Earth Science Vocabulary-Hallway 1-1
advertisement

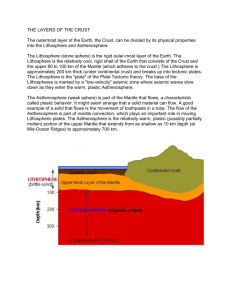
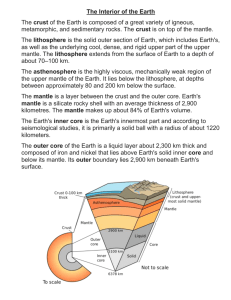
Earth Science Vocabulary Vocabulary Word Heliocentric Geocentric Big Bang Gravitational Force Relative Position Ellipse Orbit Rotation Revolution Inertia Meteor Asteroid Moon phases Ellipses Luminous Climate Tides Axis Gravity Convection current Seasons Lithosphere Asthenosphere Mesosphere Mantle Inner Core Outer Core Plate Tectonics Hot spot Subduction Definition The belief that the Sun is the center of the universe and everything revolves around the Sun. The belief that the Earth is the center of the universe and everything revolves around the Earth. The theory that states that the universe began as a single point and then exploded to start forming the universe. When a larger object attracts a smaller object in space and the larger object pulls on the smaller. The position of an object in relation to another, such as during an eclipse. The elongated, closed curve that describes Earth’s yearlong orbit around the Sun. The curved path followed by an object as it revolves around another. Spinning of Earth on its imaginary axis, which takes about 24 hours to complete and causes day and night to occur. Earth’s yearlong elliptical orbit around the Sun. The ability of an object to remain in motion or at rest unless acted on by an outside force. A meteoroid that burns up in the Earth’s atmosphere, usually producing bright streak of light in the night sky. A pieces of rock, metal or rock and metal, made up of material similar to that which make planets, mostly found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Change in appearance of the moon as viewed from the earth due to relative positions of the moon, earth, and sun. Elongated, closed curve that describes Earth’s yearlong orbit around the sun. Shining by its own light The average weather pattern in an area over a long period of time, can be classified by temperature, humidity, precipitation, and vegetation. The daily rise and fall in sea level caused for the most part of by the interaction of gravity in the earth – moon system. An imaginary vertical line that cuts through the center of the earth and around which earth spins. The natural force that causes objects to move or tend to move toward the center of the earth caused by the gravitation of the earth. Gravity causes objects to have weight. A current in which the earth’s mantle transfers heat in earth’s interior and is driving force for plate tectonics. Short period of climate change in an area caused by the tilt of Earth’s axis as Earth revolves around the Sun. The outermost, rigid layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of mantle. The soft layer of mantle on which pieces of the lithosphere move. Literally, the “middle sphere” – the strong, lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core. The layer of the Earth between the crust and the core. The solid, dense center of Earth The liquid layer of the Earth’s core that lies beneath the mantle and surrounds the inner core. The theory that the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move around on top of the asthenosphere. A place on Earth’s surface that is directly above a column of rising magma called a mantle plume. The region where an oceanic plate sinks down into the asthenosphere at a convergent boundary, usually between to continental and oceanic plates.