Acid-Base: Introduction to Ac
advertisement

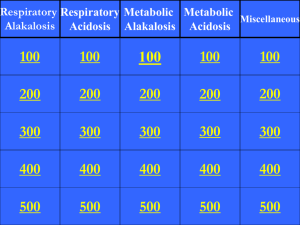
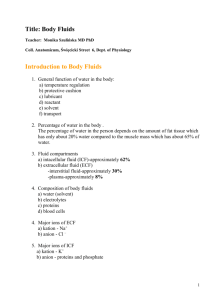
Imperial Valley College Division of Nursing Education and Health Technologies VN 112 Module C-2: Acid-Base: Introduction to Acidosis and Alkalosis 1. Statement of Purpose As nurses become increasingly involved in physical assessment of their clients, a comprehensive knowledge of significant signs and symptoms becomes an essential module to build on the normal physiological principles of the acid-base balance process, its pathologies and treatment. By understanding these principles the student will be better able to anticipate, observe for, and report imbalances that may occur, as well as to relate the principles to assessment of physiological alterations. This module emphasizes both the assessment of acid-base imbalances and the nursing care involved. 2. Terminology Review terminology for Module C-1 Metabolic alkalosis Metabolic acidosis Respiratory alkalosis Respiratory acidosis 3. Classroom Content 3.1 Classroom Objectives a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. Identify metabolic and respiratory acidosis and alkalosis, given laboratory values for arterial blood gases. Describe signs and symptoms of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis for clients of all ages. Describe signs and symptoms of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis for clients of all ages. Identify altered function in metabolic acidosis caused by diabetes, renal insufficiency/failure, severe diarrhea, and malnutrition. Identify altered function in metabolic alkalosis caused by ingestion of excess sodium bicarbonate, excessive vomiting, gastric lavage or levin tube, and administration of potent diuretics. Identify altered function in respiratory acidosis caused by emphysema, sedatives (narcotics), pneumonia, and brain trauma. Identify altered function in respiratory alkalosis caused by hysteria, drugs (acetylsalicylic acid), oxygen-lack, and ventilators. Analyze data from a given situation and identify the acid base imbalance. Discuss concept map development in a client with an acid-base imbalance. 3.2 Learning Activities a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. 3.3 References a. b. c. d. e. f. 4. Kozier, Fundamentals of Nursing Anatomy & Physiology text. Doenges, Nursing Care Plans. Videotapes & CAI as assigned. Springhouse,Fluids & Electrolytes Made Incredibly Easy Hogan, Fluids, Electrolytes, & Acid-Base Balance, Reviews & Rationales Clinical Objectives a. b. c. d. e. 5. Know terminology. Review the major acid and base by-products of cellular metabolism Review the chemical symbols of sodium, chloride, potassium, hydrogen, oxygen, ammonia, ammonium, carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, and bicarbonate. Review the relationship between hydrogen ions and normal pH, acidosis and alkalosis. Review the interaction between the body's chemical buffers, lungs, cells and kidneys Review assigned chapters in Kozier, Fundamentals of Nursing View videotapes as assigned. Complete CAI as assigned. Given a client=s lab values for arterial blood gases, identify normals, deviations from normal, and label these deviations as either metabolic or respiratory alkalosis or acidosis Reflect on the concept map, the nursing interventions appropriate to the client care situation. Administer medication (not IV') to the assigned client. Complete a concept map on the assigned client. Apply principles of Standard Precautions to the assigned client. Skills Laboratory Requirements Continue skills form Modules A, B-1,B-2, C-1. Imperial Valley College Division of Nursing Education and Health Technologies VN 112 Study Guide Module C-2 Introduction to Acidosis/Alkalosis I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Acid-Base Balance A. General information B. Definitions 1. Alkalosis 2. Acidosis 3. pH C. Buffer systems 1. Carbonic Acid-Sodium Bicarbonate 2. Protein 3. Phosphate Acid-Base Imbalances A. General information B. Respiratory imbalances 1. Respiratory acidosis a. Definition b. What happens c. Compensation 2. Respiratory alkalosis a. Definition b. What happens c. Compensation C. Metabolic imbalances 1. Metabolic acidosis a. Definition b. What happens c. Compensation 2. Metabolic alkalosis a. Definition b. What happens c. Compensation D. Blood gas disturbances E. Fluid balance disturbances 1. ECF deficit 2. ECF excess 3. Plasma -- interstitial shift 4. Interstitial -- plasma shift Respiratory Acidosis A. Causative conditions B. Nursing observations Respiratory Alkalosis A. Causative conditions B. Nursing observations Metabolic Acidosis A. Causative Conditions B. Nursing observations Metabolic Alkalosis A. Causative Conditions B. Nursing observations