ARP Basics Addressing Local Packets
advertisement

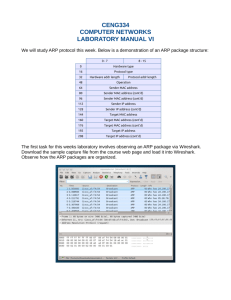
2015-11-13 ARP Basics based on Chapter 7 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers Addressing Local Packets • When the destination network and the source network are the same, the packet travels directly – Nodes on local networks are identified by MAC addresses (hardware addresses) • ARP – Address Resolution Protocol – Matches IP addresses with MAC addresses – ARP table – locally cached IP-MAC pairs – ARP requests and replies • local-broadcast queries and answers for IPMAC pairings 1 2015-11-13 ARP Tables The "arp" command, in both Linux and Windows, displays (and can modify) the current contents of the ARP table. ARP Headers st bit numbers st 1 word 2 nd word rd word 3 0 1 2 1 byte 3 4 nd 5 6 7 8 9 rd Hardware type Hardware address length Protocol type th Opcode Protocol Address Length Sender hardware address Sender protocol address (high-order two bytes) 4th word 5 word Sender protocol address (low-order two bytes) th Target hardware address th Target protocol address 6 word 7 word th 2 byte 3 byte 4 byte 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 • ARP supports multiple hardware protocols, upper-layer protocols • Sender fills in hardware (MAC) address and protocol (IP) address • If opcode is "request", Target addresses are 0 • If opcode is "reply", Target addresses are original requester's addresses 2 2015-11-13 An ARP Transaction ARP packets - Request • ARP request ("who-has") broadcasts a request for the MAC address matching a given IP address 3 2015-11-13 ARP packets - Reply • ARP reply ("is-at") is sent by a node with the requested IP address, showing its MAC address (also in the SRC header) ARP packets – Gratuitous Reply • Gratuitous ARP – an ARP reply with no preceding request – broadcast, advertising the sender (this one is an Access Point) 4 2015-11-13 ARP activity – maybe do this at home • Start wireshark – Display filter: arp && eth.addr==<your MAC address> • Find your gateway: – route or route -n (Windows: route print ) • Flush the ARP table: – sudo arp –d <gateway> • ping a non-local site: – ping google.com Or see the ARP worksheet • Observe ARP traffic to find the gateway • ping a “fake” local site: – ping <your network-ID>.<fake host-ID> • Observe ARP search for local site 5