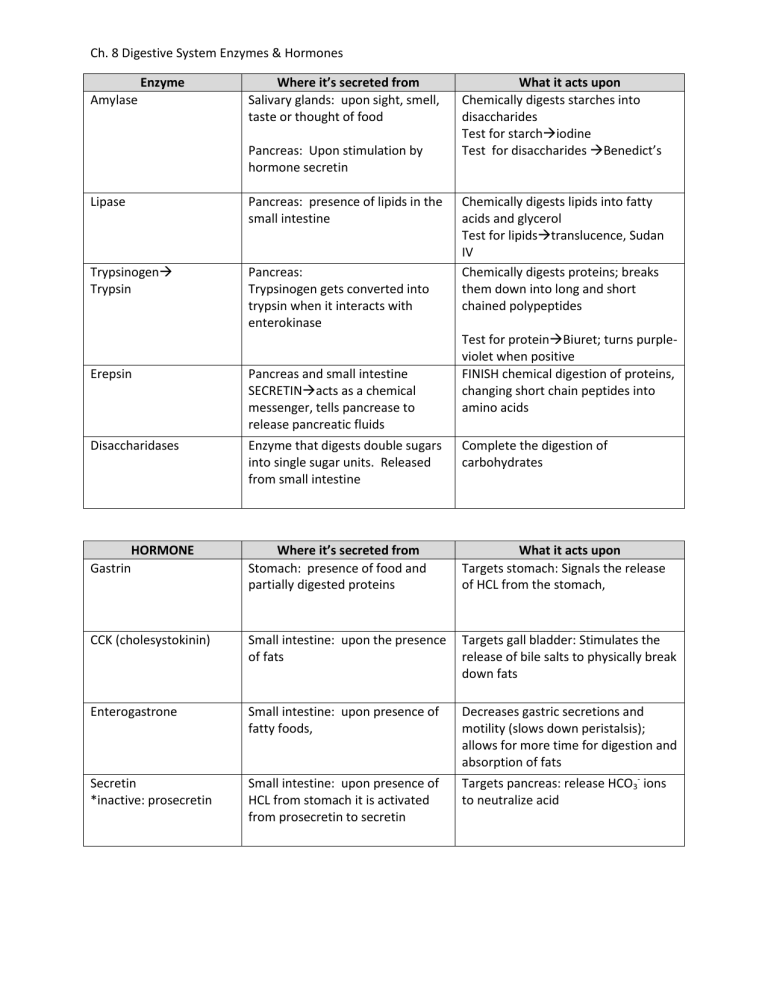
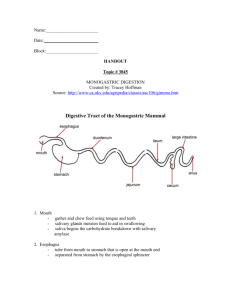
Ch. 8 Digestive System Enzymes & Hormones Enzyme Amylase Where it’s secreted from Salivary glands: upon sight, smell, taste or thought of food Pancreas: Upon stimulation by hormone secretin Lipase Pancreas: presence of lipids in the small intestine Trypsinogen Trypsin Pancreas: Trypsinogen gets converted into trypsin when it interacts with enterokinase What it acts upon Chemically digests starches into disaccharides Test for starchiodine Test for disaccharides Benedict’s Chemically digests lipids into fatty acids and glycerol Test for lipidstranslucence, Sudan IV Chemically digests proteins; breaks them down into long and short chained polypeptides Test for proteinBiuret; turns purpleviolet when positive FINISH chemical digestion of proteins, changing short chain peptides into amino acids Erepsin Pancreas and small intestine SECRETINacts as a chemical messenger, tells pancrease to release pancreatic fluids Disaccharidases Enzyme that digests double sugars into single sugar units. Released from small intestine Complete the digestion of carbohydrates HORMONE Gastrin Where it’s secreted from Stomach: presence of food and partially digested proteins What it acts upon Targets stomach: Signals the release of HCL from the stomach, CCK (cholesystokinin) Small intestine: upon the presence of fats Targets gall bladder: Stimulates the release of bile salts to physically break down fats Enterogastrone Small intestine: upon presence of fatty foods, Decreases gastric secretions and motility (slows down peristalsis); allows for more time for digestion and absorption of fats Secretin *inactive: prosecretin Small intestine: upon presence of HCL from stomach it is activated from prosecretin to secretin Targets pancreas: release HCO3- ions to neutralize acid