erosion

SPECIFICATION TARGET: to be able to explain the impact of weathering, erosion and mass movement on river landscapes .
Key Point
Rivers are channels of water which drain the land’s surface. They erode, transport and deposit materials, creating steep valleys and wide floodplains. As river’s cut into the landscape they expose bedrock, leading to further change through weathering and mass movement.
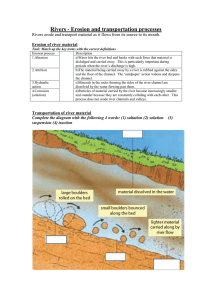
Processes of river erosion
Hydraulic action
Corrosion
Attrition Abrasion
Definitions
Hydraulic Action
This process involves the force of water against the bed and banks.
Abrasion/Corrasion
This is the process by which the bed and banks are worn down by the river’s load.
The river throws these particles against the bed and banks, sometimes at high velocity.
Attrition
Material (the load) carried by the river bump into each other and so are smoothed and broken down into smaller particles.
Corrosion
This is the chemical action of river water. The acids in the water slowly dissolve the bed and the banks.
Do you know your processes of erosion?
Freeze thaw
Weathering
Chemical
Biological
Soil creep
• Individual particles of soil move slowly down a slope under gravity and then collect at the bottom. The river may then erode this material.
slumping
• When the bottom of the valley side is eroded by the river. This makes the slope steeper and the valley side material can slide downwards in a rotational manner, often triggered by rain which lubricates the rock and makes it much heavier.