PROCAINAMIDE
advertisement

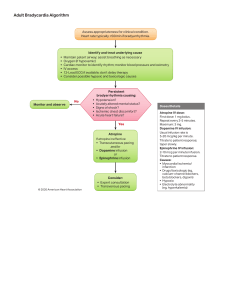
EMERGENCY EDUCATION CENTER UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN HOSPITAL AND CLINICS Course: Pharmacology Content: PROCAINAMIDE (PRONESTYL) A. Actions 1. 2. 3. 4. Decreases myocardial excitability and automaticity in the atria, Purkinje fibers and ventricles (Inhibits ectopic pacemaker) Prolongs repolarization of myocardial cells which may terminate reentry dysrythmias Peripheral vasodilator Negative inotrope B. Indications From the AHA 1. Wide variety of arrhythmias, including stable monomorphic VT with normal QT interval and preserved LV function 2. IF BP stable-Reentry SVT uncontrolled by adenosine and vagal maneuvers 3. Stable wide complex tachycardia of unknown origin 4. Atrial fibrillation with rapid rate in WPW C. Side Effects 1. 2. 3. 4. D. Precautions 1. 2. E. Hypotension Change in mental status AV conduction defects Torsades de Pointes CHF or renal dysfunction May produce dysrythmias in the setting of an AMI, low potassium or low magnesium Contraindications 1. 2. 3. 4. Use with other drugs that prolong QT (ex Amiodarone) or patients known to have prolonged QT Ventricular pacemaker with heart rate less than 100 Asystole/PEA Torsades de Pointes or patients with prolonged QT intervals F. Dosage 1. Recurrent pulseless V Fib/V Tach a. 20 mg/min IV infusion b. 50 mg/min IV infusion in urgent situations c. administered to a total of 17 mg/kg d. use in cardiac arrest limited by need for slow infusion and uncertain efficacy G. H. 2. Pulses present a. 20 mg/min IV infusion b. administered to a total of 17 mg/kg 3. Maintenance infusion a.1-4 mg/min (in D5W or NS) Administration 1. Procainamide may be given until: dysrythmia is suppressed QRS duration increases by >50% hypotension occurs total dose of 17 mg/kg is administered 2. If cardiac or renal dysfunction is present reduce maximum total dose to 12mg/kg and maintenance infusion to 1-2 mg/min 4. BP and ECG must be monitored continuously Miscellaneous 1. Procainamide Oral procainamide is an outpatient cardiac medication