Intestines
advertisement

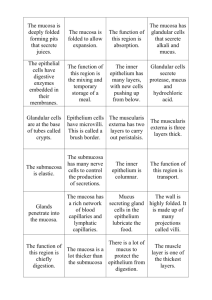
Intestine, liver, gall bladder, and pancreas 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract central lacteal rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells Lamina propria Muscularis mucosa Submucosa Muscularis externa (tunica muscularis) Serosa Slide #37 (Ed 904-64b). Small intestine, donkey. Mesothelium of serosa tunica muscularis the myenteric (“Auerbach’s) plexus located between the inner circular and outer longitudinal smooth muscle layers of the tunica muscularis neuronal cell bodies of the submucosal (“Meissner’s) plexus submucosal (Brunner’s) glands intestinal crypts (glands of Lieberkuhn) muscularis mucosa lamina propria central lacteal muscularis mucosa Slide #37 (Ed 904-64b). Small intestine, donkey. Intestinal absorptive cells Simple columnar epithelium Paneth cells Goblet cell Paneth cell brush” or “striated” border = High density of non-branching microvilli of uniform length. Microfilaments are the cytoskeleton component in microvilli Slide #37 (Ed 904-64b). Small intestine, donkey Paneth cells Absorptive cells Enteroendocrine Cells (EC cells) Mitotic figures Slide #37 (Ed 904-64b). Small intestine, donkey. Enteroendocrine cells in fundic stomach, rabbit (toluidine blue) To see the distribution of EC cells among glands 244 Chief cells Parietal cell Enteroendocrine cells monkey 146 Duodenum, Enteroendocrine cell Crypts of Lieberkühn Goblet and absorptive cells, Muscularis mucosa Lamina propria. Submucosa Submucosal Brunner's glands. 152 Duodenum Brunner’s glands Absorptive cells Goblet cells Paneth cell Enteroendocrine cell Intestinal villus Slide #37 (Ed 904-64b). Small intestine, donkey. Enteroendocrine cells DEMO SLIDE BOX 57 -‐ Small intestine (ileum), dog. Goblet cell Intestinal crypts (glands Or Crypts of Lieberkuhn Smooth Muscle in Intestinal villus Peyer’s patches lamina propria of the villi central lacteals DEMO SLIDE BOX 57 -‐ Small intestine (ileum), dog. Enteroendocrine cell Intestinal crypts (glands Or Crypts of Lieberkuhn DEMO SLIDE BOX 225 (C-‐H-‐73). Small intestine (jejunum), dog. Absorptive cells epithelial Modifications = Brush border and goblet cells central lacteal Strips of Muscularis mucosa lamina subglandularis muscularis mucosa submucosa DEMOSLIDE BOX 225 (C-‐H-‐73). Small intestine (jejunum), dog. lamina subglandularis stratum granulosum stratum compactum muscularis mucosa submucosa Enteroendocrine cells Paneth cells lamina subglandularis Absorptive cells DEMOSLIDE BOX 225 (C-‐H-‐73). Small intestine (jejunum), dog. Crypts of Lieberkuhn submucosa tunica muscularis lamina subglandularis muscularis mucosa Submucosal (“Meissner’s”) Smooth muscle cells serosa. Mesothelium of serosa myenteric (“Auerbach’s”) plexuses Slide #192 (Pf 5-‐84d). Small intestine (jejunum), pig. . submucosa Absorptive cells lamina propria muscularis mucosa tunica muscularis Slide #192 (Pf 5-‐84d). Small intestine (jejunum), pig. central lacteal Brush border of absorptive cells Intestinal absorptive cells Simple columnar epithelium Smooth muscle cells of the muscularis mucosa lamina propria Goblet cell Paneth cells Enteroendocrine cells Slide #89 (83 DF1) – Small intestine, puppy (dog). Epithelium Lamina propria Muscularis mucosa Submucosa tunica muscularis Serosa Slide #89 (83 DF1) – Small intestine, puppy (dog). Lymph nodules Intestinal crypts (glands Or Crypts of Lieberkuhn Small intestinal villi central lacteal Slide #89 (83 DF1) – Small intestine, puppy (dog). Dividing cells Epithelium Lamina propria myenteric (“Auerbach’s”) plexuses Muscularis mucosa (developing) Submucosa with lymphoid cell infiltration tunica muscularis Serosa Serosa mesothelium Compare luminal surfaces of the small and large intestines small intestines Villi large intestines NO Villi DEMO SLIDE BOX 167 (C003-‐H-‐29) -‐ Large intestine (cecum), dog. villi are absent Epithelium Lamina propria Muscularis mucosa Submucosa tunica muscularis Smooth muscle Serosa Lymph nodules Peyer’s patches Intestinal crypts (glands Or Crypts of Lieberkuhn DEMO SLIDE BOX 167 (C003-‐H-‐29) DEMO SLIDE BOX 167 (C003-‐H-‐29) -‐ Large intestine (cecum), dog. villi are absent Intestinal crypts (glands Or Crypts of Lieberkuhn Epithelium Lamina propria Muscularis mucosa absorptive cells and goblet cells Enteroendocrine cells DEMO SLIDE BOX 61. Large intestine (colon), cat. Epithelium Lamina propria Muscularis mucosa (developing) Submucosa with lymphoid cell infiltration tunica muscularis Serosa DEMO SLIDE BOX 61. Large intestine (colon), cat. Intestinal crypts (glands Or Crypts of Lieberkuhn Epithelium Lamina propria absorptive cells goblet cells Muscularis mucosa Submucosa DEMO SLIDE BOX 171 (E3-‐H-‐38). Large intestine (colon), horse. the taenia coli; a gross thickening of the longitudinal layer of tunica muscularis in the horse. taenia coli Lymph nodules Intestinal crypts (glands Or Crypts of Lieberkuhn DEMO SLIDE BOX 168 (C003-‐H-‐38) -‐ Large intestine (colon), dog. Intestinal crypts (glands Or Crypts of Lieberkuhn Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells Lamina propria Muscularis mucosa Submucosa Muscularis externa (tunica muscularis) Serosa DEMO SLIDE BOX 168 (C003-‐H-‐38) -‐ Large intestine (colon), dog. Enteroendocrine cells Intestinal crypts (glands Or Crypts of Lieberkuhn Slide #43 (K9-‐1). Anal region, dog. the recto-‐anal junction and regional skin. skin rectum goblet cells located in the crypts nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium rectum regional skin circumanal glands (perianal glands) which can become neoplastic Slide #43 (K9-‐1). Anal region, dog. keratinized stratified squamous epithelium Slide #43 (K9-‐1). Anal region, dog the circumanal glands (perianal glands) in this region CCT Walled off with CCT parasite external anal sphincter = bundles of skeletal muscle al upt mous DEMO SLIDE BOX 62-‐ Rectum and anal canal, dog. the circumanal (perianal) glands skin large invagination of the anal sac. rcular at cter. region nized rectum simple columnar epithelium DEMO SLIDE BOX 62-‐ Rectum and anal canal, dog. keratinized stratified squamous the circumanal (perianal) glands skeletal muscle fibers are part of the external anal sphincter skin skin nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium rectum tunica muscularis (smooth muscle) is somewhat thickened to form the internal anal sphincter. large invagination of the anal sac. rectum Slide #77 (C007-‐H-‐107A). Pancreas, dog. pancreatic islets CENTROACINAR CELLS ARE THE BEGINNING CELLS OF THE INTERCALATED DUCTS THAT DRAIN THE SECRETORY ACINI OF THE PANCREAS. THEY SECRETE BICARBONATE serous acini INTERCALATED DUCTS Bile Canaliculi Bile luminal surfaces 155 Bile duct Blood luminal surface Slide #77 (C007-‐H-‐107A). Pancreas, dog. INTERCALATED DUCTS pancreatic islets Pancreas has Islets and centroacinar cells, but no striated ducts The salivary gland has striated ducts, but no Islets and centroacinar cells Striations in base of duct cells Demo 186 Salivary gland Slide #193 (GT-‐1-‐102). Pancreas, goat. CENTROACINAR CELLS pancreatic islets INTERCALATED DUCTS DEMO SLIDE BOX 180– Small intestine (duodenum) and pancreas, dog. (157) CENTROACINAR CELLS pancreatic islet Slide #93 (1017) -‐ Pancreas and duodenum, cat.) Pancreas duodenum Dispersed pancreatic islet cells CENTROACINAR CELLS Portal radicles containing: A bile duct 155 Branch of portal vein, Branch of hepatic artery Lymphatic vessel (usually) or portal canals Liver 155 Cords of hepatocytes Liver Bile Canaliculi Bile luminal surfaces 155 Bile duct Blood luminal surface DEMO SLIDE BOX 169 (P001-‐H-‐84B) – Liver, pig. hepatic lobules hepatocytes Sinusoids discontinuous DEMO SLIDE BOX 169 (P001-‐H-‐84B) – Liver, pig. Hepatic sinusoids flow between rows of hepatocytes toward the central vein. venule which is a branch of the portal vein hepatic lobule capsule portal triad. arteriole, which is a branch of the hepatic artery either simple cuboidal or simple columnar epithelium Of bile duct. interlobular connective tissue are larger veins, not accompanied by an artery and a duct, named sublobular veins Slide #45 (Pig 1-‐87c). Liver, Pig. hepatic lobule portal triad. venule bile duct artery Central vein DEMO SLIDE BOX 170 (E3-‐H-‐84-‐1). Liver, horse. Hepatic sinusoids flow between rows o hepatocytes toward the central vein. Space of Disse portal triad. HEPATOCYTE SPACE OF DISSE BILE CANALICULI Slide #48 (PF5-‐76B). Liver & gall bladder, pig. Kupffer cells Mesothelium of capsule central vein portal triad. capsule Sinusoids discontinuous Slide #48 (PF5-‐76B). Liver & gall bladder, pig. Mesothelium of capsule Kupffer cells portal triad. Kupffer cells (i.e. the liver macrophages lining the sinusoids) are noticeable because they ingested black Kupffer cells Slide #48 (PF5-‐76B). Liver & gall bladder, pig. Microvilli occur apically but are difficult to see gallbladder No muscularis mucosae occurs so the lamina propria blends with the submucosa. Note the tunica muscularis is not well organized. The thick layer of CCT outside the tunica muscularis is called the “perimuscular connective tissue” layer. Slide #48 (PF5-‐76B). Liver & gall bladder, pig. gallbladder Slide #167 (M-‐1 87F). Liver, monkey Central vein Kupffer cells Slide #111 (87NG)—Liver, goat Slide #117 (SP-‐1-‐61) -‐ Liver and gallbladder, sheep. Slide #117 (SP-‐1-‐61) -‐ Liver and gallbladder, sheep. Slide # 94 (Rbt-‐87G)—Liver, rabbit. DEMO SLIDE BOX 58 -‐ Liver and gallbladder, dog.