8 - KUET
advertisement

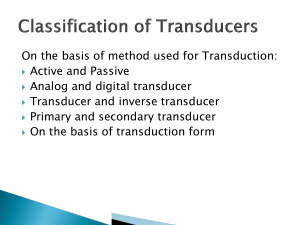
Presented byMd. Bashir Uddin Roll: 1215502 Dept. of BME KUET, Khulna-9203 A transducer is a device that changes one form of energy into another. Microphone Sound Speaker Electric signal A Electric signal Sound transducer is placed at the input of a measurement system. A physiological transducer is a device that changes physiological variables into electrical signal. Physiological variable Transducer Electrical Signal Block diagram of physiological transducer A variable associated with the physiological process of the body is called Physiological variable Ionic potentials & currents Mechanical movements Hydraulic pressure & flow Temperature Chemical reaction and many more Electrical Electro-mechanical Electromagnetic Photonic Photovoltaic, or any other form of energy. Transducer consists of 2 parts Sensing or detector element Transduction element Sensing or detector element senses or responses to physical phenomena or change in a physical object/body. Transduction element transforms the output of sensing to an electrical output. Accuracy Sensitivity Threshold Noise Linearity 5 categories: Based on principal of transduction Primary or Secondary Passive or Active Analog or Digital Transducer and Inverse Transducer Thermo electric Magneto resistive Electro kinetic Optical Resistive Inductive Capacitive Bourdon tube acts as a primary transducer which converts pressure into displacement. The linear displacement then convert into electrical voltage by linear variable differential transformer which acts as a secondary transducer. Active Transducer: No external power reqd. to produce I/p. It draws power from input applied. Example: Piezo electric x’tal used for accelartion measurement. Passive Transducer: External power required for transduction. So it is externally powered. Example : Resistive (Strain Gauge), Inductive (LVDT), Capacitive Transducers. Analog Transducer: Convert I/p quantity into an analog o/p. Analog o/p is a continuous function of time. Example: Strain gauge, LVDT, thermocouple Digital Transducer: Converts I/p quantity into an electrical o/p in the form of pulses. Example: Digital Encoder Transducer: Convert nonelectrical variables into electrical parameters. Example: Microphone Inverse Transducer: Converts electrical signal to physical quantity. Example: Speaker Physical variable Types of transducer Force Piezoelectric Unbounded strain gage Displacement Variable Resistance Variable inductance Variable capacitance Linear Variable differential transducer Mercury strain gage Velocity Magnetic Indection Temperature Thermocouple Thermostat Light Photo voltaic Photo electric Magnetic field Hall effect