CELL ORGANELLES
advertisement

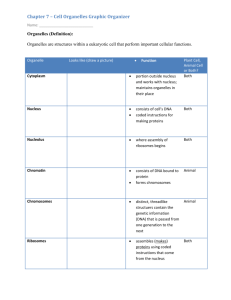
CELL ORGANELLES Nucleus – Not found in prokaryotes - contains most of the cell’s DNA (chromatin is DNA and proteins in nucleus) - control center of cell (regulates growth, reproduction, metabolism, etc.) - contains the hereditary information Nucleolus – site of ribosome synthesis (manufactures ribosomes) Ribosomes – Smallest and most numerous of the organelles - site of protein synthesis - located on rough endoplasmic reticulum or floating freely in the cytoplasm Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – covered with ribosomes (ex. in pancreas) - newly synthesized proteins are modified, transported, and stored here. - assists in the production of proteins for secretion and the cell membrane - acts as an “internal highway” for proteins Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum – no ribosomes on surface (ex. in liver) - site of lipid and steroid synthesis - modifies and detoxifies toxic compounds Golgi Apparatus – named after a scientist - modifies and packages proteins into vesicles - often these packaged proteins are secreted out of the cell - many proteins that enter the Golgi apparatus are received from the rough ER Mitochondrion – “powerhouse” of the cell - site of cellular respiration – produces ATP - energy is released from food molecules to power cellular activities - your mitochondria are inherited from your mother’s egg cell Lysosomes – animal cells, not plant cells (ex. in macrophages) - contain digestive enzymes that break down compounds for cell’s use - breakdown worn out organelles for recycling or removal from cell Cytoskeleton – - consists of a network of protein filaments and tubules that support the cell and help maintain shape of cell - assists in the movement of cytoplasm and cellular materials Cytoplasm – (cytoplasm = cytosol + most organelles) - includes gel-like fluid inside the cell membrane and all organelles other than the nucleus Vacuoles – - sacs that store a variety of materials such as water, salts, pigments, sugars, etc. - plants have a large vacuole that is involved in maintaining high pressure for support of cells and structures (as in leaves and flowers) - animal vacuoles tend to be smaller Chloroplast – Plant cells, not animal cells - site of photosynthesis - contains the pigment chlorophyll Cell Wall – found in plants, fungi, algae, and bacteria. - provides support and protection to the cell - prevents cell from bursting while under high pressure - plant cell walls contain large amounts of the polysaccharide cellulose Centrioles – animal cells, not plant cells - structures near the nucleus that help form the mitotic spindle (fibers) Cilia – Short, hairlike structures on the surface of a cell. They move in a wavelike motion. They usually occur in large numbers. Ex. on a paramecium, line the trachea (windpipe). Flagella – Long, hairlike structures that move in a whiplike motion. They usually occur singly or in pairs. Ex. used for movement in some bacteria or protozoa such as Euglena and Giardia. Human sperm cells also have flagella. Prokaryote – Refers to a cell that does NOT have a nucleus. Ex. bacteria Eukaryote – Refers to a cell that does have a nucleus. Ex. animal, plant, fungi, and protist cells Chromatin – DNA and proteins in the nucleus of a cell that is not dividing. Chromosomes – DNA and proteins in the nucleus of a cell that is dividing. Metabolism – All the chemical reactions that occur in an organism. (includes digestion and synthesis reactions) Specialization is the development of cells to perform specific functions more efficiently → It represents a division of labor where work is divided among the parts of the body. Cells differentiate into various types and forms. Advantages: The structural modifications of the cell (produced by specialization) allow it to work more efficiently. (form follows function) Limitations: Specialized cells don’t perform all of the organism’s functions. Therefore these cells are interdependent and if one type of these cells fail, the whole organism may suffer. LIMITS ON CELL GROWTH (Surface Area to Volume ratios) As a cell grows, the surface area to volume ratio decreases. Cells divide to solve this problem. VOLUME – SURFACE AREA – SURFACE AREA/VOLUME RATIOS -