knobology 101
advertisement

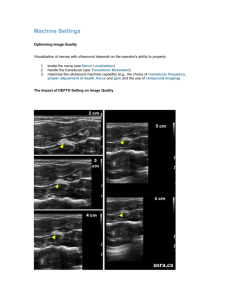
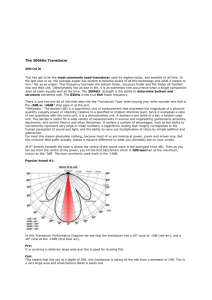
AMSSM Beginner Ultrasound Course KNOBOLOGY 101 David M. Harsha, MD St.Vincent Sports Performance January 17th, 2014 Ultrasound Components Pulser - applies high amplitude voltage to energize the crystals Transducer - converts electrical energy to mechanical (ultrasound) energy and vice versa Receiver - detects and amplifies weak signals Display - displays ultrasound signals in a variety of modes Memory - stores video display Generation of image Electrical signal sent to transducer Transducer produces sound waves Sound waves transmit into soft tissues and interact with soft tissue interfaces, some of which reflect back to the transducer Transducer converts sound waves into electrical current to produce an image Attenuation Attenuation • Loss of amplitude, power, and intensity as sound travels. • Three contributing factors: • Absorption • Scatter • Reflection • Sound degrades 0.5dB/1MHz/1cm • @3cm, 6dB w 4MHz Compound spatial imaging Transducers Band Width-Range of frequencies that come out of a transducer Frequency of transducer determines image quality Higher frequency Higher resolution and less sound beam penetration Lower frequency Lower resolution and increased depth of sound beam penetration Transducer types Curved Increase field of view Generate lower frequency waves than linear transducers and provide images of lower resolution Increased depth of penetration Transducer types Linear Field of View Large >40mm Medium<40mm Small-hockey stick Transducer Movement Heel-Toe Maneuver Transducer Movement Tilting Transducer Movement Rotation Modes B mode (brightness) M mode (motion) • Most common standard • Represents movement of scanning mode • 2-D cross sectional view of the underlying structures • Made up of numerous Bmode (brightness mode) scan lines. • Field of view is the tissues that are intersected by the scanning plane structures over time • Initially a 2-D image is acquired and a single scan line is placed along the area of interest • M-mode will then show how the structures intersected by that line move toward or away from the probe over time Modes Power Doppler • Very sensitive assessment of presence of flow • Does not show direction of flow or Velocity of flow Important to adjust the color gain optimally or Doppler imaging causes artifact Color Doppler • Shows presence of vascularity and direction of flow • Does not show flow Velocity • Useful for differentiating vascular from non vascular structures Modes GE Logic e Sonosite Edge Power Doppler PD detects flow only And not direction Color Doppler Color Doppler detects Bidirectional flow Frequency Higher frequency Higher resolution and less sound beam penetration Lower frequency Lower resolution and increased depth of sound beam penetration Select the highest frequency transducer possible for the required depth of penetration Frequency Frequency Depth • Structures get smaller and smaller as the depth is increased • Select the appropriate depth setting to target the structure of interest • Center structure of interest Depth GE Logic e Sonosite Edge Depth Focus Number of focal zones Focal zones will decrease frame rate that produces a windshield-wiper effect • • • Image quality and beam focus best at the focal zone Move depth of focal zones to depth where structure is located in order to optimize resolution Sonosite has auto-focus feature Near field Focal zone Far Field Focus Focus Focus Proper focal points Focal point too deep Gain • Compensates for attenuation (reduction in sound amplitude) as sound travels deeper into tissue • Returning signals amplified by receiver-turning up the volume! • Displayed image is brighter and more visible • • • Near field Far field Entire field (overall gain) • Gain can be adjusted • Excessive GAIN will cause "noise" to the image. • Time gain compensation (TGC) is adjusted to selectively amplify weaker signals Gain GE Logic e Sonosite Edge Gain Time Gain Compensation Time Gain Compensation Auto-optimization • Machine provides optimal • Gain • Frequency • Only available in B and Doppler modes Image Optimization 1. Select Transducer and Frequency 2. Adjust Depth 3. Adjust Focal Zones if present 4. Adjust Gain/TGC Other Features • Instructors can explain as needed: • Virtual Convex • Measurement • Extended Field of View • Beam steer or SonoMBe for needle guidance • Saving images to the machines Measurement Measurement