HISTOLOGY lecture one
advertisement

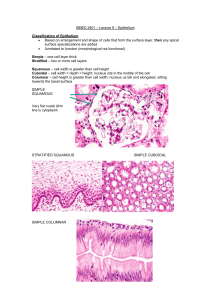
HISTOLOGY Lecture one DR. ASHRAF SAID Start Of this lecture TISSUES TISSUE: A DEFINITION A group of connected and interdependent cells that cooperate to perform a specific function Categories of Tissue 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Epithelial Tissues • General Features Cellular Layer + Basement Membrane Epithelial Tissues • General Features Cellular Layer + Basement Membrane No Direct Circulation/Blood Supply Touch Each Other Rapid Rate of Cell Reproduction • Structural Classification Cell Shapes EPITHELIAL TISSUES Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Epithelial Tissues • Structural Classification Cell Shapes Cell Layers Simple Stratified Epithelial Tissues • Major Types Simple Squamous Epithelium Simple Squamous Epithelium Function: Exchange Sample Locations: Alveoli, capillaries Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified Squamous Epithelium Function: Protection Sample Locations: Skin, Mouth, Repro tracts Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Function: Absorption or Secretion Sample Locations: Kidney, Hormone Glands Simple Columnar Epithelium Function: Absorption (or Secretion) Sample Location: Digestive Tract Microvilli Simple Columnar Note goblet cells Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Note cilia Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Function: Absorption, Secretion, Movement Sample Locations: Respiratory & Repro Ducts Transitional Epithelium Function: Stretchability Sample Location: Urinary Bladder What kind of tissue is this? Epithelium cont. Epithelium that lines cavities sits on lamina propria. – Supports epithelium – Binds epithelium to other tissue – Provides nutrition Sides of cells are named – Basal – Apical (free) – Lateral Basal Lamina-Lamina Propria Specializations of Cell Surface Microvilli – Found mainly on absorptive cells – Brush border, 1m high Cilia / flagella – Cylindrical, motile structures, 5-10m high – Contain microtubules – Basal bodies Microvilli Apical region of an intestinal epithelial cell seen with TEM. Filaments that constitute the core of the microvilli are clearly seen. An extracellular cell coat (glycocalyx) is bound to the plasmalemma of the microvilli. x45,000. Cilia Concept 1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry Isolating Organelles by Cell Fractionation Cell fractionation – Takes cells apart and separates the major organelles from one another The centrifuge – Is used to fractionate cells into their component parts Epithelium Epithelium that lines cavities sits on lamina propria. – Supports epithelium – Binds epithelium to other tissue – Provides nutrition Sides of cells are named – Basal – Apical (free) – Lateral Basal Lamina-Lamina Propria Specializations of Cell Surface Microvilli – Found mainly on absorptive cells – Brush border, 1m high Cilia / flagella – Cylindrical, motile structures, 5-10m high – Contain microtubules – Basal bodies Microvilli Apical region of an intestinal epithelial cell seen with TEM. Filaments that constitute the core of the microvilli are clearly seen. An extracellular cell coat (glycocalyx) is bound to the plasmalemma of the microvilli. x45,000. Microvilli (Cs) Actin filaments can be seen inside the structure. Cilia Simple Squamous Epithelium (endothelium) Simple cuboid epithelium Simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) Lines a body cavity Such as abdominal cavity. Simple columnar epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium (non-keratinized) Transitional epithelium Pseudostratified epithelium