Light and Lenses
advertisement

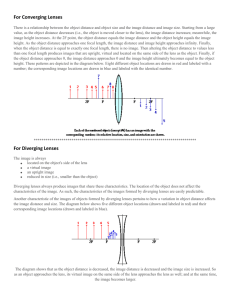
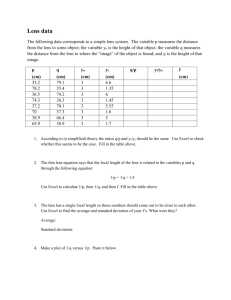
Optics: Light and Lenses TEACHER WORKSHEET Year Levels 5-7 OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the basics of how an eye works 2. Determine the focal point of a converging lens works BACKGROUND INFORMATION Seeing an object starts with the lens of your eye focusing on an image. This image is then projected onto a light-sensitive membrane within your eye called the retina. The retina then converts patterns of light into neuron signals that are sent to the brain. A camera works in a similar way to your eye. Light from an object enters through the lens and is focused onto the film containing light-sensitive chemicals, which are changed by the image-forming light rays. Lenses are transparent devices that refract or bend light. Differently shaped lenses refract light differently. A converging lens makes the light rays bend towards the centre, thus focusing the light whereas a diverging lens spreads or diverges the light. Once they were made of glass but now, to reduce weight they are made of plastic. When looking through a converging lens you will be able to see an inverted image. In this experiment we will make a pinhole camera to demonstrate how an eye sees an image and use a glass and water to make a lens. WHAT YOU NEED Part 1: Making a pinhole camera • Cardboard or shoe box • Black cardboard • Transparent/tracing paper • Aluminum foil • Electrical tape • Drawing pin • Scissors Part 2: Crossing light through a lens • Glass jar • Water • Sheet of white paper • Shoe box • Stanley knife • Torch • Darkened room WHAT TO DO Part 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Use a shoebox or make a cardboard box from the template provided. At one end of the box cut a square hole 1.5cm x 1.5cm in the centre. Cover this hole by taping a piece of aluminum foil over it. Use the drawing pin to make a hole no bigger than 2mm wide. By careful to make the whole as “clean” as possible. At the other end of the box cut a wider hole so that a 2cm edge of the box is remaining. Attached the transparent paper to this end of the box using the tape. Cut another piece of cardboard to cover the viewing end of the box. This should be ~10cm wide and the length should equal the length of the box plus 5cm either side to bend down the side of the box. Point the pinhole end at an Exit sign in the room or a well light object eg. A candle or light coming in through the window. You should see an image on the viewing side of the camera. TIP: When looking at an image through your pinhole camera make sure you are in a dark area and the object you are viewing is well light. Eg. Inside a dark room looking outside a window to a sunlight area. © Harper, A., Isoardi, G. and Nickels, K. 2008. Queensland University of Technology. Optics: Light and Lenses TEACHER WORKSHEET Year Levels 5-7 Part 2 10. At one end of the shoebox, cut two slits in the middle about 2.5cm apart. 11. Place the white paper in the shoebox and place the glass of water ~1/3 toward the slits. 12. Turn off the lights and shine the torch through the holes. 13. Measure the distance from the glass to where the light crosses (focal point). QUESTIONS 1. In part 1, is the image projected on the viewing screen right side up or upside down? Explain. The image will be inverted as rays from the top of the object are projected onto the bottom of the screen after passing through the pinhole, while rays from the bottom of the object project onto the top of the screen. 2. In part 2, where does the focal point appear? Answer will vary depending on glass thickness and curvature. 3. What factors would affect/change this focal point? Glass thickness and curvature of the glass. 4. How do you think our eye adjusts its focus? Our eye adjusts its focus by changing the shape of its lens. This is achieved by muscles attached to the lens that contract or relax to focus on objects at different distances. REAL WORLD APPLICATIONS OF LIGHT AND LENSES Human vision. The human eye contains a flexible lens. As people age, the lens becomes less flexible, making it difficult to refocus the eyes from close objects to far objects. People with such problems often require corrective lenses or glasses. The compound microscope uses a lens to produce an enlarged real image which is then magnified as a virtual image through the eyepiece. Lighthouses. The beam from a lighthouse is only effective if is projected as a focused, parallel beam, which is achieved by placing the light source at the focal length. CURRICULUM Essential Learnings: Energy and Change Years 5-9 -Energy can be transferred from one object to another. -Energy can be transferred from one medium to another. -Transfer of energy can vary according to the medium in which it travels. RESOURCES 1. Cunningham, J. and Herr, N. 1994. Hands-on Physics Activities with Real-Life Applications. The Centre for Applied Research in Education. United States of America. 2. Baxter, N. and Sweet, S. 2004. My Book of Science Experiments: Hundreds of experiments you can do at home. Bookmart Limited. England. © Harper, A., Isoardi, G. and Nickels, K. 2008. Queensland University of Technology.