Decomposers
advertisement

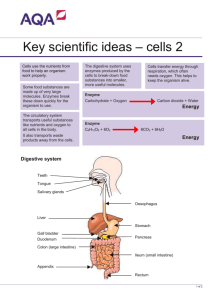
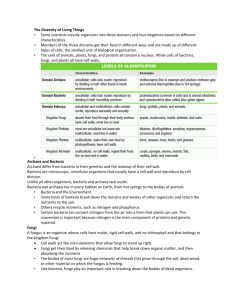
Decomposers; When plants and animals die, they become food for decomposers like bacteria, fungi and earthworms. Decomposers or saprotrophs recycle dead plants and animals into chemical nutrients like carbon and nitrogen that are released back into the soil, air and water There are 4 general classes of decomposers. Bacteria, Legumes, Fungi and worms. 1 Bacteria: Bacteria can be found everywhere. They live in the water, in the air and on land. Bacteria are prokaryotic, which means they don't have a nucleus or a mitochondrea like other single‐celled organisms. There are more bacteria on Earth than all the other organisms combined. (5 nonillion (5x1030)). Bacteria are among the smallest forms of life on Earth. In fact, you may have up to 100 million bacteria in your body right now! Some bacteria are harmful and cause diseases like typhoid and cholera. Other bacteria are helpful. Bacteria species are divided according to their shapes; Spheres, rods and spirals. 2 3 Legumes: Most species of legumes (alfalfa, lentils, beans, chick‐peas, peas, peanuts) have bacteria with which they maintain a symbiotic relationship. A symbiotic relationship is one in which two species benefit each other. The roots of most of these plants have a nitrogen‐fixing bacteria, rhizobium, that changes nitrogen in the air into the nitrates the plants need to synthesize proteins. 4 Fungi; Fungi like mushrooms, mildew, mold and toadstools are not plants. They don't have chlorophyll so they can't make their own food. Fungi release enzymes that decompose dead plants and animals. Fungi absorb nutrients from the organisms they are decomposing! There are over 50,000 species of fungi. Most fungi are very, very small! There are many fungi that are helpful. Penicillin and other antibiotics are made from fungi. Some fungi like mushrooms, truffles and yeast are edible or used in making food. Other fungi are harmful. 5 6 Earth Worms; There are over 1,800 species of earthworms. Earthworms need moist environments to survive. If they dry out, they have trouble burrowing into the soil and they will die. Earthworms eat dead plants and animals. When they eat, they also take in soil and tiny pebbles. They take in nutrients from microorganisms in the material they ingest. Earthworms then excrete wastes in the form of casts. Casts are rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potash. In addition to breaking down organic materials and adding nutrients to the soil, earthworms also help loosen the soil so air can circulate. This helps plants grow. 7 8 Eco­Dome 9