study guide digestive system
advertisement

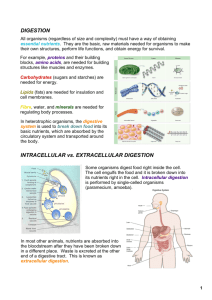
Name_______________________ Date_______ Period____ Nutrition and Digestion Study Guide Unit Objectives: Contrast heterotrophs and autotrophs Define the terms calorie and kilocalorie and explain how the energy content of food is measured Describe the functions of the six basic types of nutrients found in the human diet Distinguish between mechanical and chemical digestion of food Describe the functions of the different parts of the human digestive system - mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, rectum, anus List the principle enzymes, where they are produced, the type of food they act upon, and the end product of chemical digestion Part I Nutrition: 1. a. Define nutrition. b. List and define the two parts of nutrition. 2. What is the difference between a heterotroph and an autotroph. Give an example of each. 3. a. What do calories measure? 4. Which nutrients (carbs, lipids, or proteins) contain the most energy per gram? 5. What is the difference between unsaturated fats and saturated fats? 6. What are the dangers of excess saturated fats in the diet? 7. List two functions of each of the following nutrients: a. Proteins: b. Carbohydrates: c. Lipids 8. Describe the differences and similarities of vitamins and minerals. 9. List two digestive diseases and explain how they disrupt homeostasis. 10. List examples of foods where the following nutrients are found. a. Carbohydrates b. Proteins c. Lipids d. Vitamin C e. Vitamin A f. Calcium 11. Why is water considered such an essential nutrient? 12. a. What type of nutrient is roughage? b. Why is roughage (fiber) an important part of a healthy diet? Part II Digestion: 13. a. Explain the difference between intracellular digestion and extracellular digestion. b. Give an example of an organism that uses each type of digestion. 14. a. What is the difference between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion? b. List two areas where mechanical digestion occurs. c. List two areas where chemical digestion occurs. 15. List the three structures that are found in the mouth and describe the function of each. 16. Describe the structure and function of the esophagus. 17. Describe the process of peristalsis. 18. Describe the structure and function of the stomach. 19. List and describe the 2 processes of digestion. 20. List two digestive functions of hydrochloric acid. 21. In which organ does most chemical digestion take place. 22. Why do you suppose the small intestine is such a long organ. 23. Describe the structure and function of villi and microvilli in the small intestine. 24. Describe the structure and function of the large intestine (colon). 25. Why are the liver, pancreas, and gall bladder considered accessory organs to the digestive system? 26. Describe the digestive function of the liver. 27. What is the digestive function of bile? 28. What does it mean to emulsify a lipid? 29. Describe the structure and function of the gall bladder. 30. Complete the following table Type of enzyme secreted Nutrient digested by pancreas (substrate broken down) a. d. b. e. c. f. Products of nutrient digestion g. h. i. 31. The digestive enzymes above actually begin breaking down food in which organ? 32. What do you suppose would happen if 10 feet of your small intestine were removed? 33. What would happen if food went into your trachea (windpipe)? 34. What structure prevents food from entering the trachea? ****Know how to label a digestive system diagram with the following structures: Mouth Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus Liver Pancreas Gall bladder Appendix