Types of Microcomputers
advertisement

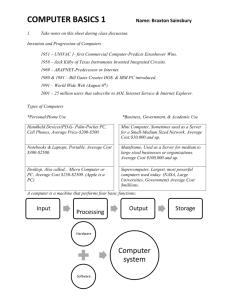
AL LE 2. Different Types of Computers M INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION There are many different types of computer available today. They are categorised into different types depending upon their size and processing power: G H What are the categories? 1. DESKTOP PC In the early days (1980's) these types of machine were called a micro-computer eT The desktop PC has a central processing unit housed in a metal case (often a 'tower'). Along with a keyboard, mouse and monitor. 1 Engineering work - designing kitchens at a showroom Video work - for handling your camcorder Music - creating, playing and storing Entertainment and information - internet. ADVANTAGES M Office applications such as wordprocessing, spreadsheets and databases. AL LE DESKTOPS ARE USED FOR: They can be easily upgraded to include new software or hardware They are relatively robust and can be used almost continually for very long periods of time. It is possible to 'mix and match' specifications and components, in effect creating a custom made machine. It is easy to replace an individual part if damaged or worn out. They can run a vast range of software, often simultaneously. G H DISADVANTAGES Desktop PCs are not easily portable. They are large and heavy. They require a large amount of permanent office space. They need a fan to prevent overheating. Thus they can be fairly noisy. They can only be run on mains electricity and need to be situated near to a power point. New advances in technology means that PCs get out of date very quickly. eT 2 ADVANTAGES They are portable and very easy to carry around. They can be used almost anywhere e.g. airports They are light to carry. Older laptops were fairly heavy, but advances in technology and much improved batteries have allowed them to become very lightweight. They are compact and can be easily stored in a standard briefcase. They are quiet to run as unlike a Desktop PC, there is often only a small (or no) cooling fan creating a noise. G H Laptop computers generally cost more than a Desktop PC with exactly the same specification because they are more difficult to design and manufacture. M The key difference between a Desktop PC and a laptop is that the laptop is built as a relatively small one-piece unit. AL LE 2. LAPTOPS DISADVANTAGES They are easily damaged if dropped eT They are more expensive to purchase than a similar Desktop PC They cannot be expanded in the same way as a Desktop PC e.g. new graphics cards, more memory. Can run on battery power for only a relatively short time, usually between 1-6 hours. They are attractive to thieves and can be easily stolen. The screen may be small if needed for detailed work e.g. CAD/CAM design 3 ADVANTAGES AL Palmtops are very similar to PDAs in their use. The main difference is that Palmtops have a built in keyboard. M Originally developed as an electronic organiser. Rapid development has resulted in palm tops and PDAs becoming almost cut down computers LE 3. PDA Small, can easily be fitted into a pocket or handbag. Lightweight to carry - typically 200g Long battery life compared with laptop (up to 30 hours) Power up immediately when they are turned on, no need to go through boot up sequence. Many have cut down versions of common office software They can be connected to a desktop PC or Laptop and the files can be transferred over. Many (but not all) Palmtops and PDAs are much lower in cost than H G PCs or Laptops DISADVANTAGES The screen is small Keyboards tend to be small and cramped eT They cannot be easily upgraded They cannot be used for such a wide range of tasks as the laptop or Desktop They are easy to steal They can be damaged if dropped They have a relatively small amount of memory and cannot store large amounts of data 4 Large, powerful computers that can carry out different tasks for many people at the same time They execute billions of process large volumes of data MAINFRAMES They are usually AL simultaneously. • They are operated by specialist, trained personnel and kept in air-conditioned rooms away from the office or factory floor. LE instructions per second and can M 4. MAINFRAMES connected to a large number of peripherals e.g. printers, disc drives, terminals and so on Very expensive an average mainframe would cost around 4 million G H pounds to build. MAINFRAMES ARE USED FOR: Mainframe computers are often used to control an entire factory assembly line - recording the movement of materials, paying of bills, sending invoices and so on eT Gas and Electricity suppliers - for Billing Banks - for managing your accounts Insurance companies - looking after your policies Airlines - handling your tickets Police - crime detection Car companies - managing factories 5 and most expensive computers in the world They are used for performing trillions of complex calculations in a very short AL time. M Supercomputers are the fastest LE 5. SUPERCOMPUTERS SUPERCOMPUTERS ARE USED FOR: Weather forecasting Space exploration Military establishment weapons research. Pharmaceutical \ Drug testing G H Advanced scientific research BLUE GENE/L reported to operated at 280.6 teraflops per second processors eT 130,000 32 trillion bytes of memory 400 TBytes of Hard Disk Storage 2.500 square feet of floor space built to simulate the physics of a nuclear explosion 6 M SUPERCOMPUTERS CONT… Whilst they are working, supercomputers generate so much heat that an air conditioning system is required. • The atmosphere must be kept free of dust particles. Special filters have to be installed to ensure that the air is kept clean. AL The supercomputer usually requires its own electricity generator LE There can be many miles of cables which connect the computer to the various peripherals. 6. EMBEDDED COMPUTERS The embedded computer is a single chip that contains all the elements that are essential for any computer i.e. RAM / ROM CPU Input / Output Another term often used for an embedded computer is a 'microcontroller'. H Clock G EMBEDDED COMPUTERS CONT… Computer chips are now cheap enough to install in everyday items. They offer eT many functions that would otherwise be far too expensive to produce. Telephones Televisions Microwaves Washing Machines Cars 7