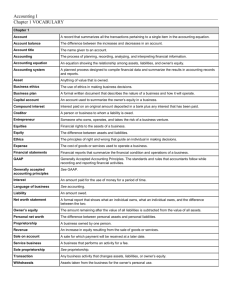
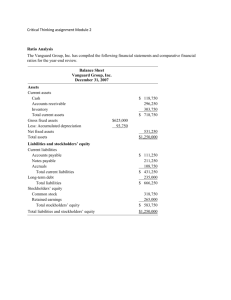
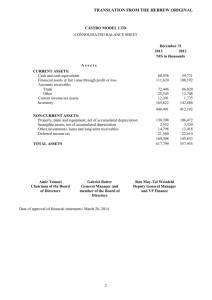
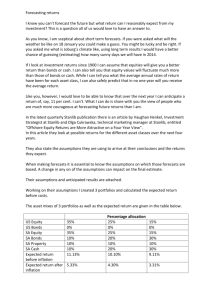
Accounting and the Business Environment
advertisement

64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 1 2:21 PM Page 1 Accounting and the Business Environment WHAT YOU PROBABLY ALREADY KNOW You want to purchase a cell phone and service plan. It would be easy to visit the closest store and buy the phone and company service plan the salesperson recommends. But would that necessarily be the selection that best services your needs with the least cost? Perhaps not. Before making this decision, it might make sense to: 1. gather information from reliable sources; 2. identify the various options and relevant costs; 3. evaluate the cost/benefit relationship of the different plans; and 4. make the decision. Financial decisions require thoughtful analysis utilizing accurate, reliable, and relevant information. The choice may be finding the best investment for your savings, deciding to purchase or lease a car, or choosing the optimal cell phone service plan. The process that is undertaken to manage our personal financial lives is the same as that employed by managers and owners of businesses. This chapter will explain the importance of accounting to the many users of financial information and how such data are accumulated and reported. Learning Objectives/Success Keys Define accounting vocabulary. Accounting is an information system that measures business activities, processes that information into reports, and communicates the results to decision makers. It is often referred to as the language of business. It’s important as you begin your study of accounting to understand the basic accounting vocabulary. Make sure you review the first three sections in Chapter 1 of the textbook carefully, as well as the list of interchangeable terms commonly used in accounting. Review Exhibit 1-3 (p. 4) in the main text to observe the flow of information between accounting and related organizations and users. Compare the three forms of business organization in Exhibit 1-4 (p. 7). 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 2 Define the users of financial information. Financial accounting information is used by individuals, businesses, investors, creditors, and taxing authorities. These users are known as decision makers. In other words, these people are reading the financial accounting information because they are hoping that it will assist them in coming to a decision about the accounting entity to which the statements relate. Describe the accounting profession and the organizations that govern it. All businesses need accountants. Accountants must deal with everything in a company in order to record all of its activities and therefore accountants often have the broadest view of what’s going on in that company. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) formulates accounting standards in the United States, while Certified public accountants, or CPAs, are licensed professional accountants who serve the general public. Indentify the different types of business organizations. Businesses can be organized as proprietorships, partnerships, or corporations. To allow for more liability protection, the Limited-Liability Partnership (LLP) and Limited-Liability Company (LLC) business organizations can also be used. Review Exhibit 1-4 (p. 7) in the text to see the differences among these types of organizations. Delineate the distinguishing characteristics and organization of a proprietorship. Sole proprietorships are businesses owned by a single person, who is usually also the main managed of the business. Proprietorships are distinct from their owners, and have separate accounting. Apply accounting concepts and principles. The basic accounting concepts and principles include the entity concept, the reliability (objectivity) principle, the cost principle, the going-concern principle, and the stablemonetary-unit concept. Make sure you understand these concepts and principles and how they are applied in the business world. Define and use the accounting equation. It is critical to understand each of the basic components of the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity 2 Chapter 1 | Learning Objectives/Success Keys 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 3 Review carefully “The Accounting Equation” section of the main text to understand these important components. Owner’s equity can be confusing. Pay special attention to Exhibit 1-6 (p. 11), which summarizes the four types of transactions that affect owner’s equity. Depict accounting for business transactions. A business transaction is an event that can be measured and affects any of the components of the accounting equation: assets, liabilities, or owner’s equity. Use the accounting equation to record the effects of each business transaction. Make sure that the amount of the increase or decrease on the left side of the equation (assets) is the same as that on the right side (liabilities and owner’s equity.) This is a simple but crucial concept to understand. Review the analysis of transactions in Exhibit 1-7 (p. 13). Explain and prepare the financial statements. Business transactions are analyzed, recorded, classified, and reported in the financial statements. Financial statements are commonly prepared on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis and include the income statement, statement of owner’s equity, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows. Refer to Exhibit 1-8 (p. 19) for examples of the four financial statements. Use financial statements to evaluate business performance. Financial statements communicate important information necessary for users to make business decisions. Together the financial statements provide useful information to evaluate business performance. Learning Objectives/Success Keys | Chapter 1 3 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 4 Demo Doc 1 Basic Transactions Learning Objectives 1–10 Rick Baldwin opened Rick’s Delivery Service on August 1, 2011. He is the sole proprietor of the business. During the month of August, Rick had the following transactions: a. Rick invested $6,000 of his personal funds in the business. b. The business paid $650 cash for supplies. c. The business purchased bicycles, paying $1,000 in cash and putting $2,000 on account. d. The business paid $700 on the accounts to the bicycle store. e. The business performed delivery services for customers totaling $1,200. These customers paid in cash. f. The business performed delivery services for customers on account, totaling $2,400. g. The business collected $550 on account. h. The business paid rent (for the month of August) of $850. i. The business paid employees $1,800 for the month of August. j. Rick purchased groceries for his own use, paying $100 cash from his personal bank account. k. The business received a telephone bill for $175. As of August 31, 2011, it had not been paid. l. Rick withdrew $900 cash from the business for personal use. Requirements 1. What type of business organization is Rick’s Delivery Service? Describe this type of organization. Does this business need accountants? 2. Analyze the preceding transactions in terms of their effects on the accounting equation of Rick’s Delivery Service. 3. Prepare the income statement, statement of owner’s equity, and balance sheet of the business as of August 31, 2011. 4. Was the delivery service profitable for the month of August? Given this level of profit or loss, do you think the withdrawal of $900 was appropriate? 5. Who will likely be the primary user of the financial statements for Rick’s Delivery Service? 4 Chapter 1 | Demo Doc 1 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 5 Demo Doc 1 Solutions Describe the accounting profession and the organizations that govern it Requirement 1 What type of business organization is Rick’s Delivery Service? Describe of this type of organization. Does this business need accountants? Part 1 Identify the different types of business organizations Delineate the distinguishing characteristics and organization of a proprietorship Part 3 Part 4 Part 5 Part 6 Part 7 Demo Doc Complete Rick’s Delivery Service is a sole proprietorship. The accounting records of a sole proprietorship do not include the proprietor’s (owner’s) personal records. However, from a legal perspective, the business is the proprietor. All businesses need accountants, including Rick’s Delivery Service. Requirement 2 Analyze the preceding transactions in terms of their effects on the accounting equation of Rick’s Delivery Service. Part 1 Use accounting vocabulary Part 2 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Part 5 Part 6 Part 7 Demo Doc Complete The accounting equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity Apply accounting concepts and principles It is critical to understand each of these basic components: Define and use the accounting equation Assets are economic resources that should benefit the business in the future. Common examples of these would be cash, inventory, equipment, and furniture. Depict accounting for business transactions Liabilities are debts or obligations to outsiders. The most common liability is an account payable, an amount owed to a supplier for goods or services. A note payable is a written promise of future payment and usually requires the payment of interest in addition to the repayment of the debt, unlike accounts payable. Owner’s equity represents the owner’s interest in the business. It is the amount remaining after subtracting liabilities from assets. Transaction analysis is a critical first step in understanding how individual transactions are treated in accounting. a. Rick invested $6,000 of his personal funds in the business. Rick is using his own money, but he is giving it to the business. This means that the business is involved and it is a recordable transaction. From the business’s perspective, this increases Cash (an asset) by $6,000 and increases Rick Baldwin, Capital (owner’s equity) by $6,000. Demo Doc 1 Solutions | Chapter 1 5 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 6 b. The business paid $650 cash for supplies. The supplies are an asset that increased by $650. Because they were paid for with cash, the Cash account (an asset) is decreased by $650. c. The business purchased bicycles, paying $1,000 in cash and putting $2,000 on account. The Bicycles account (an asset) is increasing. But by how much? What is the cost of the bicycles? If $1,000 is paid in cash and $2,000 is bought on account, the total cost is $1,000 + $2,000 = $3,000. Why? This is the total amount that the business will (eventually) end up paying in order to acquire the bicycles. This is consistent with the cost principle. So the Bicycles account (an asset) is increased by $3,000, whereas the Cash account (an asset) is decreased by $1,000. The $2,000 on account relates to accounts payable (because it will have to be paid later). Because we now have more money that has to be paid later, it is an increase in Accounts Payable (a liability) of $2,000. The end result is that Bicycles (an asset) is increased by $3,000, Cash (an asset) is decreased by $1,000, and Accounts Payable (a liability) is increased by $2,000. d. The business paid $700 on the payable to the bicycle store. Think of Accounts Payable (a liability) as a list of companies to which the business owes money. In other words, it is a list of companies to which the business will pay money at some future time. In this particular problem, the business owes money to the company from which it purchased bicycles on account (see transaction c). When the business pays the money in full, it can cross this company off the list of companies to which it owes money. Right now, the business is paying only part of the money owed to the bicycle store. This decreases Accounts Payable (a liability) by $700 and decreases Cash (an asset) by $700. e. The business performed delivery services for customers totaling $1,200. These customers paid in cash. When the business performs services, it means that it is doing work for customers. Doing work for customers is the way that the business makes money. By performing services, the business is earning revenues. This means that Service Revenues is increased (which increases owner’s equity) by $1,200. Because the business receives the cash the customers paid, Cash is also increased (an asset) by $1,200. f. The business performed delivery services for customers on account, totaling $2,400. Again, the delivery service is performing services for customers, which means that it is earning revenues. This results in an increase in Service Revenues (owner’s equity) of $2,400. However, this time the customers charged the services on account. This is money that the business will receive in the future (when the customers eventually pay) so it is called accounts receivable. Accounts Receivable (an asset) is increased by $2,400. 6 Chapter 1 | Demo Doc 1 Solutions 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 7 g. The business collected $550 on account. Think of Accounts Receivable (an asset) as a list of customers from whom the business will collect money. In other words, it is a list of customers from whom the business will receive money at some future time. In this particular situation, these customers received services but did not pay at that time (see transaction f). Later, when the business collects (receives) the cash in full from any particular customer, it can cross that customer off the list. This is a decrease to Accounts Receivable (an asset) of $550. Because the cash is received, Cash (an asset) is increased by $550. h. The business paid rent (for the month of August) of $850. The rent has already been used. By the end of August, the service has been operating and using the space for the entire month. This means that the benefit of the rent has already been received or used up. This means that this is a rent expense. [Note that if the rent was paid for September, it would not yet be used up and would still be a future benefit (an asset) and not an expense. This issue will be discussed in Chapter 3.] So Rent Expense is increased by $850, which is a decrease to owner’s equity. The question states that the rent was paid. This means it was paid in cash. Therefore, Cash (an asset) is decreased by $850. i. The business paid employees $1,800 for the month of August. Again, the transaction states that the business paid the employees, meaning that it paid in cash. Therefore, Cash (an asset) is decreased by $1,800. The work the employees have given to the business has already been used. By the end of August, the delivery service has had the employees working and delivering for customers for the entire month. This means that the benefit of the work has already been received, so it is a salary expense. Salary Expense is increased by $1,800, which is a decrease to owner’s equity. j. Rick purchased groceries for his own use, paying $100 cash from his personal bank account. These groceries were purchased with Rick’s personal money for Rick’s personal use. Therefore, this purchase does not relate to the business and is not a recordable transaction for the delivery service. k. The business received a telephone bill for $175. As of August 31, 2011, it had not been paid. Utilities (such as water, gas, electricity, phone, and Internet service) are generally not billed until after they have been used. If these utilities have already been used, then they are utilities expenses. So, Utility Expense is increased by $175, which is a decrease to owner’s equity. Because the bill has not yet been paid as of August 31, it is an account payable. This increases Accounts Payable (a liability) by $175. Demo Doc 1 Solutions | Chapter 1 7 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 8 l. Rick withdrew $900 cash from the business for personal use. Although Rick is taking the money, the cash is coming from the business, so this is a recordable transaction for the business. There is a decrease of $900 to Cash (an asset). Because Rick is the owner, this results in an increase of $900 to Owner Withdrawals, which is a decrease to owner’s equity. Requirement 3 Prepare the income statement, statement of owners equity, and balance sheet of the business as of August 31, 2011. Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 LIABILITIES ASSETS a. Accounts receivable –650 c. –1,000 d. –700 Supplies + Bicycles OWNER’S EQUITY Owner investment +1,200 Service revenue –2,400 Service revenue +$2,000 +$3,000 –700 = –550 –850 –850 i. –1,800 –1,800 Rent expense Salary expense Not a transaction of the business. +175 k. l. TYPE OF OWNER’S EQUITY TRANSACTION +6,000 h. j. Demo Doc Complete Rick Baldwin, Capital Accounts payable +2,400 +550 Part 7 +$650 +1,200 f. g. + + +$6,000 b. e. + Part 6 Here’s how the transactions from Requirement 1 look in the accounting equation: Define and use the accounting equation Cash Part 5 –900 $1,850 $650 $1,850 $7,350 Explain and prepare the financial statements $3,000 –175 Utilities expense –900 Owner withdrawal $5,875 $1,475 $7,350 Remember that financial statements communicate important information necessary for users to make business decisions. An overview of the financial statements is as follows: • Income Statement—Lists the revenues and expenses to determine net income or net loss for a period. Net income results if revenues exceed expenses; the reverse results in a net loss. 8 Chapter 1 | Demo Doc 1 Solutions 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 9 • Statement of Owner’s Equity—Shows the changes in owner’s equity during the period. Investments from owners and net income increase equity; owner withdrawals and net losses decrease equity. • Balance Sheet—Lists the assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity at a point in time, usually at the end of a month. • Statement of Cash Flows—Report of cash receipts (inflows) and cash payments (outflows) for a period of time. (The statement of cash flow is covered in Chapter 17.) The income statement is the first statement that should be prepared because the other financial statements rely on the net income number calculated on the income statement. The income statement lists all revenues and expenses. It uses the following formula to calculate net income: Revenues – Expenses = Net income So, to create an income statement, we only need to list the revenue accounts and then subtract the list of expense accounts to calculate net income. We can read these amounts from the accounting equation work sheet. There are two transactions impacting service revenue: e and f. Transaction e increases service revenue by $1,200 and transaction f increases service revenue by $2,400. This means that total service revenue for the month was: $1,200 + $2,400 = $3,600 Rent expense of $850, salary expense of $1,800, and utilities expense of $175 were recorded in transactions h, i, and k (respectively). RICK’S DELIVERY SERVICE Income Statement Month Ended August 31, 2011 Revenue: Service revenue Expenses: Rent expense Salary expense Utilities expense Total expenses Net income $3,600* $ 850 1,800 175 2,825 $ 775 *(= $1,200 + $2,400) Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Part 5 Part 6 Part 7 Demo Doc Complete Demo Doc 1 Solutions | Chapter 1 9 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 10 Net income is used on the statement of owner’s equity to calculate the new balance in the Capital account. This calculation uses the following formula: Beginning capital amount + Owner investments + Net income – Owner withdrawals = Ending capital amount Again, we just have to recreate this formula on the statement: RICK’S DELIVERY SERVICE Statement of Owner’s Equity Month Ended August 31, 2011 Rick Baldwin, capital, August 1, 2011 Add: Investment by owner Net income for month $ 0 6,000 775 6,775 (900) $5,875 Less: Withdrawals by owner Rick Baldwin, capital, August 31, 2011 Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Part 5 Part 6 Part 7 Demo Doc Complete The ending capital amount is used on the balance sheet. The balance sheet is just a listing of all assets, liabilities, and equity, with the accounting equation verified at the bottom: RICK’S DELIVERY SERVICE Balance Sheet August 31, 2011 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Supplies Bicycles Total assets 10 Chapter 1 | Demo Doc 1 Solutions Liabilities $1,850 1,850 650 3,000 $7,350 Accounts payable $1,475 Equity Rick Baldwin, capital Total liabilities and equity 5,875 $7,350 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 11 Requirement 4 Was the delivery service profitable for the month of August? Given this level of profit or loss, do you think the withdrawal of $900 was appropriate? Part 1 Use the financial statements to evaluate business performance Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Part 5 Part 6 Part 7 Demo Doc Complete Evaluating business performance is critical to making sound business decisions. For example, reviewing the income statement shows the results of operations, how much the business generated in net income, or if it incurred a net loss. The statement of owner’s equity indicates what caused the change in owner’s equity for the period. The balance sheet is a statement of financial condition or financial position, which includes the ending owner’s equity. The statement of cash flows would identify the cash receipts and cash payments from operating, investing, and financing activities. From the income statement prepared in Requirement 2, we can see that the delivery service earned $775 of profit during the month of August. The level of withdrawals ($900) seems high given that it is more than the amount of profit earned during the month. Requirement 5 Who will likely be the primary user of the financial statements for Rick’s Delivery Service? Part 1 Define the users of financial information Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Part 5 Part 6 Part 7 Demo Doc Complete As the sole owner and manager, Rick Baldwin will likely be the primary user of the financial statements for Rick’s Delivery Service. Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Part 5 Part 6 Part 7 Demo Doc Complete Demo Doc 1 Solutions | Chapter 1 11 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 12 Quick Practice Questions True/False 1. Financial accounting produces financial information and reports to be used by managers inside a business. 2. An audit is a financial examination performed by independent accountants. 3. The top financial position in private accounting is the rank of partner. 4. Professional accounting organizations and most companies have standards of ethical behavior. 5. A proprietorship’s owners are called shareholders. 6. An advantage of the partnership form of business is that the life of the entity is indefinite. 7. The life of a sole proprietorship is limited to the owner’s choice or death. 8. The entity concept separates business transactions from personal transactions. 9. A business has a net loss when total revenues are greater than total expenses. 10. The statement of owner’s equity reports the cash coming in and going out. Multiple Choice 1. What is the private organization that is primarily responsible for formulating accounting standards? a. The Internal Revenue Service b. The Securities and Exchange Commission c. The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants d. The Financial Accounting Standards Board 2. What is the watchdog agency created by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act? a. The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants b. The Public Companies Accounting Oversight Board c. The Internal Revenue Service d. The Financial Accounting Standards Board 3. Financial accounting provides financial statements and financial information that are intended to be used by whom? a. Management of the company b. Potential investors c. Employees of the company d. The board of directors 12 Chapter 1 | Quick Practice Questions 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 13 4. What is the purpose of financial accounting information? a. Help managers plan and control business operations b. Comply with the IRS rules c. Help investors, creditors, and others make decisions d. Provide information to employees 5. What characteristic is necessary for information to be useful? a. Relevance b. Reliability c. Comparability d. All of the above 6. Sue Mason owns a bagel shop as a sole proprietorship. Sue includes her personal home, car, and boat on the books of her business. Which of the following is violated? a. Entity concept b. Going-concern concept c. Cost principle d. Reliability principle 7. Which of the following is the accounting equation? a. Assets – Liabilities = Owner’s Equity b. Assets + Liabilities = Owner’s Equity c. Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity d. Assets + Liabilities = Net income 8. If the assets of a business are $410,000 and the liabilities total $200,000, how much is the owner’s equity? a. $150,000 b. $160,000 c. $210,000 d. $610,000 9. Which financial statement contains a listing of assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity? a. Balance sheet b. Statement of owner’s equity c. Income statement d. Statement of cash flows 10. What is the claim of a business owner to the assets of the business called? a. Liabilities b. Owner’s equity c. Revenue d. Withdrawals Quick Practice Questions | Chapter 1 13 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 14 Quick Exercises 1-1. Fill in the statements that follow with the correct type of business organization. a. A is a separate legal entity approved by the state. b. A is an entity with one owner where the business and not the owner is liable for the company’s debts. c. A is an entity with two or more owners who are personally liable for the company’s debts. 1-2. Match the following terms with the best description. Terms a. b. c. d. e. Entity concept Reliability principle Cost principle Going-concern concept Stable-monetary-unit concept Description An organization or part of an organization is separate from other organizations and individuals. An item should be recorded at the actual amount paid. An entity is expected to remain in business in the future. Assumption that the dollar’s purchasing power is constant. Accounting data should be neutral, unbiased information that can be confirmed by others. 1-3. Determine the missing amounts: a. Assets = $50,000; Liabilities = $30,000; Owner’s Equity = b. Liabilities = $35,000; Owner’s Equity = $75,000; Assets = c. Assets = $105,000; Owner’s Equity = $50,000; Liabilities = 1-4. a. Write a brief explanation for the following transactions: ASSETS LIABILITIES Cash + Accounts receivable + Supplies Accounts payable 20,000 1,000 –2,500 5,200 3,000 –3,000 a. b. c. d. e. 14 OWNER’S EQUITY Capital = 1,000 –2,500 d. e. + 20,000 b. c. ? ? ? Chapter 1 | Quick Practice Questions 5,200 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 15 1-5. On which of the following three financial statements would you expect to find the items (a)–(f)? Income Statement (IS) Balance Sheet (BS) Statement of Cash Flows (CF) a. Accounts Payable b. Service Revenue c. Collections from Customer d. Utilities Expense e. Office Supplies f. Payments to Suppliers Quick Practice Questions | Chapter 1 15 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 16 Do It Yourself! Question 1 Jennifer Hill opened a Laundromat business on October 1, 2011. She is the sole proprietor of the business. Requirement Use accounting vocabulary Apply accounting concepts and principles 1. For each transaction of the business during the month of October, analyze the transaction in terms of its effect on the accounting equation of Jennifer’s Laundromat. a. Jennifer invested $10,000 of her personal funds in the business. Define and use the accounting equation Depict accounting for business transactions b. The Laundromat purchased washing machines, paying $4,000 in cash and putting another $5,000 on account. c. Jennifer purchased a washing machine for use in her home costing $2,100 on her personal account. d. The business paid $500 cash for supplies. e. The Laundromat performed cleaning services for customers totaling $2,500. These customers paid in cash. 16 Chapter 1 | Do It Yourself! Question 1 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 17 f. The Laundromat also performed cleaning services for customers on account totaling $3,700. g. The Laundromat paid rent (for the month of October) of $1,000. h. The business paid employees $1,500 for the month of October. i. The Laundromat received a utility bill for $750. As of October 31, 2011, it had not been paid. j. Jennifer withdrew $2,000 cash from the business for personal use. k. The Laundromat collected $2,250 on account. l. The amount of $2,400 was paid on the account to the washing machine store. Do It Yourself! Question 1 | Chapter 1 17 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 Define and use the accounting equation 2:21 PM Page 18 2. Prepare the income statement, statement of owner’s equity, and balance sheet of the business as of October 31, 2011. Explained the financial statements ASSETS 18 Chapter 1 | Do It Yourself! Question 1 LIABILITIES EQUITY TYPE OF OWNER’S EQUITY TRANSACTION 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 19 Do It Yourself! Question 1 | Chapter 1 19 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 20 Quick Practice Solutions True/False 20 F 1. Financial accounting produces financial information and reports to be used by managers inside a business. False—Financial accounting produces information for people outside the company. (p. 3) T 2. An audit is a financial examination performed by independent accountants. (p. 5) F 3. The top financial position in private accounting is the rank of partner. False—The top financial position in private accounting is the chief financial officer. (p. 4) T 4. Professional accounting organizations and most companies have standards of ethical behavior. (p. 5) F 5. A proprietorship’s owners are called shareholders. False—A corporation’s owners are called shareholders. A proprietorship’s owners are called proprietors. (p. 6) F 6. An advantage of the partnership form of business is that the life of the entity is indefinite. False—The life of a partnership is limited by the owners’ choices or death. (p. 7) F 7. The owner of a sole proprietorship is not personally liable for the debts of the business. False—The owner of a sole proprietorship is personally liable for the debts of the business. (p. 7) T 8. The entity concept separates business transactions from personal transactions. (p. 10) F 9. A business has a net loss when total revenues are greater than total expenses. False—A business has net income when total revenues are greater than total expenses. (p. 12) F 10. The statement of owner’s equity reports the cash coming in and going out. False—The statement of owner’s equity shows the changes in owner’s equity during a time period. The statement of cash flows reports cash coming in and going out. (p. 20) Chapter 1 | Quick Practice Solutions 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 21 Multiple Choice 1. What is the private organization that is primarily responsible for formulating accounting standards? (p. 4) a. The Internal Revenue Service b. The Securities and Exchange Commission c. The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants d. The Financial Accounting Standards Board 2. What is the watchdog agency created by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act? (p. 5) a. The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants b. The Public Companies Accounting Oversight Board c. The Internal Revenue Service d. The Financial Accounting Standards Board 3. Financial accounting provides financial statements and financial information that are intended to be used by whom? (p. 3) a. Management of the company b. Potential investors c. Employees of the company d. The board of directors 4. What is the purpose of financial accounting information? (p. 3) a. To help managers plan and control business operations b. To comply with the IRS rules c. To help investors, creditors, and others make decisions d. To provide information to employees 5. What characteristic is necessary for information to be useful? (p. 5) a. Relevance b. Reliability c. Comparability d. All of the above 6. Sue Mason owns a bagel shop as a sole proprietorship. Sue includes her personal home, car, and boat on the books of her business. Which of the following is violated? (p. 10) a. Entity concept b. Going-concern concept c. Cost principle d. Reliability principle 7. Which is the accounting equation? (p. 11) a. Assets – Liabilities = Owner’s Equity b. Assets + Liabilities = Owner’s Equity c. Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity d. Assets + Liabilities = Net income Quick Practice Solutions | Chapter 1 21 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 22 8. If the assets of a business are $410,000 and the liabilities total $200,000, how much is the owner’s equity? (p. 11) a. $150,000 b. $160,000 c. $210,000 d. $610,000 9. Which financial statement contains a listing of assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity? (p. 20) a. Balance sheet b. Statement of owner’s equity c. Income statement d. Statement of cash flows 10. What is the claim of a business owner to the assets of the business called? (p. 12) a. Liabilities b. Owner’s equity c. Revenue d. Withdrawals Quick Exercises 1-1. Fill in the statements that follow with the correct type of business organization. (p. 7) a. A corporation is a separate legal entity approved by the state. b. A limited-liability corporation is an entity with one owner where the business and not the owner is liable for the company’s debts. c. A partnership is an entity with two or more owners who are personally liable for the company’s debts. 1-2. Match the following terms with the best description. (p. 10) Terms a. b. c. d. e. Entity concept Reliability principle Cost principle Going-concern concept Stable-monetary-unit concept Description a c d e b 22 Chapter 1 | Quick Practice Solutions An organization or part of an organization is separate from other organizations and individuals. An item should be recorded at the actual amount paid. An entity is expected to remain in business in the future. Assumption that the dollar’s purchasing power is constant. Accounting data should be neutral, unbiased information that can be confirmed by others. 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 23 1-3. Determine the missing amounts: (p. 11) a. Assets = $50,000; Liabilities = $30,000; Owner’s Equity = $20,000 ($50,000 – $30,000) b. Liabilities = $35,000; Owner’s Equity = $75,000; Assets = $110,000 c. Assets = $105,000; Owner’s Equity = $50,000; Liabilities = $55,000 1-4. a. ASSETS LIABILITIES Cash + Accounts receivable + Supplies Accounts payable 20,000 = OWNER’S EQUITY Capital 1,000 –2,500 –2,500 5,200 3,000 + 20,000 1,000 d. e. ($105,000 – $50,000) Write a brief explanation for the following transactions: (p. 14) b. c. ($35,000 + $75,000) 5,200 –3,000 a. The owner invested $20,000 cash in the business. b. Purchased $1,000 of supplies on account. c. Paid $2,500 for an expense or the owner withdrew $2,500 for personal use. d. Performed services for customer on account, $5,200. e. Received $3,000 cash from customers on account. 1-5. On which of the following three financial statements would you expect to find the items (a)–(f)? (p. 20) Income Statement (IS) Balance Sheet (BS) Statement of Cash Flows (CF) a. BS Accounts Payable b. IS Service Revenue c. CF Collections from Customer d. IS Utilities Expense e. BS Office Supplies f. CF Payments to Suppliers Quick Practice Solutions | Chapter 1 23 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 24 Do It Yourself! Question 1 Solutions Requirement 1. For each transaction of the business during the month of October, analyze and describe the transaction in terms of its effect on the accounting equation of Jennifer’s Laundromat. a. Jennifer invested $10,000 of her personal funds in the business. Cash (an asset) is increased by $10,000 and Jennifer Hill, Capital (owner’s equity) is increased by $10,000. b. The Laundromat purchased washing machines, paying $4,000 in cash and putting another $5,000 on account. Washing Machines (an asset) is increased by $9,000, whereas Cash (an asset) is decreased by $4,000. Accounts Payable (a liability) is increased by $5,000. c. Jennifer purchased a washing machine for use in her home costing $2,100 on her personal account. This does not relate to the business and is not a recordable transaction for the Laundromat. d. The business paid $500 cash for supplies. Supplies (an asset) is increased by $500 and Cash (an asset) is decreased by $500. e. The Laundromat performed cleaning services for customers totaling $2,500. These customers paid in cash. Service Revenues (owner’s equity) is increased by $2,500. Cash (an asset) is increased by $2,500. f. The Laundromat also performed cleaning services for customers on account totaling $3,700. Service Revenues (owner’s equity) is increased by $3,700. Accounts Receivable (an asset) is increased by $3,700. g. The Laundromat paid rent (for the month of October) of $1,000. Rent Expense is increased by $1,000, which is a decrease to owner’s equity. Cash (an asset) is decreased by $1,000. h. The business paid employees $1,500 for the month of October. Salary Expense is increased by $1,500, which is a decrease to owner’s equity. Cash (an asset) is decreased by $1,500. 24 Chapter 1 | Do It Yourself! Question 1 Solutions 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 25 i. The Laundromat received a utility bill for $750. As of October 31, 2011, it had not been paid. Utility Expense is increased by $750, which is a decrease to owner’s equity. Accounts Payable (a liability) is increased by $750. j. Jennifer withdrew $2,000 cash from the business for personal use. This is a recordable transaction for the business. Cash (an asset) is decreased by $2,000. This results in an increase of $2,000 to Owner Withdrawals, which is a decrease to owner’s equity. k. The Laundromat collected $2,250 of accounts receivable. Accounts Receivable (an asset) is decreased by $2,250. Because the cash is received, Cash is increased (an asset) by $2,250. l. The amount of $2,400 was paid on the accounts payable to the washing machine store. Accounts Payable (a liability) is decreased by $2,400 and Cash (an asset) is decreased by $2,400. 2. Prepare the income statement, balance sheet, and statement of owner’s equity of the business as of October 31, 2011. LIABILITIES ASSETS Cash + Accounts receivable + Supplies + Washing Machines b. +$10,000 +$9,000 –4,000 TYPE OF OWNER’S EQUITY TRANSACTION Jennifer Hill, Capital Accounts payable +$10,000 a. + OWNER’S EQUITY Owner investment +$5,000 Not a transaction of the business. c. –$500 d. +2,500 +$500 = +$3,700 e. +2,500 Service revenue +3,700 Service revenue f. –1,000 –1,000 Rent expense g. –1,500 –1,500 Salary expense –750 +750 h. i. –2,000 j. +2,250 –2,000 –2,250 Owner withdrawal k. –2,400 l. Utilities expense $3,350 –2,400 $1,450 $14,300 $500 $9,000 $10,950 $3,350 $14,300 Do It Yourself! Question 1 Solutions | Chapter 1 25 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 26 JENNIFER’S LAUNDROMAT Income Statement Month Ended October 31, 2011 Revenue: Service revenue Expenses: Salary expense Rent expense Utilities expense Total xpenses e Net income $6,200* $1,500 1,000 750 3,250 $2,950 *(= $2,500 + $3,700) JENNIFER’S LAUNDROMAT Statement of Owner’s Equity Month Ended October 31, 2011 Jennifer Hill, capital, October 1, 2011 Add: Investment by owner Net income for month $ 0 10,000 2,950 12,950 (2,000) $10,950 Less: Withdrawals by owner Jennifer Hill, capital, October 31, 2011 JENNIFER’S LAUNDROMAT Balance Sheet October 31, 2011 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Supplies Washing machines Total assets 26 Chapter 1 | Do It Yourself! Question 1 Solutions Liabilities $3,350 1,450 500 9,000 $14,300 Accounts payable $3,350 Equity Jennifer Hill, capital Total liabilities and equity 10,950 $14,300 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 27 The Power of Practice For more practice using the skills learned in this chapter, visit MyAccountingLab. There you will find algorithmically generated questions that are based on these Demo Docs and your main textbook’s Review and Assess Your Progress sections. Go to MyAccountingLab and follow these steps: 1. Direct your URL to www.myaccountinglab.com. 2. Log in using your name and password. 3. Click the MyAccountingLab link. 4. Click Study Plan in the left navigation bar. 5. From the table of contents, select Chapter 1, Accounting and the Business Environment. 6. Click a link to work tutorial exercises. The Power of Practice | Chapter 1 27 64817_01_ch1_p001-028 11/7/08 2:21 PM Page 28