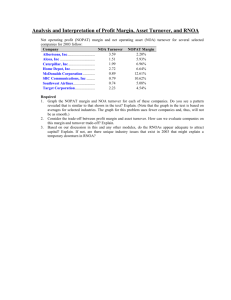
Additional Practice with the Financial Ratios

Additional Practice with the Financial Ratios
1. A small manufacturing business has the following accounts at the end of the year (note, the
Retained Earnings has already been adjusted).
Notes Payable
Capital Stock
Taxes
Sales Revenue
$600
$150
$ 50
$1,000
Selling & Admin. Expenses
Accounts Receivable
Retained Earnings
Interest Expense
Cost of Goods Sold
$100
$100
$ 50
$150
$500 Accounts Payable $200
Inventory $300 a. Construct the income statement and balance sheet, along with the common-size version of each. b. Calculate and briefly explain the following ratios: Current Ratio, Quick Ratio c. Calculate and briefly explain the following ratios: Asset Turnover, Fixed-Asset Turnover d. Calculate and briefly explain the following ratios: Debt Ratio, Long-Term Debt Ratio e. Calculate and briefly explain the following ratios: Gross Profit Margin, Net Profit Margin f. Calculate and briefly explain the following ratios: Return on Assets, Return on Equity g. Calculate and briefly explain the following ratios: Debt-Equity, Equity Multiplier h. Calculate and briefly explain the following ratios: Inventory Turnover; Days’ in Inventory i. Calculate and briefly explain the following ratios: A/R Turnover; Days’ in A/R
2. You are forecasting sales of $1,000 for next year. The cost of goods sold has been running at about 50% of sales while the inventory turnover rate has been steady at 5, and the accounts receivable at 10. What is your forecast for next year’s inventory and accounts receivable?
3. This year sales were $1,000. You are forecasting sales to increase by 20% and the profit margin to remain at 10%. You have already forecasted total assets to be $500 and total debt (i.e., liabilities) to be $260. What is your forecast for net income, return on assets, and return on equity?
4. The fixed asset turnover has been running at 4 and the net profit margin 10%.
Management is considering purchasing a new fixed asset for $10 million. What is your projection for the change in sales and net income as a result of this purchase?
5. You are projecting sales to be $1,000 next year. In the current year, cost of goods sold were 80% of sales and selling & administrative expenses 10% of sales. In addition, you know that the tax rate will be a 30%. The times interest earned ratio has been 10.
Construct the forecast for your income statement.
6. You are projecting sales to be $1,000 next year with a net profit margin of 10%. This year retained earnings were $200. The corporation has a dividend pay-out rate of 40%.
What is your forecast for next year’s retained earnings?
1
7. The manager of an office supply store has noticed that the accounts receivable turnover ratio has been increasing during the past few years. Is this a good or bad trend?
What might be driving this trend?
8. The finance department of a corporation is considering paying off the balance of a bank loan early. What will be the impact of this decision on the times interest earned ratio and debt-equity ratio? Very briefly indicate whether the impact on these ratios is generally considered good or bad.
9. A corporation has used cash to purchase a new fixed asset. What is the impact of this decision on the corporation’s current ratio and Debt-Equity ratio? In general, is the impact of on the ratios positive or negative?
10. A company has the following ratios. Attempt to complete the income statement and balance sheet using the information.
Gross Profit Margin = .60 (or, 60%)
Current Ratio = 5
Net Profit Margin = .05 (or, 5%)
Inventory Turnover = 30
Fixed Asset Turnover = 20
Total Asset Turnover = 10
Times Interest Earned = 3
Long-Term Debt Ratio = .30
Accounts Rec. Turnover = 50
COGS
SA&G
EBIT
. Inventory
Current Assets
1,000 .
Total Assets
Notes Payable
Interest
EBT
.
Owners’ Equity
Tax
Net Income .
2
The following (11-18) scenarios occur in a small manufacturing company.
11. In order to make a sale, the manger gives the customer a 5% price discount. What happens to the profit margin? Return on Assets? Debt-Equity ratio?
12. The manager purchases additional inventory by paying cash. What happens to the current ratio? Quick ratio?
13. The manager purchases an additional piece of machinery for $100. Assume the asset turnover ratio remains constant at 2 and profit margin remains constant at .10. What will be the expected change in sales? Net income?
14. The manager purchases an additional piece of machinery financed by a bank loan.
What will happen to the Debt-Equity ratio? Current ratio?
15. The workforce unionizes and obtains a 10% increases in hourly wages. What will happen to the profit margin? Return on assets? Debt-Equity ratio?
16. The manager decides to raise the selling price of the product. What will most likely happen to the gross profit margin? Inventory turnover?
17. The manager notices that his return on assets have been declining lately even though his gross profit margin has been increasing. What might explain this situation?
3
18. Place the letter next to the formula.
(A) LTD-Equity
(D) Gross Profit Margin
(B) Debt Ratio (C) Return on Assets
(E) Current Ratio (F) Times Interest Earned
(G) Total Asset Turnover
.
Gross Pr ofit
Sales
Total
.
Total
Debt
Assets
EBIT
.
Interest Expense
.
Long Term
Total
Debt
Equity
.
Sales
Total Assets
Current
.
Current
Assts
Liabilitie s
EBIT
.
Assets
20. For each of the following, determine what type of ratio it is.
A . Liquidity or Debt Ratio B . Efficiency Ratio C . Profitability Ratio
1. . Asset Turnover 2. . Net Profit Margin
3. . Return on Equity
5. . Debt to Equity
7. . Return on Assets
9. . Inventory Turnover
4. . Current Ratio
6. . Accounts Receivable Turnover
8. . Quick Ratio
10. . Debt Ratio
4