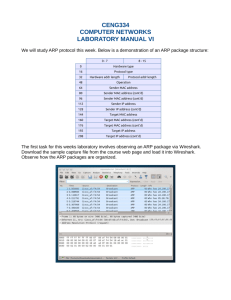
Wireshark_lab_arp
advertisement

Introduction to Networking & Network Management Engineering Science Department Wireshark_arp Experiment Your Name: Your Station: Your Computer: You Partners: Date: A. Objectives 1. Learn what protocol analysis means 2. Learn how to use Wireshark 3. Monitor traffic at specific port & capture the arp protocol data on an interface 4. Analyze the arp protocol, its format & contents 5. Understand the arp operation & the difference between the arp request & response protocols B. Configuration & Network Setup No configuration is needed for this experiment. Each student needs to do the experiment on her/his own & submit the report. Note that you can save the Wireshark captures in your Ubuntu Document folder with your name. C. Procedure 1. Turn off the computer to flush the arp table (on some computers/OSes the arp table may not be flushed!). Boot the computer watch for the display to show a list of OSs (e.g., Ubuntu, Ubuntu backup, & Windows 7) for you to choose. Select & highlight UBUNTU (NOT Ubuntu Backup) & Enter for the UBUBTU OS to boot. You may need to enter the password that your instructor provides to be able to see the UBUNTU screen after timeout. 2. Open a Terminal page by the command & enter sudo arp –a to see the arp table (see man arp). Enter “sudo wireshark -i eth0 -c 6” to open the Wireshark screen. Make sure you see for the “Capture Options”: Interface = eth0, Capture Filter = arp, & Stop Capture = after “6” packets. Then click “Start”. You should see the captured packets pop up in the top panel of the Wireshark screen. On the Wireshark screen go to View at the top menu & drop down ”Expand All” is checked & the Link, Network layers are enabled. Note the encapsulations arp packet by the Ethernet frame”. Question Computer you used (A, B, C, D) Write the content of the arp table List the packets in Wireshark top panel 3. Answer Now select the first arp segment on the top panel & use the middle & bottom panels of the Wireshark to identify the following fields, write the # of bytes for each field & the content in the table below. The ifconfig command & arp packet format https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Address_Resolution_Protocol can help answering/verifying some of the questions. Question # of byte s in Dec # of byte s in Hex Content The source eth0 address in the frame Is it the same as the source computer eth0 address? The destination eth0 address in the frame Under ARP packet in the middle Question AMK # of byte s in Dec # of byte s in Hex Content 2/6/2016 1 Introduction to Networking & Network Management Engineering Science Department Hardware Type Protocol Type Hardware size Protocol size Operation code What it signifies Sender MAC address Sender IP address Target MAC address Target IP address 4. Do the above for the second arp packet. Question # of byte s in Dec # of byte s in Hex Content Hardware Type Protocol Type Hardware size Protocol size Operation code What it signifies Sender MAC address Sender IP address Target MAC address Target IP address 5. In this section, you need to work with one of your partner & identify the hardware address of your partner’s computer by using arp. Connect the two computers using eth2 of each computer. Do not ping the computers yet. Open a new terminal & enter “sudo wireshark -i eth2 -c 6” to open the Wireshark screen. Make sure you see for the “Capture Options”: Interface = eth0, Capture Filter = arp, & Stop Capture = after “6” packets. Then click “Start”. Now open a new terminal & ping your partner’s computer by 3 pings to capture the arp request & reply packets on eth2 of your computers. The ifconfig command & arp packet format https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Address_Resolution_Protocol can help you answering/verifying some of the questions. Question # of byte s in Dec # of byte s in Hex Content Hardware Type Protocol Type Hardware size Protocol size Operation code What it signifies Sender MAC address Sender IP address Target MAC address Target IP address AMK 2/6/2016 2 Introduction to Networking & Network Management Engineering Science Department 6. Do the above for the second arp packet. Question # of byte s in Dec # of byte s in Hex Content Hardware Type Protocol Type Hardware size Protocol size Operation code What it signifies Sender MAC address Sender IP address Target MAC address Target IP address Explain how the arp request / reply differ in their contents. D. Report 1. Type all your responses to the questions in the tables above including your observations & comments neatly. 2. Make sure to power off all the devices, remove the cables & return them to the cabinet, & clean up your station. 3. Submit your report by the due date. AMK 2/6/2016 3