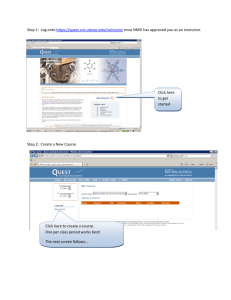
Wisecampus.com Uploads Notescans Test5questionbank
advertisement

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Use this information for questions (1 thru 10) that refer to the Centerville Retailers and Wholesalers case. Carol Lamb has lived in Centerville all her life. She owns a retail store that sells hobby and craft supplies. She bought the store after working there for 7 years. Carol has just been asked to head up the Retailers and Wholesaler Group of the Centerville Chamber of Commerce. The most active chamber members in her group are described below: Walden's Leather is part of a regional chain of stores that sells leather goods - mostly men's and women's clothing - with the upscale Walden's brand name. Walden's primarily relies on its own stores where knowledgeable salespeople offer great service. Walden products are also sold, on a limited basis, in some fine department stores. Publisher's Helper is a small business started by Audrey Yang that provides and stocks display racks for paperback books and magazines. Most retailers welcome the service Audrey provides, in part because she does her own research to determine which paperback books and magazines sell best in Centerville. Cuzco's is Centerville's alternative to Wal-Mart. The store sells a wide variety of merchandise. The company used to concentrate its product mix on small appliances - but now Cuzco's carries any product that it can sell profitably. Its low prices stimulate faster turnovers and higher sales volumes. Games Unlimitedsells video games. Jamie Carraway, who owns the local store, signed a contract with Games Unlimited and follows strict rules covering her store's operations and the Games Unlimited marketing strategy. she pays that company a fee for promotion it provides as well as commissions on her sales. Johnson's Health and Beauty Supplies sells cosmetics and other health and beauty products to retailers and salons throughout the greater Centerville area. It owns the goods it sells to these retailer customers, and it provides all the wholesaling functions they need. Valu Groceris an independent grocery store that belongs to an organization sponsored by a large food wholesaler. The fifty stores grocery stores that share the Valu Grocer name are linked by contracts that include basic operating procedures, storefront designs, and joint promotion efforts. Reddy and Sonssells equipment for several different manufacturers of plastic molding in the Centerville area. It earns a commission from each manufacturer on the products it sells for that manufacturer, but it does not take ownership of the equipment it sells nor does it install the equipment. Katrina's Salonstarted out as a low-status, low-price, low-margin hair salon 15 years ago. After some success, the company moved into a nicer storefront, raised prices, and now operates in the middle of the market. 1. Which of the following terms best describes Publisher's Helper business? A. Rack jobber B. Broker C. Drop shipper D. Selling agent 2. Which of these businesses is a franchise? A. Reddy and Sons B. Cuzco's C. Publisher's Helper D. Games Unlimited 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3. Which of these business uses scrambled merchandising as a big part of its strategy? A. Katrina's Salon B. Johnson's Health and Beauty Supplies C. Cuzco's D. Publisher's Helper 4. Which of these businesses has followed the wheel of retailing theory? A. Games Unlimited B. Katrina's Salon C. Walden's Leather D. Valu Grocer 5. Which of these businesses would be classified as a specialty shop? A. Walden's Leather B. Cuzco's C. Publisher's Helper D. Valu Grocer 6. Which of these businesses relies on the mass-merchandising concept? A. Publisher's Helper B. Cuzco's C. Walden's Leather D. Reddy and Sons 7. Which of these businesses best fits the definition of a limited-line store? A. Johnson's Health and Beauty Supplies B. Valu Grocer C. Cuzco's D. Walden's Leather 8. ___________ would be classified as an agent wholesaler? A. Reddy and Sons B. Publisher's Helper C. Johnson's Health and Beauty Supplies D. Valu Grocer E. None of the businesses above would be classified as an agent wholesaler. 9. Which of these businesses best fits the definition of a limited-function merchant wholesaler? A. Games Unlimited B. Publisher's Helper C. Reddy and Sons D. Valu Grocer E. Cuzco's 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10. Which of these businesses best fits the definition of a service merchant wholesaler? A. Publisher's Helper B. Valu Grocer C. Reddy and Sons D. Johnson's Health and Beauty Supplies 11. A producer has a few territories where many big customers are concentrated, but most of its target customers are spread all over the country. A. The company should use manufacturers' agents in the best territories and sales branches in the others, since good agents won't work the smaller territories. B. The company should use sales branches everywhere, since it will cost more to use manufacturers' agents. C. The company will probably have to rely only on manufacturers' agents, since they will only be willing to take the widely scattered markets if they can have the good territories too. D. The company should use sales branches in the concentrated territories and manufacturers' agents in the others—assuming the concentrated territories are large enough to support sales branches. E. All of the above are good alternatives. 12. McGovern's Supply stocks electronic repair parts and related supplies and tools from various producers. McGovern's sells primarily to small TV and electronic repair shops throughout the country that only want to order one or two items at a time. Orders are usually shipped out on UPS trucks. It appears that McGovern's is a A. single-line wholesaler. B. manufacturers' agent. C. drop-shipper. D. truck wholesaler. E. rack jobber. 13. If a small U.S. producer with limited financial resources and little marketing know-how wants to sell its products in international markets, it should use: A. an export commission house. B. a factor. C. an export agent. D. a combination export manager. E. an export broker. 14. The U.S. Bureau of the Census defines wholesaling as being concerned with the activities of those persons or establishments that sell A. to retailers and other merchants, but that do not sell in large amounts to final consumers. B. to consumers. C. to industrial, institutional, and noncommercial users. D. through export in large amounts; seldom to individuals. E. both A and C. 3 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15. A manufacturer of which of the following product lines would be most likely to use a specialty wholesaler? A. Electric appliances B. Hardware items C. Lumber D. Plastic materials E. Industrial cleaning supplies 16. The "wheel of retailing" theory says that: A. retailers go through cycles from high costs and prices to lower costs and profits. B. general stores will dominate U.S. retailing in the next century. C. new types of retailers enter as low-status, low-margin, low-price operators and eventually offer more services and charge higher prices. D. all of the above are true. E. none of the above are true. 17. Which of the following is NOT a franchise operation? A. Midas Muffler B. Panera Bread C. Jiffy Lube D. Ace Hardware E. Taco Bell 18. Regarding wholesalers, which of the following descriptions is TRUE? A. MANUFACTURERS' AGENT: does not own the products, usually carries stocks, represents several competing manufacturers within a geographic area. B. MERCHANT WHOLESALER: does not take title to products, takes possession, provides full service, and usually handles a broad variety of products. C. BROKER: does not own the products, does not take possession, major function is selling, and does not anticipate customer needs. D. SELLING AGENT: does not own the products, does the whole marketing job nationally, and may handle competing lines. E. All of the above are true. 19. U.S. Census data show that: A. only about 11 percent of all retailers have annual sales over $1 million. B. very large retailers account for a small percentage of total retail sales. C. manufacturers and wholesalers are more numerous than retailers in the United States. D. only about 11 percent of all retailers have annual sales over $5 million. E. All of the above. 20. Telephone and direct-mail retailers: A. have real trouble selling because they only target the really wealthy. B. have real trouble reaching their target markets, since their customers are so dispersed geographically. C. can do well with products that would be unprofitable for a local retailer to carry. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 4 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------21. Which of the following statements about selling agents is FALSE? A. They take over the whole marketing job for a producer. B. They may handle the entire output of one or more producers, even competing producers. C. They may provide a producer with working capital. D. They may even take over the affairs of the producer's whole business. E. None of the above is false. 22. Regarding direct-mail retailers, which of the following statements is TRUE? A. They emphasize low-price "commodities" that can be found in local stores. B. Their profit margins are rising. C. Their competition is decreasing. D. Some aim at very narrow target markets. E. All of the above are true. 23. Department stores: A. are basically a group of limited-line stores under one roof. B. are decreasing in number, average sales per store, and share of retail business. C. usually aim at customers seeking shopping products. D. All of the above are true. E. Only B and C are true. 24. Regarding wholesalers, which of the following types has the LOWEST operating expenses as a percent of sales? A. Specialty wholesalers B. Merchant wholesalers C. Manufacturers' sales branches D. Agent wholesalers E. Service wholesalers 25. U.S. Census data show that: A. retailers are more numerous than manufacturers and wholesalers combined. B. only about 11 percent of all retailers have annual sales over $5 million. C. over 56 percent of all retailers have annual sales less than $1 million. D. all of the above. E. none of the above. 26. Regarding retailer store size, it is true that: A. almost 70 percent of all retail sales are made by smaller stores—those with annual sales less than $1 million. B. almost 70 percent of all retail sales are made by the largest stores—those with annual sales over $5 million a year. C. small retailers are unimportant and can safely be ignored by most manufacturers and wholesalers. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 5 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------27. A wholesaler that carries only health foods instead of a full line of groceries is a A. general merchandise wholesaler. B. limited-function wholesaler. C. general-line wholesaler. D. cash-and-carry wholesaler. E. specialty wholesaler. 28. Truck wholesalers: A. usually sell perishable products that other wholesalers prefer not to carry. B. don't own the products they sell. C. usually sell in large quantities, e.g., truckloads. D. don't stock the products they sell. E. All of the above. 29. Specialty shops: A. offer fewer services than the typical limited-line store. B. have trouble deciding what to carry because it's hard for them to get to know what their customers want. C. rely heavily on knowledgeable salesclerks. D. All of the above. E. None of the above. 30. The development of new types of retailers can be best explained by applying: A. the rule of franchising. B. target marketing and product life cycle concepts. C. the corporate chain hypothesis. D. the wheel of retailing theory. E. the law of retail gravitation. 31. Retailer-sponsored groups formed by independent retailers that run their own buying organizations and conduct joint promotion efforts are called: A. Corporate chains B. Voluntary chains C. Cooperative chains D. Franchise operations E. Private chains 32. Wholesaling is concerned with the activities of: A. manufacturers who set up branch warehouses at separate locations. B. persons or establishments that sell to industrial, institutional, and commercial users. C. persons or establishments that sell to retailers. D. All of the above. E. Only A and B above. 6 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33. Which of the following are possible Internet approaches for a retailer? A. Using its website to supplement its bricks-and-mortar stores. B. Using its website to complement its stores and catalogs. C. Using its website to be more efficient than competitors. D. Using its website to focus on the specific needs of its target customers. E. All of the above. 34. Franchise operations provide a good example of: A. vertical integration. B. contractual vertical marketing systems. C. administered channels in which the retailers are the channel captains. D. direct-to-buyer channels. E. None of the above. 35. Sebastian and Clere Franklin bought a tire recapping facility from a man who had decided to retire. They were going to convert the building to a studio for dance lessons—so they wanted to sell off the inventory of recapped tires and equipment for whatever they could get. The Franklins don't know any buyers who might be interested in these products. Which of the following types of wholesalers would be most helpful? A. Rack jobbers B. Brokers C. Specialty wholesalers D. Selling agents E. Manufacturers' agents 36. Which of the following statements about agent wholesalers is FALSE? A. Agent wholesalers do not own the products they sell. B. Their main purpose is to help in buying and selling. C. They normally specialize by customer type and by product or product line. D. They are more common in international trade than in domestic trade. E. They usually provide a larger number of functions than limited-function wholesalers. 37. Regarding types of wholesalers, which of the following has the HIGHEST operating expenses as a percent of sales? A. Manufacturers' sales branches (with stock) B. Merchant wholesalers C. Brokers D. Manufacturers' agents E. Agent wholesalers 38. Which of the following is a characteristic of agent wholesalers? A. They are more common is domestic trade than in international trade. B. They operate at relatively high costs. C. They own the products they sell. D. They normally specialize by customer type and by product or product line. E. None of the above. 7 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------39. Mass-merchandisers: A. face a bright future and increasing profits—because of decreasing competition. B. usually operate with low margins on individual items. C. operate on the "buy low, sell high" philosophy. D. try to reduce costs by reducing inventory turnover. E. All of the above are true. 40. Department stores: A. are large stores which emphasize depth and distinctiveness rather than variety. B. have declined since the 1970s because of competition from well-run limited-line stores and massmerchandisers. C. are usually weak in customer service. D. usually emphasize specialty products. E. All of the above are true. 41. Cooperative chains: A. are sponsored by wholesalers to try to compete with corporate chains. B. are experiencing declining sales. C. are formed by independent retailers to run their own buying organizations and conduct joint promotion efforts. D. are consumer groups who run nonprofit buying associations. E. All of the above are true. 42. Which of the following is a limited-function merchant wholesaler? A. An auction company B. A broker C. A manufacturers' agent D. A general-line wholesaler E. A rack jobber 43. Manufacturers' agents: A. don't cost the producer anything until something sells. B. aren't very useful for introducing new products. C. usually perform storing and transporting functions. D. usually handle the competing lines of several manufacturers. E. All of the above. 44. A "supercenter": A. tries to provide all of a customer's routine needs—at a low price. B. probably would not affect nearby supermarkets. C. is just another name for a mass-merchandiser. D. is a large department store which uses supermarket methods. E. All of the above are true. 8 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------45. Which of the following is NOT a full-service merchant wholesaler? A. Broker B. Single-line wholesaler C. General-line wholesaler D. General merchandise wholesaler E. Specialty wholesaler 46. A full-service wholesaler in Madrid takes title to the "oriental foods" she sells to supermarkets, gourmet shops, and restaurants. This wholesaler is a: A. manufacturers' agent. B. specialty wholesaler. C. selling agent. D. single-line wholesaler. E. general merchandise wholesaler. 47. __________ are a type of limited-function wholesaler that owns products they sell, but do not actually handle, stock, or deliver them. A. Rack jobbers B. Catalog wholesalers C. Drop-shippers D. Truck wholesalers E. Cash-and-carry wholesalers 48. Which of these Internet approaches is LEAST likely to succeed? A. Online-only retailer Amazon differentiates its offering by being more efficient than its competitors. B. Multichannel retailer Williams-Sonoma uses its website to complement its stores and catalogs. C. Catalog operator L.L. Bean uses its website to focus on the specific needs of targeted customers. D. Large chain operator Home Depot uses its website to supplements its stores and other promotion. E. All of the above are valid approaches and likely to succeed. 49. A number of independent drugstores are working with a wholesaler to obtain economies of scale in buying. They were organized by this wholesaler after a recent meeting to discuss ways of competing with corporate chains. These drugstores are now part of a: A. corporate chain. B. voluntary chain. C. consumer cooperative. D. cooperative chain. E. franchise chain. 50. Convenience (food) stores: A. have no competitors. B. charge about the same prices as nearby supermarkets. C. try to earn better profits by high margins on a narrow assortment which turns over quickly. D. offer greater width of assortment but less depth than most supermarkets. E. none of the above. 9 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------51. Until recently, Triad Equipment, Inc. took trade-ins when it sold new equipment to manufacturers. Now, Triad has a new owner who wants to sell the inventory of used equipment quickly to the best available buyer. He should look for: A. a manufacturers' sales branch. B. a broker. C. a selling agent. D. a manufacturers' agent. E. sales finance company. 52. "Scrambled merchandising" refers to: A. retailers shifting from one product-market to another (e.g., a food retailer shifting to clothing). B. limited-line retailers carrying wide assortments. C. retailers carrying any product lines they can sell profitably. D. displays of impulse products in supermarkets. E. incompatible price and promotion policies. 53. The "Fashion Place" carries a carefully selected and distinctive assortment of traditional women's business clothing and accessories for upper-class executives in Boston. It emphasizes customer service with its well-trained salesclerks. The store is probably a: A. small department store. B. specialty shop. C. convenience store. D. single-line store. E. specialty store. 54. Which of the following is NOT a franchise operation? A. Subway (food). B. H & R Block (tax work). C. Kinko's (copy center). D. 7-Eleven (convenience store). E. All of the above are franchises. 55. Which of the following is NOT an agent wholesaler? A. A drop-shipper B. An auction company C. A selling agent D. A broker E. A manufacturers' agent 56. Will Bishop sells a wide assortment (in small quantities) of "emergency" home repair items (fuses, electrical tape, small packets of nails) to grocery and convenience stores. He owns the products he handles, and displays them for his customers. Bishop is a: A. manufacturers' agent. B. selling agent. C. rack jobber. D. cash-and-carry wholesaler. E. truck wholesaler. 10 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------57. Supermarkets are A. stores offering "hard goods" at substantial price cuts to customers. B. large, self-service stores with many departments that emphasize "soft goods" and staples but still follow the discount house's emphasis on lower margins to get faster turnover. C. large stores specializing in groceries with self-service and wide assortments. D. very large stores that try to carry not only food and drug items but all goods and services that the consumer purchases routinely. E. a convenience-oriented variation of the conventional limited-line food stores. 58. Which of the following wholesalers would be most helpful to a small manufacturer of computer components who wants to obtain distribution in several major markets and still retain control of the marketing of its products? A. Manufacturers' agents B. Rack jobbers C. Selling agents D. Brokers E. Manufacturers' sales branches 59. Identify the wholesaler type that carries a very narrow range of products, but offers more information and service than other service wholesalers. A. General merchandise B. Limited-function C. General-line D. Specialty E. Catalog 60. Retailing on the Internet: A. makes it hard for consumers to compare products or prices. B. is limited to only a few mass-merchandisers. C. makes shopping very convenient for some consumers. D. is not expected to grow very fast. E. all of the above. 61. A grocery store chain has decided to sell a small assortment of fast moving auto repair items—but is not certain what stock to carry in which stores and does not want to leave the decision to the local store manager. The chain should probably get help from a A. broker. B. cash-and-carry wholesaler. C. specialty wholesaler. D. rack jobber. E. manufacturers' agent. 62. Scrambled merchandising is carrying A. any product lines that a store thinks that they can sell profitably. B. discounted product lines. C. a specific product line and offering yearly discounts. D. a number of product lines and offering a clearance sale twice a year. E. a limited product line at a high price aimed at a small number of consumers. 11 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------63. Voluntary chains are A. firms that own and manage more than one store. B. retailer-sponsored groups formed by independent retailers that run their own buying organizations and conduct joint promotion efforts. C. wholesaler-sponsored groups that work with "independent" retailers. D. franchisors who develop good marketing strategies, and who carry out the strategy in their own units. E. firms that own a single-store but operate through multiple franchisors. 64. A good marketing manager for a retailer knows that: A. economic needs are more important than emotional needs in choosing a store. B. shopping atmosphere has little comparative importance. C. consumers only go to stores that offer the lowest possible prices. D. individual consumers have different economic and emotional needs. E. All of the above are true. 65. The percentage of new retailing ventures which fail during their first year is: A. two-thirds. B. three-fourths. C. one-half. D. one-fourth. E. one-third. 66. A good share of total U.S. wholesale sales are made by manufacturers' sales branches because: A. they are well-managed. B. branches are usually placed in the best market areas. C. costs are lower because some marketing functions are eliminated. D. about half of all wholesale businesses are owned by manufacturers. E. All of the above. 67. The biggest advantage of this limited-function wholesaler is that they promptly deliver perishable products that regular wholesalers prefer not to carry. A. Catalog wholesalers B. Rack jobbers C. Truck wholesalers D. Drop-shippers E. Specialty wholesalers 68. A _________ aims at a carefully defined target market by offering a unique product assortment, knowledgeable salesclerks, and better service. A. General store B. Mass-merchandising shop C. Specialty shop D. Department store E. Convenience store 12 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------69. Drop-shippers: A. have high operating costs because they do transporting and storing. B. do not stock the products they sell. C. do not take title to the products they sell. D. do not emphasize selling. E. Both C and D. 70. Which of the following is NOT a limited function merchant wholesaler? A. A truck wholesaler B. A general-line wholesaler C. A rack jobber D. A drop-shipper E. A catalog wholesaler 71. The wheel of retailing concept A. is consistent with the emergence of supermarkets in the 1930s. B. explains the early success of convenience (food) stores. C. explains the early success of vending machines. D. suggests that new types of retailers usually emerge as high-price, high-cost operations, and then cut their prices as competitors enter the market. E. None of the above is true. 72. Traditionally, auction companies would MOST likely be used for: A. children's clothing. B. sports equipment. C. antique furniture. D. small appliances. E. industrial chemicals. 73. Warehouse clubs such as Sam's Club and Costco A. usually operate in large, no-frills facilities. B. have been successful targeting small-business customers. C. emphasize homogeneous shopping products. D. usually charge consumers an annual membership fee. E. All of the above are true. 74. Telephone and direct-mail retailing: A. profit margins have been falling because of increased competition. B. have not had much success with expensive items, but do well with low prices on general merchandise. C. was once popular, but the Internet put all these firms out of business. D. is generally a mass marketing approach. E. All of the above are true. 13 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------75. Which of the following statements about limited-function wholesalers is TRUE? A. Cash-and-carry wholesalers serve small retailers but don't provide credit. B. Truck wholesalers sell perishable products which other wholesalers prefer not to carry. C. Rack jobbers specialize in nonfood products that sell in small quantities. D. Catalog wholesalers sell hardware, jewelry, sporting goods, and general merchandise—often catering to small industrial or retailer customers. E. All of the above are true. 76. Some differences between online and in-store customers include: A. In-store customers can usually inspect and immediately use the product. B. Online customers are usually younger, better educated, and more upscale. C. In-store customers usually get better customer service. D. Online customers usually have better access to comparative information about products. E. All of the above. 77. Which of the following is best illustrated by a supermarket that carries Nintendo video games? A. The "superstore" concept B. Scrambled merchandising C. The "wheel of retailing" D. Target marketing E. Mass merchandising 78. Limited-line stores A. specialize in certain lines of related products rather than a wide assortment. B. carry anything they can sell in reasonable volume. C. are a type of unconventional general store. D. are larger stores that are organized into many separate departments and offer many product lines. E. seldom build good relationships with their customers. 79. A corporate chain is defined as A. a firm that owns and manages more than one store. B. retailer-sponsored groups formed by independent retailers that run their own buying organizations and conduct joint promotion efforts. C. wholesaler-sponsored groups that work with "independent" retailers. D. franchisors who develop good marketing strategies, and who carry out the strategy in their own units. E. a firm that owns a single-store but operates through multiple franchisors. 80. Regarding retailing, which of the following is LEAST LIKELY to occur in the future? A. Vertical integration will increase in importance in the channels. B. Internet shopping will become less popular. C. More manufacturers will go into retailing. D. Along with larger stores, there will also be more smaller stores. E. Scrambled merchandising will continue to increase. 14 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------81. Which of the following statements about retailing on the Internet is(are) true? A. More product information is readily available. B. Product assortments available are not limited by the customer's location. C. Price comparisons are easy. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 82. Andy Cole sells fiberglass resins and fiberglass wire to the many small sailboat manufacturers in southern California. He takes title to the products but does not handle them. Instead, the resins are shipped in 50 gallon barrels directly from the producer to the sailboat manufacturers. Cole is a: A. selling agent. B. cash-and-carry wholesaler. C. manufacturers' agent. D. specialty wholesaler. E. drop-shipper. 83. A full-service wholesaler in Santa Fe takes title to the products it stocks—a full line of home repair products for independent hardware stores. This wholesaler is a: A. selling agent. B. broker. C. specialty wholesaler. D. rack jobber. E. single-line wholesaler. 84. Meg O'Brien is just starting as a rack jobber. She will: A. do what a lot of grocery store managers don't want to do. B. need a lot of money to get started, since all her customers will expect 30 days to pay their bills. C. not have to know very much about the preferences of the consumers who buy the products she handles. D. never actually handle or deliver the products in her line. E. probably get tired of visiting farmers' markets. 85. Identify the characteristics of vending machines, and door-to-door retailing. A. Expanded assortment, reduced margins, and more information. B. Added convenience and higher than conventional margins, usually reduced assortment. C. Expanded assortment and/or reduced margins and service. D. Expanded assortment and service. E. Expanded assortment and service, and more information. 86. Drop-shippers: A. are used because it is cheaper for producers to ship to them by rail and let the drop-shipper drop the products off at local retailers with small trucks. B. never take title to the products they sell. C. typically sell large shipments, e.g., rail carloads. D. have very high operating expenses. E. are full-service merchant wholesalers. 15 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------87. ____________ wholesalers are service wholesalers that carry a wide variety of nonperishable items. A. General merchandise B. Limited-function C. General-line D. Specialty E. Drop-shipper 88. Vending machine A. sales now account for almost 20 percent of consumer spending. B. retailing requires a lower margin to cover costs than for comparable products sold in stores. C. retailing has been declining. D. sales now include higher-margin products like digital cameras and iPods. E. None of the above is true. 89. All of the following are true of brokers except A. they bring buyers and sellers together. B. they are especially useful when buyers and sellers do not come into the market very often. C. they usually have a permanent relationship with the buyer and seller. D. the broker's product is information about what buyers need and what supplies are available. E. they earn commissions based on completion of transactions between buyers and sellers. 90. Merchant wholesalers A. own the products they sell. B. often specialize by certain types of products or customers. C. take title to the products they are selling for some period before selling to customers. D. constitute almost 90 percent of the wholesaling establishments in the United States. E. all of the above. 91. Expanded assortment and/or reduced margins and service are characteristic of A. supermarkets. B. convenience stores. C. specialty shops. D. Internet. E. department stores. 92. Which of the following statements about current retailing and wholesaling is true? A. Retailers are opening new websites instead of new stores. B. Catalogs have moved online. C. E-mails are supplementing toll-free phone orders. D. Auction sites are now popular for all kinds of products. E. All of the above are true. 16 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------93. Business firms that sell to retailers and other merchants, and/or to industrial, institutional, and commercial users—but which do not sell in large amounts to final consumers—are: A. retailers. B. collaborators. C. producers. D. wholesalers. E. intermediaries. 94. Regarding retailing, which of the following statements is NOT true? A. Supermarkets average about $17 million in sales per year. B. Single-line mass-merchandisers have not been successful—probably because their assortments are so limited. C. Mass-merchandisers put less emphasis on knowledgeable salespeople than more conventional retailers. D. Discount houses got their start selling "hard goods" at lower prices. E. None of the above. 95. Regarding the future of wholesalers, which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Most high-cost wholesalers will disappear in the near future. B. Modern wholesalers are seeing that vertical integration with producers provides their only assurance of long-run survival. C. Some small high-cost wholesalers will probably survive due to the specialized services they offer some market segments. D. Net profit margins in wholesaling have been increasing in recent years. E. All of the above are true. 96. A national grocery store chain has decided to sell an assortment of hobby, gardening, and cook books. Buyers in the chain's main office are not certain what to stock because they think that consumers in different areas of the country will probably be interested in different books. The store managers have said they don't know what to order either. The chain should probably get help from a A. broker. B. cash-and-carry wholesaler. C. specialty wholesaler. D. rack jobber. E. manufacturers' agent. 97. Which of the following statements about retailing in different nations in NOT true? A. Mass-merchandisers are especially popular in less-developed nations. B. Japan's Large Store Law has effectively blocked retail change in that country. C. Supermarkets started in the U.S. D. Supercenters started in Europe. E. New retailing formats that succeed in one country are quickly adapted to other countries. 17 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------98. Corporate chains A. have continued to grow—and now account for about half of all retail sales. B. have an advantage relative to independent stores when it comes to promotion and use of dealer brands. C. increase their buying power by centralizing at least some of the buying for different stores. D. all of the above. E. none of the above. 99. Regarding discount houses, which of the following statements is TRUE? A. The early discount houses emphasized hard goods. B. While some conventional retailers cut price on competitive items, discount houses regularly sell all of their products at smaller markups. C. As early discounters were able to offer full assortments, they also sought "respectability" and moved to better locations. D. Discount houses are fast-turnover, price-cutting operations. E. All of the above are true. 100. ___________ stores are usually strong in customer services, including credit, merchandise return, delivery, and sales help. A. General B. Limited-line C. Department D. Specialty E. Luxury 101. Dolly Westin calls on the many gift shops in Savannah and sells a variety of unique decorative glass items, wind chimes, and picture frames produced by the companies that she represents. The store owners can order from Dolly rather than from the three different producers she represents. Apparently, Dolly is a A. selling agent. B. rack jobber. C. drop-shipper. D. broker. E. manufacturers' agent. 102. The trend toward scrambled merchandising can be explained by: A. the "Wheel of Retailing" Theory. B. the fact that cities are getting larger and larger, and it is harder for a retailer to segment the market. C. growing consumer demand for more service in retail stores. D. the fact that some retailers have traditionally used markups which seem "too high" to other retailers. E. the growth of telephone and direct-mail retailers. 18 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------103. The "mass-merchandising" concept: A. suggests aiming at small but profitable target markets. B. focuses on increasing sales and speeding turnover by lowering prices. C. supports the conventional retailer's "buy-low and sell-high" philosophy. D. stresses the need for conventional stores. E. All of the above. 104. Which of the following is not a type of service wholesaler? A. General merchandise B. Cash-and-carry C. Specialty D. Single-line E. General-line 105. Franchise operations: A. generally have very loose ties between the franchisor and franchise holders. B. are expected to decline in the future because the service sector of the economy is failing. C. currently account for about a third of all retail sales. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 106. Door-to-door selling at consumers' homes: A. meets some consumers' needs for convenience. B. can be very useful for selling convenience products. C. accounts for more than 5 percent of total U.S. retail sales. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above are true. 107. Rack jobbers: A. don't own the products they sell. B. apply their knowledge of the local market to many stores. C. are full service merchant wholesalers. D. are different from most wholesalers because they specialize in giving small retailers long-term credit. E. All of the above. 108. Regarding supermarkets, which of the following statements is TRUE? A. It's best to think of supermarkets as "conventional retailers." B. Supermarket net profits after taxes usually are about 1 percent of sales—or less. C. Worldwide, supermarkets make up the majority of food stores. D. The early supermarkets were based on the premise that consumers would pay more for better selection and service. E. All of the above are true. 19 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------109. Rack jobbers A. specialize in hard-to-handle assortments of products that a retailer does not want to manage. B. own the products they sell but they do not actually handle, stock, or deliver them. C. promptly deliver perishable products that regular wholesalers prefer not to carry. D. sell out of catalogs that may be distributed widely to smaller industrial customers or retailers. E. are basically manufacturers' agents who specialize in international trade. 110. Which of the following are large, self-service stores with many departments that emphasize "soft goods" and staples but still follow the discount house's emphasis on lower margins to get faster turnover? A. Supermarkets B. Discount houses C. Supercenters D. Mass-merchandisers E. Direct-mail retailers 111. Sierra Plumbing, Inc. buys plumbing supplies, pipes, and tools from different manufacturers and resells them to construction companies. Sierra is MOST LIKELY: A. a rack jobber. B. a service (merchant) wholesaler. C. a drop-shipper. D. an agent wholesaler. E. a manufacturers' agent. 112. Which of the following statements about agent wholesalers is FALSE? A. Agent wholesalers based in a foreign market can be helpful in working through government red tape because they know the local business customs. B. Export and import brokers bring together buyers and sellers from different countries. C. Manufacturers' agents can call on international customers at no cost to the producer until something sells. D. Export and import agents are basically selling agents who specialize in international trade. E. Agent wholesalers are common in international trade. 113. Sandi Barefoot sells the entire output of several small companies based in Silicon Valley. Each of the companies designs and produces remote control devices. Sandi has almost complete control of pricing and selling—because the engineers who started the companies are mainly interested in inventing things. In addition, Sandi often provides working capital to the producers, who have very limited financial resources. Sandi is paid a substantial commission on all sales. Sandi is a: A. broker. B. selling agent. C. field warehouser. D. manufacturers' agent. E. factor. 20 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------114. Which of the following is LEAST likely to be sold by a supercenter? A. Trash compactor B. Photo finishing C. Lawn care materials D. Aspirin E. Milk 115. Corporate chains: A. can get a cost advantage over independent stores by spreading management costs to many stores. B. account for nearly 10 percent of retail sales. C. usually cannot obtain economies of scale in distribution. D. are declining in importance. E. All of the above are true. 116. A limited-line store is to a single-line store as A. a tennis shop is to a sporting goods store. B. a paint store is to a drugstore. C. quality is to price. D. a CD and tape store is to a movie theater. E. full service is to self-service. 117. In recent years, changes in the social and cultural environment have had a significant effect on door-to-door selling. Which of the following is MOST likely given the changes that have occurred? A. Fuller Brush has seen a dramatic increase in profits from its door-to-door selling operations. B. Sarah Coventry Jewelry has started distributing its products through jewelry stores because of the difficulties of finding someone at home during the day. C. Avon Cosmetics has found that it needs a larger door-to-door sales force because dual career families have more income and more demand. D. None of the above is likely. 118. General-line wholesalers are wholesalers that A. carry a very narrow range of products and offer more information and service than other service wholesalers. B. carry a wide variety of nonperishable items. C. operate like service wholesalers except that the customer must pay cash. D. provide only some wholesaling functions. E. carry a narrower line of merchandise than general merchandise wholesalers. 119. Mass-merchandisers: A. locate only in large downtown areas with large sales potential. B. are large, self-service stores which stress low price to get faster turnover. C. emphasize nationally-advertised "hard goods." D. usually have about as much floor space as the average supermarket. E. Both A and D are true. 21 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------120. Manufacturers' agents: A. are frequently used by manufacturers to help introduce a new product. B. typically have a temporary relationship with a manufacturer, until a specific item is sold. C. usually handle products for only a few companies since the cost of adding additional lines is quite high. D. usually handle a full assortment of products from competing manufacturers. E. buy large inventories from small manufacturers—helping them acquire working capital. 121. The idea that retailers will start to sell a new product that offers a profit margin higher than what they achieve on their traditional product line is consistent with the A. marketing concept. B. operating philosophy of most limited-line retailers. C. wheel of retailing concept. D. scrambled merchandising concept. E. none of the above. 122. A manufacturers' agent sells A. similar products for several noncompeting producers for a commission on what is actually sold. B. different products for several noncompeting producers for a commission on what is actually sold. C. similar products for several competing producers for a commission on what is actually sold. D. different products for several competing producers for a commission on what is actually sold. E. different products for several competing producers for a fixed salary irrespective of sales. 123. Which of the following is NOT retailing? A. A vacuum cleaner manufacturer hires its own sales force to sell door to door. B. A private ambulance service takes an accident victim to a hospital and charges him $100. C. A group of students sell donuts to people passing by their dorm. D. A book wholesaler has a mail-order catalog which offers discounts to final consumers who buy by mail. E. All of the above are retailing. 124. Which of the following statements about single- and limited-line stores is TRUE? A. Many are small, with high expenses relative to sales. B. They usually believe in a "buy low and sell high" philosophy. C. Such stores face the costly problem of having to stock some slow-moving items in order to satisfy their target markets. D. Most conventional retailers are single- or limited-line stores. E. All of the above are true. 125. ___________ are basically manufacturers' agents who specialize in international trade. A. Selling agents B. Auction companies C. Brokers D. Export or import agents E. Drop-shippers 22 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------126. Which of the following products is most likely to be sold by a drop-shipper? A. Skis B. Toothpaste C. Greeting cards D. Printing supplies E. Coal 127. Mass-merchandisers: A. usually operate with low margins on individual items. B. are facing declining profits—because of the intense competition. C. generally run a self-service operation. D. are concerned with maintaining high inventory turnover. E. All of the above are true. 128. A manufacturers' agent: A. sells noncompeting products for several manufacturers in a limited territory. B. is often replaced by a manufacturer's own sales force when sales rise. C. is paid a commission on sales. D. can be especially useful to a small manufacturer with a narrow line of new products. E. All of the above. 129. Expanded assortment, reduced margins, and more information are characteristics of A. club stores. B. specialty shops. C. mail order. D. Internet. E. department stores. 23 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 13chprvw17edso Key 1. (p. 361) A 2. (p. 354) D 3. (p. 352) C 4. (p. 352) B 5. (p. 345) A 6. (p. 343) B 7. (p. 344) D 8. (p. 361) A 9. (p. 359) B 10. (p. 359) D 11. (p. 358) D 12. (p. 359) A 13. (p. 362) D 14. (p. 356) E 15. (p. 359-360) D 16. (p. 352) C 17. (p. 354) D 18. (p. 362) D 19. (p. 354) D 20. (p. 349) C 21. (p. 362) E 22. (p. 349) D 23. (p. 345) D 24. (p. 358) D 25. (p. 354) D 26. (p. 354) B 27. (p. 359) E 28. (p. 361) A 29. (p. 345) C 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30. (p. 353) B 31. (p. 354) C 32. (p. 356) D 33. (p. 351-352) E 34. (p. 354) B 35. (p. 362) B 36. (p. 361) E 37. (p. 358) B 38. (p. 361) D 39. (p. 346) B 40. (p. 345) B 41. (p. 354) C 42. (p. 360) E 43. (p. 361) A 44. (p. 347) A 45. (p. 359) A 46. (p. 359) B 47. (p. 360) C 48. (p. 351-352) E 49. (p. 354) B 50. (p. 348) C 51. (p. 362) B 52. (p. 352) C 53. (p. 345) B 54. (p. 354) E 55. (p. 360-361) A 56. (p. 361) C 57. (p. 345) C 58. (p. 361) A 59. (p. 359) D 60. (p. 349-350) C 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------61. (p. 361) D 62. (p. 352) A 63. (p. 354) C 64. (p. 342-343) D 65. (p. 342) B 66. (p. 358) B 67. (p. 361) C 68. (p. 345) C 69. (p. 360) B 70. (p. 360) B 71. (p. 352) A 72. (p. 362) C 73. (p. 347) E 74. (p. 349) A 75. (p. 360-361) E 76. (p. 350) E 77. (p. 352) B 78. (p. 344) A 79. (p. 354) A 80. (p. 349-350) B 81. (p. 350) D 82. (p. 360) E 83. (p. 359) E 84. (p. 361) A 85. (p. 344, 348-349) B 86. (p. 360) C 87. (p. 359) A 88. (p. 348) D 89. (p. 362) C 90. (p. 359) E 91. (p. 344-345) A 3 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------92. (p. 363) E 93. (p. 356) D 94. (p. 347) B 95. (p. 358) C 96. (p. 361) D 97. (p. 355) A 98. (p. 354) D 99. (p. 346) E 100. (p. 345) C 101. (p. 361) E 102. (p. 352) D 103. (p. 345) B 104. (p. 359) B 105. (p. 354) C 106. (p. 349) A 107. (p. 361) B 108. (p. 345) B 109. (p. 361) A 110. (p. 346) D 111. (p. 359) B 112. (p. 362) D 113. (p. 362) B 114. (p. 347) A 115. (p. 354) A 116. (p. 344) A 117. (p. 349) B 118. (p. 359) E 119. (p. 346) B 120. (p. 361) A 121. (p. 352) D 122. (p. 361) A 4 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 13 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------123. (p. 341) E 124. (p. 344) E 125. (p. 362) D 126. (p. 360) E 127. (p. 346) E 128. (p. 361) E 129. (p. 344, 349) D 5 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Use this information for questions (1 thru 10) that refer to the Yummy Ice Cream case. Kelly Stich, marketing manager for Yummy Ice Cream Products, is thinking about some of her products and her promotion plans for the coming year. Yummy Ice Cream Products is introducing a new ice cream treat called PlanetSavers. This treat uses ice cream produced with environmentally friendly processes that save energy and protect the ozone. Yummy plans to send articles to magazines, local newspapers, and environmental groups that explain the environmentally safer treat. The product also has a unique texture and different flavor. Stich wants to use counter cards and in-store signs to let people know about Cherry Walrus, the company's new flavor. She is also developing sales training materials that will teach ice cream scoopers in Yummy's ice cream stores to promote the product. Right after Cherry Walrus is introduced each store will also hand out coupons that are good for one day only. Yummy Mondaes is a product that has been around for 25 years. It is Yummy's take on the classic ice cream sundae, but white-brownie and coffee-flavored crumbles are added to make it extra special. The company sells this product in one and two quart containers through major grocery store chains. It relies on personal selling and price discounts to retailers to move more of the product. The company does very little consumer promotion for this product. Yummy Fudge on a Stick is a new product of fudge-flavored ice cream on a stick. Yummy plans to sell it through retail grocery stores also and is launching an aggressive advertising program that will use television, radio, newspaper, magazines, and the Internet. Most of its promotion will be directed at consumers. Two years ago the company introduced Yummy Fruit on a Stick, an all-natural frozen fruit product on a stick. The product category has been popular, continues to grow, and is in the market growth stage of the product life cycle. 1. The plan for PlanetSavers emphasizes which element of the promotion blend? A. Advertising B. Publicity C. Personal selling D. Sales promotion E. Direct-response promotion 2. If Yummy relies on a sales contest to stimulate sales of Cherry Walrus, this would be an example of: A. advertising B. personal selling C. sales training D. sales promotion E. publicity 3. For a new product like PlanetSavers, which of the following would you expect to be a primary objective of the promotion that is planned? A. control of the message channel B. increased promotional push C. informing consumers D. reminding ice cream shop managers and retailers E. persuading consumers who overwise wouldn't eat ice cream. 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4. If Yummy wanted to target opinion leaders, which of the following groups is most likely to include them? A. innovators B. early adopters C. laggards D. late majority E. early majority 5. Which of the following AIDA promotion objectives is best achieved by coupons for Cherry Walrus? A. attention B. interest C. desire D. action 6. The promotion for Yummy Mondaes is a good example of: A. pushing B. direct-response promotion C. pulling D. integrated marketing communications E. noise in the communication process 7. The Yummy Fudge on a Stick promotion plan relies on: A. direct-response promotion B. integrated marketing communications C. pushing D. pulling E. noise in the communication process 8. According to your textbook, with a new product like PlanetSavers, a marketing manager should: A. attempt to obtain publicity B. target initial communications toward innovators and early adopters C. use an informing promotional objective D. all of the above E. none of the above 9. The brand manager who puts together a promotion blend for Yummy Mondaes should: A. realize that the right blend depends more on what customers expect than what the firm wants to accomplish. B. determine who the firm is trying to influence. C. determine the one right promotion blend and then implement it. D. be primarily concerned with informing rather than persuading. 10. Based on where the product category is in the product life cycle, promotion for Yummy Fruit on a Stick should: A. emphasize ways that Yummy Fruit on a Stick is best. B. be cut back or dropped so that money can be used on products that contribute to customer equity. C. use reminder advertising. D. build primary demand. 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11. Which of the following illustrates communication "noise"? A. A radio ad for Planet Savers is recorded at a higher volume than the music. B. A consumer waiting in line for an ice cream cone can't see the sign promoting Cherry Walrus because the store is so crowded. C. A consumer who thinks that environmentally friendly ice-cream is a stupid idea decides to try the new Planet Savers flavor anyway. D. A TV ad for Yummy Fudge on a Stick features a large group of children singing and eating Yummy ice cream. E. All of these illustrate "noise." 12. Which of the following illustrates customer-initiated interactive communication? A. People who enter Yummy's online contest receive a "2 for 1" coupon for Yummy's new flavors. B. A customer goes to Yummy's website to see if Yummy has an ice cream shop that is nearby. C. A consumer goes to the CNN website and selects a video clip from World Cup Soccer, but at the start of the clip there is a short ad that shows kids eating Yummy Mondaes. D. A "gamer" at an online website ends a game and encounters a pop-up ad for Yummy Fruit on a Stick. E. Consumers who participate in an online marketing research survey are later called and interviewed about which of Yummy's ads they remember. 13. To get the most out of its promotion spending, Yummy should probably develop its budget by: A. allocating some fixed percentage of net sales. B. matching expenditures with competitors. C. allocating money to the needs of new products first, then use any leftover money for other products. D. using the "task method." E. spending all available funds. 14. Regarding promotion blends, which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Consumer products producers should rely almost completely on personal selling in the market maturity stage. B. Reminding becomes important in the market introduction stage. C. More targeted promotion is needed during the sales decline stage of the product life cycle. D. Informing becomes important in the market growth stage. E. None of the above is true. 15. Regarding opinion leadership, which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Opinion leaders are easy to identify because people seek them out for advice on all kinds of topics. B. It is very important to reach the innovators—because this adopter group is the highest in opinion leadership. C. "Word of mouth" always does the real selling job—so Promotion is not necessary. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 3 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------16. A firm with a product in the maturity stage of the product life cycle is likely to focus on which basic promotion objective? A. pioneering B. publicizing C. informing D. lagging E. persuading 17. A retailer's target market consists of people who usually will not consider a new idea until others have tried it—and liked it. These potential customers have a lot of contact with mass media and salespeople, but usually are not opinion leaders. These target customers are: A. early adopters. B. laggards. C. innovators. D. the early majority. E. the late majority. 18. Integrated direct-response promotion: A. isn't necessary or useful when the channel of distribution involves intermediaries. B. is usually part of a pushing effort rather than part of a pulling approach. C. focuses on achieving a measurable, direct response from specific target customers. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 19. Relative to other promotion methods, _____ can usually be implemented quickly and get results sooner. A. mass selling B. advertising C. publicity D. personal selling E. sales promotion 20. Determining the blend of promotion methods is a strategy decision which is the responsibility of the A. brand ambassador. B. finance manager. C. personnel manager. D. marketing manager. E. recruitment manager. 21. Nantucket Hammocks, Inc. uses dealer incentives, discounts, and sales contests in order to encourage retailers to give special attention to selling its products. Nantucket Hammocks is using A. exclusive distribution. B. a corporate channel system. C. dual distribution. D. an administered channel system. E. pushing. 4 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------22. Regarding adopter groups, which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Innovators rely on the mass media and salespeople. B. The early majority usually aren't opinion leaders. C. Laggards rely primarily on opinion leaders. D. Early adopters make little use of salespeople. E. The late majority make the most use of salespeople. 23. In the market introduction stage A. the main job is to persuade customers to buy, and keep buying, the company's product. B. the basic promotion objective is informing. C. more competitors enter the market. D. promotion emphasis shifts from building primary demand to stimulating selective demand. E. mass selling and sales promotion dominate the promotion blends of consumer products firms. 24. When firms promote products to their own employees as part of an internal marketing effort, they are using a A. digital marketing approach. B. pulling approach. C. personal selling approach. D. telemarketing approach. E. pushing approach. 25. Typically the _____ is responsible for building good distribution channels and implementing "place" policies. A. public relations manager B. sales manager C. advertising manager D. human resources manager E. recruitment manager 26. Business firms in the late majority group A. are willing to take the risk of doing something new. B. tend to be older and less well educated. C. are the smallest businesses with the least specialization. D. tend to be highly specialized. E. tend to be conservative, smaller-sized firms with little specialization. 27. Regarding PROMOTION BUDGETS and PROMOTION BLENDS: A. A national TV ad might cost less per person reached than a local TV ad. B. The total cost of mass media may force small firms to use promotion alternatives that are more expensive per person. C. A city-wide newspaper ad might cost less per person reached than a neighborhood newspaper ad. D. There are some economies of scale in promotion. E. All of the above are true. 5 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------28. Advertising A. tries to attract attention to the firm and its offerings without having to pay media costs. B. is any unpaid form of nonpersonal presentation of ideas, goods, or services. C. must be paid for, while another form of mass selling—publicity—is "free." D. is the main form of personal selling which includes the use of traditional media as well as new media. E. involves direct spoken communication between sellers and potential customers. 29. Identify the false statement regarding promotion to intermediaries. A. When suppliers offer similar products and compete for attention and shelf space, intermediaries usually pay attention to the one with the best profit potential. B. Sales managers handle most of the important communication with intermediaries who do not want empty promises. C. Sales promotions targeted at intermediaries usually focus on short-term arrangements that will improve the intermediary's profits. D. Trade ads usually encourage intermediaries to contact the supplier for more information, and then a salesperson takes over. E. During sales promotion, intermediaries want to know what they can expect in return for their cooperation. 30. The best way to reach EARLY adopters is through: A. impersonal and scientific information media. B. salespeople and mass media. C. innovators. D. the mass media. E. opinion leaders. 31. The "adoption curve" shows that: A. most new products are introduced too slowly. B. the marketing plan for a new product should schedule most of the promotion spending right when the product is first introduced. C. some groups accept a new idea before others. D. a firm should stick to the same promotion effort as time passes. E. All of the above. 32. Producers and wholesalers that target business customers typically emphasize A. publicity. B. mass selling. C. personal selling. D. advertising. E. sales promotions. 6 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33. Regarding promotion methods, which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Personal selling can provide immediate feedback. B. Publicity is "free," but usually is ineffective for really new products. C. Advertising is usually more tailored to the individual needs and attitudes of target customers than personal selling. D. Sales promotion activities produce results very slowly compared to advertising. E. All of the above are true. 34. Which of the following is not likely to be an ethical concern raised by direct-response methods? A. Harvesting trees to make paper for direct-response junk mail. B. Getting direct-promotion telephone solicitations at any time. C. Using a direct-response database that includes personal information. D. Sending out weekly specials via an e-mail newsletter on a request only basis. E. Coping with the constant flow of spam in e-mail boxes. 35. Early adopters A. tend to rely on information sources that are not controlled by marketers. B. tend to be opinion leaders. C. are the first adoption curve group to buy a product. D. all of the above. E. none of the above. 36. Which of the following is NOT an example of sales promotion? A. A "10 cents off" coupon promotion. B. Point-of-purchase displays. C. Trade show exhibits. D. Free samples. E. A wholly new kind of ad. 37. Integrated direct-response promotion: A. got its start in the area of direct-mail advertising. B. is often part of an integrated marketing communications program. C. focuses on achieving feedback from a target customer that is immediate and measurable. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 38. Clearwater Office Supply sells frequently purchased office supplies to businesses in a metropolitan area. It is a well established company with a large share of the market. Its promotion should probably focus on A. reminding. B. stimulating primary demand. C. informing. D. innovators. E. making the demand curve less elastic. 7 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------39. A marketing manager should realize that the adoption curve concept implies A. that the firm's promotion target should be the innovators. B. that the laggards are cautious, but that they are willing to adopt a new product quickly if advertising gets their attention. C. using different promotional mixes for different adopter groups. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 40. The task method for budgeting marketing expenses: A. means that a company budgets roughly what competitors budget for each item. B. budgets last year's marketing expense ratio times FORECASTED sales. C. might result in very different marketing expenses from year to year. D. is the most commonly used method of setting budgets. E. None of the above is true. 41. MASS SELLING, in contrast to personal selling: A. is less expensive when the target customers are numerous and scattered. B. doesn't provide immediate feedback. C. is less flexible in adapting to customers' needs and attitudes. D. All of the above. 42. The innovators are the group of customers who A. have fewer contacts outside their own social group or community. B. tend to have the greatest contact with salespeople. C. tend to avoid risk and wait to consider a new idea after many early adopters have tried it—and liked it. D. tend to be older, less well educated, and cling to the status quo thinking it is the safest way. E. are likely to be mobile and have many contacts outside their local social group and community. 43. Wholesalers spend the largest share of their promotion money on: A. personal selling. B. direct-mail advertising. C. advertising. D. sales promotion. E. publicity. 44. Which of the following statements about communication processes is(are) true? A. Action is more immediate in customer-initiated interactive communication. B. The seller starts the communication in the traditional communication process. C. Noise can distract the process in traditional and customer-initiated interactive communication. D. The buyer starts the communication in the customer-initiated interactive communication process. E. All of the above are true. 8 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------45. In the customer-initiated interactive communication process: A. the message channel is no longer a factor. B. noise is no longer a factor. C. messages typically must be very short and simple. D. the buyer starts the process. E. none of the above is true. 46. Which of the following best illustrates communication "noise"? A. Magazine sales reps telephone consumers to offer low-price subscriptions. B. A TV ad is recorded at a higher volume than is used for most TV shows. C. A political candidate rides through town in a car with a loud speaker—asking pedestrians to vote for her. D. All of the above illustrate "noise." E. None of the above clearly illustrates "noise." 47. In addition to snail mail, direct-response promotion may include: A. broadcast B. telephone C. e-mail D. the Internet E. any of the above 48. When marketing a truly new product, a marketing manager should: A. use an informing promotion objective. B. target communication towards innovators and early adopters. C. attempt to obtain publicity. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 49. A research report shows that a magazine's readers are well respected by their peers and high in opinion leadership. They tend to be younger, more mobile, and more creative than later adopters. But they have fewer contacts outside their own social group or community than innovators. A firm might advertise to the readers of this magazine if it is targeting: A. laggards. B. innovators. C. the early majority. D. early adopters. E. the late majority. 50. A retailer's target customers are skeptical and cautious about new ideas. Strong social pressure from their own peer group may be needed before they adopt a new product. These target customers are: A. the early majority. B. laggards. C. innovators. D. early adopters. E. the late majority. 9 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------51. All of the following are true of the market growth stage except A. in the market growth stage, the main job is to persuade customers to buy, and keep buying, the company's product. B. in the market growth stage, the promotion must build primary demand and not just for the company's own brand. C. in the market growth stage, more competitors enter the market and mass selling becomes more economical. D. in the market growth stage, the promotion emphasis shifts to stimulating selective demand. E. in the market growth stage, salespeople and personal selling work towards expanding the number of outlets and cementing relationships with channel members. 52. Identify the true statement pertaining to publicity. A. It is any paid form of nonpersonal presentation of ideas, goods, or services by a sponsor. B. It is the main form of mass selling which includes only the use of traditional media. C. If a firm has a really new message, publicity may be less effective than advertising. D. A major disadvantage is that the media does not always say or show what the firm intends. E. It tries to attract attention to the firm and its offerings by paying substantial media costs. 53. In this method of budgeting, the spending level might be based on the number of new customers desired and the percentage of current customers that the firm must retain to leverage investments in already established relationships. A. Basing the budget on the job to be done. B. Basing the budget on any uncommitted revenue. C. Setting the budget as a certain number of cents or dollars per sales unit. D. Matching expenditures with competitors. E. Setting the budget based as a certain number of dollars per person. 54. A retailer's target customers are young, well educated, and mobile—with many contacts outside their local social group and community. They are eager to try new ideas and are willing to take risks. These target customers are: A. innovators. B. laggards. C. early adopters. D. the late majority. E. the early majority. 55. The AIDA model's four basic promotion jobs are concerned with: A. attention, interest, desire, action. B. action, interest, desire, acceptance. C. awareness, interest, demand, action. D. attention, internalization, decision, action. E. awareness, interest, decision, acceptance. 10 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------56. A producer is likely to focus its promotion effort on stimulating selective demand at what stage in the product life cycle? A. Market introduction B. Market growth C. Market maturity D. Sales decline E. When primary demand is exhausted. 57. Which of the following is NOT true concerning adoption curve groups? A. The early adopter group tends to have the greatest contact with salespeople. B. Early adopters are often unusual people who are not seen as opinion leaders. C. Innovators rely more on impersonal sources of information than on salespeople. D. Business firms in the innovator group are usually large and rather specialized. E. The early majority group have a lot of contact with mass media, salespeople, and opinion leaders. 58. Direct-response promotion may include: A. interactive video B. mail C. website D. broadcast E. all of the above 59. In promotion to final consumers: A. advertising and sales promotion are the dominant promotion methods. B. aggressive personal selling is usually found only in expensive channel systems. C. reminder ads may be all the promotion that is needed for products that have won brand preference or insistence. D. personal selling is effective for consumer electronics and automobiles. E. all of the above. 60. The best way to reach INNOVATORS is through: A. the mass media. B. salespeople. C. local opinion leaders. D. impersonal and scientific information sources. E. salespeople and the mass media. 61. Which of the following is NOT true about the relation between promotion blends and the promotion target? A. Pushing in the channel means using normal promotion to intermediaries. B. Service-oriented companies often try to design ads targeted at customers that also communicate to their own employees. C. Promotion to intermediaries emphasizes personal selling. D. Pushing within the firm involves promotion to employees, especially salespeople. E. All of the above are true. 11 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------62. Direct-response promotion usually relies on a _____ database to target specific prospects. A. customer relationship management B. sales force management C. entity-attribute-value model D. enterprise relationship management E. multidimensional preference 63. Budgeting for marketing expenses by computing a percentage of forecasted sales: A. is especially suitable for new products. B. always results in increased expenditure levels from year to year. C. is very complicated—and thus this method is not used very often. D. may lead to a drop in marketing expenses at a time when the firm wants to maintain or expand sales. E. tends to result in large changes in marketing expenses from year to year. 64. Regarding adoption curve groups, which of the following is TRUE? A. By the time the early majority buy a product it is usually in the market maturity stage of the product life cycle. B. The early adopters have many contacts outside their own social group, and are important in spreading information to laggards. C. Business firms in the late majority group tend to be conservative, smaller-sized firms with little specialization. D. The laggard group may be slow to adopt, but it is so large that it is very important to reach them. E. None of the above is true. 65. In the market maturity stage A. sales promotion may be targeted at channel members to get them interested in selling the new product. B. mass selling becomes more economical. C. business products require less aggressive personal selling. D. mass selling and sales promotion may dominate the promotion blends of consumer products firms. E. the main job is to persuade customers to buy, and keep buying, the company's product. 66. In promotion to intermediaries: A. personal selling is the dominant promotion method. B. trade ads are used to inform intermediaries about new offerings. C. promotion must be both informative and persuasive. D. sales promotions are used to boost the intermediary's profits on a short-term basis. E. all of the above. 67. "Publicity": A. is generally less effective than advertising for promoting a really new product. B. is mass selling that avoids paying media costs. C. is any paid form of nonpersonal presentation of ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor. D. is more expensive than all other promotion methods. E. Both A and B are true. 12 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------68. The _____ can help the promotion effort by spreading word-of-mouth information and advice among other consumers. A. innovators B. late majority customer group C. laggards D. early adopters E. nonadopters 69. _____ is a promotion activity that tries to spark immediate interest in the consumer. A. Personal selling B. Advertising C. Publicity D. Sales promotion E. Press release 70. In customer-initiated interactive communication: A. the message channel has no impact. B. noise is no longer a factor. C. the source initiates the communication. D. interactive technology plays a big role. E. action is less immediate. 71. During the sales decline stage A. the total amount spent on promotion usually decreases as firms try to cut costs to remain profitable. B. firms do not need targeted promotion to reach customers. C. personal selling will probably dominate the promotion blends of consumer products firms. D. promotion emphasis shifts from stimulating selective demand to building primary demand. E. sales promotion is primarily targeted at intermediaries to get them interested in selling the product. 72. Which of the following is NOT an example of sales promotion? A. a banner ad on AOL's stock page. B. a bumper sticker that says, "Drink more milk." C. samples of a new low-fat snack cracker given away at a supermarket. D. a display of fishing equipment by a sporting goods store in a shopping mall. E. a small toy in a kid's "happy meal" at McDonald's. 73. When developing a good promotion blend, a marketing manager should: A. be more concerned with persuading the target customers than informing or reminding. B. determine who the firm is trying to influence. C. realize that the right blend depends more on what customers expect than on what the firm wants to accomplish. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 13 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------74. The adoption curve concept is most closely related to which of the following? A. "noise" in the communication process B. sales promotion aimed at a company's own sales force C. the product life cycle D. selective demand E. the AIDA model 75. A producer might use a "pulling policy" rather than a "pushing policy" if: A. intermediaries are reluctant to handle a new product. B. it is offering a very "high-tech" product to a small product-market. C. its sales force has been very successful getting wholesalers and retailers to handle its product. D. it has a very limited promotion budget. E. All of the above. 76. The early majority group A. tends to have the greatest contact with salespeople. B. tends to cling to the status quo and think it's the safe way. C. prefers to do things the way they have been done in the past and are very suspicious of new ideas. D. tends to avoid risk and waits to consider a new idea after many early adopters have tried it—and liked it. E. can help the promotion effort by spreading word-of-mouth information and advice among other consumers. 77. Which of the following adopter groups is most important to "sell"—given the importance of opinion leaders? A. Late majority B. Early majority C. Laggards D. Innovators E. Early adopters 78. The "communication process" shows that: A. sources and receivers should have a common frame of reference. B. the receiver is usually not influenced by the nature of the message channel. C. sources decode messages and receivers encode them. D. all media appear to be equally effective as message channels. E. None of the above is true. 79. Which of the following is NOT an example of sales promotion? A. a small toy in a "kid's pack" at a Wendy's fast-food restaurant. B. a half-page ad in the telephone Yellow Pages for a security service. C. an auto bumper sticker that says "Buy American." D. samples of a new brand of cheese given away at a supermarket. E. a display of fishing equipment by a sporting goods store in a shopping mall. 14 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------80. Poor communication is likely if: A. there is no "noise" in the message channel. B. the source and the receiver do not have a common frame of reference. C. the encoder and the decoder are not the same person. D. immediate feedback is not possible. E. the source and the receiver don't have personal contact. 81. Regarding PRODUCT LIFE CYCLES and PROMOTION: A. During market introduction, the basic promotion objective is to remind. B. In sales decline, the amount spent on promotion usually increases as firms use reminder promotion to increase demand. C. Persuading becomes important in the market growth stage. D. In market maturity, more competitors enter the market and the promotion emphasis must now shift to building selective demand for the firm's own brand. E. All of the above are true. 82. Integrated direct-response promotion: A. got its start when the introduction of TV made it possible for firms to use broadcast advertising to reach mass markets. B. is an alternative to integrated marketing communications, which are used when direct-response is not required. C. takes many forms, but it always involves the use of mail advertising. D. all of the above are true. E. none of the above is true. 83. The LATE MAJORITY: A. make a lot of use of mass media. B. respond more to social pressure from other late adopters than to salespeople. C. make a lot of use of salespeople. D. use salespeople and have much contact with the early majority. E. have a lot of contact with early adopters. 84. Which of the following statements about promotional expenses is true? A. People correctly think that promotion money gets spent primarily on advertising. B. The many ads that people see on the Web, in magazines and newspapers, and on TV are impressive and inexpensive. C. All the special sales promotions add up to less money than advertisements. D. Firms spend more money on advertising than on sales promotion. E. Firms spend less money on advertising than on personal selling. 85. A firm's annual sales meeting A. is a type of external marketing effort. B. is basically a variation on the pulling approach. C. is a type of internal marketing effort which is a variation on the pushing approach. D. is a method of promotion implemented where the employees' effort is an expendable part of the product. E. is a type of internal marketing effort which is a combination of both the pushing and pulling approach. 15 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------86. The EARLY MAJORITY have a lot of contact with: A. innovators. B. the mass media only. C. the mass media, salespeople, and early adopter opinion leaders. D. impersonal and scientific information sources. E. salespeople only. 87. Early adopters A. can help the promotion effort by spreading word-of-mouth information and advice among other consumers. B. tend to rely on impersonal and scientific information sources, or other innovators, rather than salespeople. C. avoid risk and wait to consider a new idea after laggards have tried it—and liked it. D. make little use of marketing sources of information—mass media and salespeople. E. tend to look to the early majority group for advice. 88. Identify the traditional communication process. A. Source-Encoding-Message channel-Decoding-Receiver-Feedback. B. Source-Encoding-Message channel-Receiver-Feedback. C. Source-Encoding-Message channel-Noise-Receiver-Feedback. D. Source-Message channel-Decoding-Receiver-Feedback. E. Source-Noise-Message channel-Receiver-Feedback. 89. Producers that advertise in GOOD HOUSEKEEPING magazine sometimes show that they have the Good Housekeeping "seal of approval." This illustrates their recognition of the importance of the ______________ in the communication process? A. feedback B. noise C. decoding D. encoding E. message channel 90. A producer is likely to focus its promotion effort on stimulating primary demand at what stage in the product life cycle? A. Market introduction B. Market growth C. Market maturity D. Sales decline E. When selective demand is over. 16 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------91. Which of the following statements about innovators is not true? A. Innovators tend to rely on impersonal and scientific information sources, or other innovators, rather than salespeople. B. Innovators often search for information on the Internet, read articles in technical publications, or look for informative ads in special interest magazines. C. Innovators tend to be young and well educated and are eager to try a new idea. D. Innovators need strong social pressure from their own peer group before they adopt a new product. E. Innovators are also constituted by specialized business firms who are willing to take the risk of doing something new. 92. The MOST COMMON method of setting the marketing budget is to A. let internal politics decide. B. estimate what competitors are spending. C. determine the cost of the tasks to be accomplished. D. use all uncommitted revenue. E. use some predetermined percentage of past or forecast sales. 93. "Advertising": A. is less expensive than personal selling for reaching large and widespread target markets. B. is any paid form of nonpersonal presentation of ideas, goods, or services by an identified seller. C. is not the same as publicity. D. is less flexible than personal selling. E. All of the above are true. 94. In promotion to business customers, personal selling is often the dominant promotion method because: A. there are fewer business customers than final consumers. B. the sales message may need to be adjusted to the needs of different people in the firm. C. purchases are typically large and thus justify the effort. D. buyers are more likely to have technical questions. E. all of the above. 95. "Promotion" does NOT include: A. personal selling. B. sales promotion. C. advertising. D. introductory price dealing. E. publicity. 17 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------96. Clairol Corp. is introducing a new brand of shampoo in a highly competitive market. Wholesalers might be willing to handle the new product, except that retailers are already complaining about overcrowded shelf space. Therefore, Clairol has decided to spend $10 million on TV advertising and send free samples to 3,000,000 households to convince consumers of the new product's superiority— and to get them to ask for it at their retail store. Clairol is using: A. dual distribution. B. a "pulling" policy. C. direct marketing. D. a "pushing" policy. E. a sampling distribution. 97. Decoding A. is the process of the receiver translating the message. B. is the process of the source deciding what it wants to say. C. is the process of the source translating the message into words. D. is any distraction that reduces the effectiveness of the communication process. E. is the process of transferring information from the subordinate to the superior. 98. "Noise" (in the traditional communication process) refers to: A. any distractions that reduce the effectiveness of the communication process. B. radio advertising interference only. C. messages which are too loud or bold. D. efforts by a firm's competitors to block its message channel. E. the encoded message before it is decoded. 18 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14chprvw17edso Key 1. (p. 370) B 2. (p. 371) D 3. (p. 374) C 4. (p. 387-388) B 5. (p. 375) D 6. (p. 383) A 7. (p. 384) D 8. (p. 386-388) D 9. (p. 383-385) B 10. (p. 390) A 11. (p. 376) B 12. (p. 381) B 13. (p. 390) D 14. (p. 390) C 15. (p. 387-388) E 16. (p. 389) E 17. (p. 388) D 18. (p. 378) C 19. (p. 371) E 20. (p. 372) D 21. (p. 383) E 22. (p. 388) B 23. (p. 389) B 24. (p. 383-384) E 25. (p. 372) B 26. (p. 388) E 27. (p. 390) E 28. (p. 369-370) C 29. (p. 383) B 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30. (p. 387) B 31. (p. 386) C 32. (p. 385) C 33. (p. 369) A 34. (p. 379) D 35. (p. 387) B 36. (p. 371) E 37. (p. 378) D 38. (p. 374) A 39. (p. 388) C 40. (p. 391) C 41. (p. 369) D 42. (p. 387) E 43. (p. 385) A 44. (p. 379-382) E 45. (p. 380) D 46. (p. 376) E 47. (p. 378) E 48. (p. 386-388) D 49. (p. 387) D 50. (p. 388) E 51. (p. 389) B 52. (p. 370) D 53. (p. 391) A 54. (p. 386-387) A 55. (p. 375) A 56. (p. 389) B 57. (p. 387-388) B 58. (p. 378) E 59. (p. 384) E 60. (p. 387) D 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------61. (p. 383-384) E 62. (p. 378) A 63. (p. 390) D 64. (p. 388) C 65. (p. 389) D 66. (p. 385) E 67. (p. 370) B 68. (p. 387) D 69. (p. 371) D 70. (p. 380) D 71. (p. 390) A 72. (p. 371) A 73. (p. 383-385) B 74. (p. 386) C 75. (p. 384) A 76. (p. 388) D 77. (p. 387) E 78. (p. 377) A 79. (p. 371) B 80. (p. 377) B 81. (p. 389) C 82. (p. 378) E 83. (p. 388) B 84. (p. 371) E 85. (p. 383) C 86. (p. 388) C 87. (p. 387-388) A 88. (p. 376) A 89. (p. 377) E 90. (p. 389) A 91. (p. 386-387) D 3 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 14 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------92. (p. 390) E 93. (p. 369-370) E 94. (p. 385) E 95. (p. 368-369) D 96. (p. 384) B 97. (p. 376) A 98. (p. 376) A 4 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Use this information for questions that refer to the "Salespeople" case. Wilson Alvaro graduated with a marketing degree almost a year ago. Like many of his friends, he took a job in sales and really enjoys it. A description of Wilson's job and those of some of his friends are noted below. Wilson Alvaroloves biking and has his dream job. He works for a wholesale company that sells mountain bikes for a manufacturer. He works with a small group of people who call on the buying offices for two large retail chains, Wal-Mart and Toys R Us. The group includes a finance person and a production person, and they all work together to meet the specific needs of these two big accounts; for example, sometimes they recommend a model of bike that will be available from only that retailer's stores. However, Wilson's main job focuses on building relationships and solving customer problems. Only occasionally is he expected to try to persuade the retailers to buy more bikes. Amy Bowdensells life insurance. She calls on new parents and persuades them to buy insurance products. It is difficult for a manager to control Amy's work, but she has incentive to work hard because her job security and income depend on getting sales. She is a confident self-starter, so she likes it that way. Ben Petersonworks for a fashionable men's clothing store. He enjoys spending time with customers who come in, learning about their fashion needs, and helping them pick clothes that really work for them. While the store manager can easily observe and direct Ben's activities, the manager wants Ben to have the incentive to increase customer purchases and satisfaction. Emily Wintershandles inside sales for a major industrial distributor. She deals with a regular set of established customers, most of whom know what they want. Emily talks to them on the phone and answers questions about products, delivery time, and pricing. She sometimes works with outside sales reps who visit customers and help introduce new products. Emily is the first person her customers call when there's a problem with a purchase, so she spends a lot of time dealing with customer problems. As an inside salesperson, Emily's work is easily supervised by a sales manager and she has little influence on how much her customers buy. Melissa Tranworks for a company that sells paper products (like napkins, paper towels, and paper plates) primarily through small independent grocers. Most of the grocers are regular customers, but sometimes she makes cold calls to new grocery stores. Melissa's job is to develop goodwill and try to increase sales. For example, she often sets up special promotional displays in stores. Her compensation plan gives her income security, but she also can receive a bonus for sales growth in her territory. Charlie Riggs is a telemarketer for an Internet service provider. He calls people on a list provided by his firm and tries to sign them up for Internet service. Charlie relies heavily on a presentation he learned during his training. Charlie is very good at what he does and loves that the more success he has the more he earns. 1. Which salesperson's main sales task is supporting? A. Wilson Alvaro B. Melissa Tran C. Emily Winters D. Ben Peterson 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2. Which salesperson's primary task is order taking? A. Emily Winters B. Melissa Tran C. Amy Bowden D. Wilson Alvaro E. Charlie Riggs 3. Wilson Alvaro's sales position involves: A. providing customer service. B. team selling. C. major account management. D. all of the above. E. none of the above 4. Which salesperson has a job where compensation is likely to be straight salary? A. Ben Peterson B. Amy Bowden C. Melissa Tran D. Emily Winters E. Charlie Riggs 5. What type of compensation plan should Ben Peterson have? A. straight salary B. straight commission C. a combination of salary and commission. D. a salary that is paid only if a certain sales quota is achieved. E. any of the above is equally appropriate for Ben's job. 6. Which salesperson probably does the most prospecting? A. Amy Bowden B. Wilson Alvaro C. Melissa Tran D. Charlie Riggs 7. What sales presentation approach does Charlie Riggs use? A. missionary presentation. B. prepared sales presentation. C. consultative selling approach. D. selling formula approach. E. no sales presentation approach is used because he just calls people and says what he learned during training. 8. What type of sales presentation approach does Ben Peterson use? A. Consultative selling approach. B. Prepared sales presentation. C. Missionary selling. D. Selling formula approach. E. Sales quota approach. 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9. Which salesperson does the most customer service? A. Charlie Riggs B. Melissa Tran C. Emily Winters D. Ben Peterson E. Amy Bowden 10. Which salesperson has a job that requires NO training in sales? A. Charlie Riggs. B. Melissa Tran. C. Emily Winters. D. Ben Peterson. E. All of these jobs require some training in sales. 11. Melissa Tran's company wants to have enough salespeople to serve 1,000 accounts. An effective salesperson can call on each account 12 times a year and should average about two hours per sales call. Each salesperson works 40 hours a week and takes off two weeks for vacation each year. Salespeople spend half their time on travel and administration. How many salespeople does Melissa's company need? A. 6 B. 12 C. 24 D. 40 E. There is not enough information to determine the answer. 12. At least ________ percent of the total U.S. labor force do sales work. A. 20 B. 10 C. 30 D. 50 E. 40 13. Which of the following statements about salesperson compensation is FALSE? A. Commissions reduce the need for working capital. B. Incentives must be carefully aligned with the firm's objectives. C. Compensation plans should be clear. D. Sales managers must plan, implement, and control. E. None of the above is false. 14. Order getters A. are concerned with establishing relationships with new customers and developing new business. B. sell to the regular or established customers, complete most sales transactions, and maintain relationships with their customers. C. usually handle all adjustments or complaints. D. routinely complete sales made regularly to target customers. E. are usually responsible for answering any final questions and completing the sale. 3 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15. With the ___________ approach, the salesperson assumes that a customer faced with a particular stimulus will say yes to his request for an order. A. Selling formula B. Consultative selling C. Prepared sales D. Fixed sales E. Differentiated value 16. A salesperson for cold remedy products visits pharmacists during the cold season and encourages them to use a special end-of-aisle display for his firm's cough syrup and then helps set up the display. The salesperson is a(n)____________. A. Customer service representative B. Order taker C. Technical specialist D. Missionary salesperson E. Order getter 17. Which of the following statements about a salesperson's role is TRUE? A. The salesperson rarely serves as a link between the firm and its customers. B. The salesperson represents the customer back inside the selling firm. C. The salesperson also holds titles such as management specialist and chief engineer. D. The salesperson only aims to sell the customer. E. A salesperson is seldom responsible for negotiating prices or diagnosing technical problems. 18. With the ___________ approach, the customer and the salesperson work together to satisfy the customer's needs and solve the problem. A. Prepared sales B. Fixed sales C. Selling formula D. Consultative selling E. Differentiated value 19. Missionary salespeople A. work with customers to resolve problems that arise at the time of purchase. B. work for producers calling on their intermediaries and their customers. C. provide technical assistance to order-oriented salespeople. D. work with customers to resolve problems that arise with a purchase, usually after the purchase has been made. E. provide information about products, explain company policies, and even negotiate prices or diagnose technical problems. 20. HP sells custom-made computer systems. Besides order getters, HP probably uses: A. order takers. B. missionary salespeople. C. merchandisers. D. manufacturers' agents. E. technical specialists. 4 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------21. CeCe Springer works for a large cosmetics company. She calls on retailers to tell them about her firm's new products, to train the retailers' salespeople, and to set up promotion displays. Her boss actually handles the order-related activities. CeCe is: A. an order getter. B. a manufacturers' agent. C. a technical specialist. D. an order taker. E. a missionary sales rep. 22. ______________ would be LEAST LIKELY to use supporting salespeople. A. Supermarkets B. Producers of prescription drugs C. Producers of business accessories D. Producers of consumer staples E. Merchant wholesalers of installations 23. Tyler Young sells a diverse line of conveyor systems to small manufacturers. He has found that he is most successful when he uses the sales call to help the customer solve some problem using one of his products. Tyler probably relies on A. the missionary approach. B. the prepared presentation approach. C. the selling formula approach. D. the consultative selling approach. E. Any of the above is equally likely. 24. Customer service reps A. work with customers to resolve problems that arise at the time of purchase. B. work for producers calling on their intermediaries and their customers. C. provide technical assistance to order-oriented salespeople. D. work with customers to resolve problems that arise with a purchase, usually after the purchase has been made. E. are invaluable in working with business customers, but not final consumers. 25. Regarding sales force payment methods: A. it is common to sacrifice some simplicity to gain more flexibility, incentive, or control. B. combination plans offer some degree of security, incentive, and control. C. straight commission offers the most incentive. D. straight salary provides the most security and control. E. All of the above are true. 26. Customer service reps help: A. customers buy. B. the company win customers. C. when a customer has technical questions that an order taker can't answer. D. the company keep customers. E. all of the above. 5 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------27. Which of the following descriptions of the three basic sales tasks is CORRECT? A. ORDER-TAKING: various activities aimed at getting sales in the long run. B. SUPPORTING: routine completion of sales made regularly to target customers. C. ORDER-GETTING: seeking possible buyers with a well-organized sales presentation designed to sell a good, service, or idea. D. All of the above are correct. E. None of the above is correct. 28. A producer's order taker A. usually has little opportunity to increase sales in a territory. B. is expected to help customers when something goes wrong with the marketing mix. C. doesn't have to make sales presentations or keep customers informed about new developments— order getters do these tasks. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 29. Which of the following statements is true? A. Good salespeople are born with inherent selling traits and need little training. B. All salespeople need training. C. Selling skills are best learned with interactive Web training programs. D. New salespeople should be immediately sent out on the road to get acquainted with the firm's best customers. E. Training should include on-the-job observation, but classroom and Web-based learning is rarely needed. 30. __________ involves following all the leads in the target market to identify potential customers. A. Sales presentation B. Prospecting C. Closing D. Sales quota E. Marketing 31. The ____________ method of payment uses a percentage of dollar sales in calculating compensation. A. Bonus B. Commission C. Straight salary D. Combination E. Employee discount 32. The _________ compensation plan increases the amount of sales supervision needed. A. Straight salary B. Commission pay C. Bonus plan D. Combination plan E. Profit-sharing plan 6 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33. Order getters: A. may make a sale by helping a customer solve a business problem. B. are more likely to be used with homogeneous shopping products than heterogeneous shopping products. C. are used in business markets but not in consumer markets. D. generally rely on a routine "canned" sales presentation. E. All of the above are true. 34. A producer of business supplies is using manufacturers' agents to do: A. merchandising. B. order-getting. C. order-taking. D. technical advising. E. supporting activities. 35. A customer service rep's main job is to: A. take orders. B. find a remedy when something goes wrong with a firm's marketing mix after a purchase. C. get new orders. D. set up retail displays for retail customers. E. listen to customer complaints. 36. Regarding sales force compensation, the commission method is based on: A. a percentage of dollar sales. B. the number of new accounts. C. customer satisfaction ratings. D. customer service problems resolved. E. any of the above. 37. A large producer of snack foods feels that retailers do not promote its products aggressively enough—because they also sell competitors' products. The producer should use some: A. missionary sales reps. B. more aggressive sales reps. C. order takers. D. order getters. E. manufacturers' agents. 38. A sales rep for installations probably should use a ______________ sales presentation. A. consultative selling approach B. target market C. prepared D. selling formula approach E. any of the above 7 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------39. When setting salespeople's compensation level, A. a company should pay everyone at least the going market wage for order getters. B. salespeople should be the highest-paid employees in the company. C. order takers should be paid more than order getters. D. the first step is to write job descriptions. E. All of the above. 40. A professional salesperson: A. is only expected to "get rid of the product." B. has only one basic job—to communicate the company's story to customers. C. may be given a title such as field manager or market specialist. D. is expected to overcome the customer's objection—whatever it may be. E. All of the above. 41. The selling formula approach A. makes some general benefit statements to get the customer's attention and interest. B. starts with a prepared presentation outline approach and leads the customer through some logical steps to a final close. C. involves developing a good understanding of the individual customer's needs before trying to close the sale. D. uses a memorized presentation that is not adapted to each individual customer. E. is a problem-solving approach in which the customer and salesperson work together to satisfy the customer's needs. 42. The most popular sales force payment method is: A. a combination plan. B. the consultative selling method. C. straight salary. D. straight commission. 43. Jeffrey O'Donnell works for a producer of dairy products and knows all about these products. He is responsible for only two very large chain customers. Other sales reps, like Jeffrey, call on other large chains for this producer. They regularly call on the central offices of these big retail chains and encourage them to buy the company's full line. Jeffrey is: A. a missionary salesperson. B. a retail order taker. C. a technical specialist. D. a manufacturers' agent. E. a member of his company's major accounts sales force. 8 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------44. Which of the following statements about customer service is true? A. A customer service rep may have to deal with a customer problem that is due to a customer error, not just an error by the company. B. Customer service is the service part of the benefit that a customer gets when purchasing a physical good. C. Customer service costs are likely to decrease a firm's customer equity. D. Customer service is more important for winning customers than for keeping customers. E. From a firm's perspective, customer service is a necessary evil but isn't likely to cost the firm anything. 45. An order-taking sales rep would be MOST appropriate for a producer of: A. cleaning materials for maintenance—calling on regular customers. B. designer clothing—calling on possible new retailers. C. laptop computers—selling to manufacturers who don't yet have any computers. D. airplanes—calling on possible corporate jet customers. E. a new brand of DVD system—calling on wholesalers. 46. A salesperson may have to make choices about A. which particular products in the whole line to push most aggressively. B. what specific target customers to aim at. C. how to adjust prices. D. which intermediaries to rely on or help. E. All of the above. 47. The sales manager for a producer of consumer convenience products should recognize that the company may need: A. order getters to sell its established line to regular wholesaler customers. B. missionary salespeople to support its wholesalers. C. order takers to open up new territories. D. technical specialists to sell to purchasing agents. E. All of the above. 48. These salespeople try to develop goodwill and stimulate demand, help intermediaries train their salespeople, and often take orders for delivery by intermediaries. A. Order takers B. Customer service reps C. Missionary salespeople D. Technical specialists E. Account representatives 49. A producer wants to increase the amount of time its sales reps spend on supporting activities. It also wishes to keep its sales reps motivated and aggressive, and also provide some security. Which payment plan should the firm use? A. Straight salary B. Combination plan C. Straight commission 9 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------50. "Prospecting:" A. involves following all the leads in the target market. B. should require a sales rep to spend the same amount of time with each prospect. C. refers to selection of the firm's target market. D. should use a system for allocating time to potential customers based on their potential. E. Both A and D. 51. A technical specialist: A. often has a background in product applications rather than sales. B. may call on the customer both before and after a purchase. C. may work in conjunction with an order getter to persuade new clients. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 52. The __________ involves developing a good understanding of the individual customer's needs before trying to close the sale. A. Selling formula approach B. Consultative selling approach C. Prepared sales presentation D. Fixed sales presentation E. Differentiated value approach 53. Producers who know something about their target customers' needs and attitudes often supply their relatively untrained salespeople with a sales presentation in which (1) the salesperson does most of the talking at the beginning, (2) then brings the customer into the discussion to clarify the customer's needs, and (3) tries to close the sale. They are using a: A. consultative selling approach. B. quota system. C. prepared sales presentation. D. selling formula approach. E. target market presentation. 54. Regarding personal selling, good sales managers know that: A. many orders are lost simply because the salesperson didn't ask for the order. B. salespeople should spend the same amount of time with each prospect. C. the sales rep has very little influence on a prospect's response. D. good salespeople are born—not taught. E. All of the above. 55. Even though commissions are often based on a percentage of dollar sales, they can be based on _____________ instead. A. number of new accounts. B. customer satisfaction ratings. C. customer service problems resolved in some time period. D. all of the above. E. none of the above. 10 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------56. A breakdown in any element of the marketing mix can result in a requirement for A. customer service. B. additional sales promotion. C. reimbursement. D. replacing the salesperson. E. technical specialists. 57. Which of the following statements about personal selling is FALSE? A. Good salespeople present both the advantages and the disadvantages of their products. B. Helping to buy is good selling. C. Personal selling is often a company's smallest single operating expense. D. A salesperson is often a representative of the whole company. E. None of the above is false. 58. San Oxana Insurance Company uses relatively untrained people to sell its life insurance. The sales reps learn prepared sales presentations which help them describe the firm's policies to potential customers, discover each customer's specific needs, and then lead them through some logical steps to a final close. They are using a: A. selling formula approach. B. customer service approach. C. target market presentation. D. consultative selling approach. E. prepared sales presentation. 59. With the ___________ approach, the sales rep begins by making some general benefit statements to get the customer's attention and interest. A. Prepared sales B. Fixed sales C. Selling formula D. Consultative selling E. Differentiated value 60. Customer service reps: A. are advocates for the customer. B. solve problems after a purchase. C. are advocates for the company. D. promote the customer's next purchase. E. all of the above. 11 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------61. Some sales reps try to get a prospect to do most of the talking at first—to help pinpoint the potential customer's needs. After the sales rep feels that he understands the customer's needs, he begins to enter more into the discussion, helping the customer understand his own needs, showing how his product satisfies the customer's needs, and then trying to close the sale. This type of sales presentation uses the: A. selling formula approach. B. target market presentation. C. consultative selling approach. D. prepared sales presentation. E. None of the above. 62. A job description for a sales position A. should be detailed enough that it lists the specific tasks to be performed. B. should be in writing, but should be quite general so that it doesn't reduce the sales manager's flexibility in assigning jobs. C. should look pretty much the same from one company to another. D. is not very useful, since the job is always changing. E. all of the above. 63. The selling formula approach: A. starts with a prepared presentation outline, discovers each customer's specific needs, and then leads the customer through some logical steps to a final close. B. uses the same sales presentation with every potential customer. C. usually requires a more skilled salesperson than the consultative selling approach. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 64. A producer wants to reduce sales force turnover AND obtain a more aggressive sales effort for its accessories. Which of the following sales force payment methods should it use? A. Straight salary B. Selling formula plan C. Combination plan D. Straight commission 65. Order taking involves: A. establishing relationships with new customers and developing new business. B. selling to new customers. C. seeking possible buyers with a well-organized sales presentation designed to sell a good, service, or idea. D. enhancing the relationship with the customer and getting sales in the long run. E. routinely completing sales made regularly to target customers. 66. Customer service reps: A. are order getters who sell service products. B. usually work with missionary salespeople. C. resolve problems after a purchase has been made. D. usually install technical products for customers. E. hire professional services personnel. 12 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------67. A good marketing manager organizing a new sales force knows that: A. new sales reps should start out on the major accounts sales force so they can learn the business from the bottom up. B. the most profitable approach is to start with a small number of salespeople, and then quickly add more if they can't do the job. C. it may be necessary to rely on team selling and have more than one rep call on a single customer if different skills are needed. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. 68. All of the following are true of job descriptions except A. provides a basis for how salespeople should be paid. B. lists routine prospecting and sales report writing tasks. C. provides clear guidelines about what selling tasks the job involves. D. lists general tasks to be performed but doesn't get too specific. E. provides a basis for seeing how salespeople should be trained. 69. Which sales presentation would be "best" for convenience (food) store clerks? A. Selling formula approach B. Prepared sales presentation C. Target market presentation D. Consultative selling approach E. None of the above. 70. Simon Juarez sells life insurance for a large New Mexico firm. He locates customers by selecting names out of a telephone directory and calling to arrange an appointment. He begins each presentation by explaining the basic features and merits of his product—eventually bringing the customer into the conversation to clarify the customer's insurance needs. Then he tells how his insurance policy would satisfy the customer's needs and attempts to close the sale. Simon's sales presentation is based on the: A. consultative selling approach. B. selling formula approach. C. canned presentation approach. D. target market approach. E. customer service approach. 71. Customers for complicated installations and accessories usually expect a sales rep A. to know all the technical details of the product. B. to be able to discuss general business conditions with their top executives. C. to know the details of the customer firm's particular applications of the product. D. All of the above are likely to be expected. E. None of the above is likely to be expected. 13 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------72. Carefully set territories A. can reduce travel time but increase costs. B. can reduce confusion about who has responsibility for a set of sales tasks. C. always include at least one metropolitan area. D. always reduce the cost of sales calls. E. can increase travel time while reducing costs. 73. Ali Mulhammed has been working for a producer of video games that sell through toy wholesalers to retailers. He knows all about the games sold by his company and by competitors. He goes into his wholesalers' territories and tries to get local retailer customers interested in the company's line—and even trains retailers to demonstrate the games. When a retailer is ready to buy, Ali turns the business over to the wholesaler's sales rep. Ali is a: A. member of the firm's major accounts sales force. B. missionary salesperson. C. technical specialist. D. manufacturers' agent. E. None of the above is correct. 74. A prepared sales presentation: A. is the best approach for most selling situations—since the company can control what the sales rep says. B. usually involves many questions, to be sure each customer's needs are fully understood. C. is common with high value items—to be sure the customer learns about all of the technical details. D. is best when a lot of time is available for a sales presentation. E. None of the above is true. 75. Retailers of expensive heterogeneous shopping products usually have a strong need for: A. order takers. B. technical specialists. C. merchandisers. D. order getters. E. supporting salespeople. 76. Betti Hallmark sells women's clothing and gets most of her business from regular customers who have bought from her before. Betti never tries to sell anything before first trying to determine each customer's specific needs. Once she understands the customer's needs, Betti helps the customer understand her own needs and then shows how some product will fill those needs. Betti's sales presentation uses the: A. "canned" approach. B. target market presentation. C. selling formula approach. D. consultative selling approach. E. None of the above. 14 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------77. Missionary selling: A. is another name for major accounts selling. B. is the performance of personal selling activities for a nonprofit organization. C. is the same as prospecting. D. is often an entry position for higher level sales and marketing jobs. E. is typically only used with a firm's largest or most important customers. 78. Order takers are concerned with: A. establishing relationships with new customers and developing new business. B. selling to regular customers, completing most sales transactions, and maintaining relationships with their established customers. C. seeking possible buyers with a well-organized sales presentation designed to sell a good, service, or idea. D. selling unsought and heterogeneous shopping products. E. working with customers to resolve problems that arise with a purchase, usually after the purchase has been made. 79. According to the text, a salesperson may have choices about all of the following except A. what target customers to aim at. B. which particular products to emphasize. C. which intermediaries to rely on or help. D. what to manufacture. E. how to adjust prices. 80. Kyra Hanover is an order getter for a modern wholesaler. Kyra is LEAST likely to be involved with: A. repairing products returned to retailers by customers. B. conducting demonstrations for retailers' salespeople and customers. C. checking stock to determine what retailers should order. D. helping to plan special promotions and advertising for retailers. E. serving as a marketing advisor to her retailers. 81. Providing training in selling techniques help a salesperson in all of the following ways except A. winning new customers by disparaging competitors. B. listening carefully to identify a customer's real objections. C. closing the sale. D. working with customers in difficult customer service situations. E. how to be more effective in cold calls on new prospects. 82. Dimitri Kojak works for a producer of industrial elevators. He knows all the technical details of the many different ways they are used by business customers. He makes presentations to new prospects and eventually gets a share of their business. Dimitri is: A. a member of the firm's major accounts sales force. B. a missionary salesperson. C. a technical specialist. D. a producer's order getter. E. a customer service rep. 15 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------83. The two basic decisions to be made in developing a compensation plan are the method of payment and A. designation of the salesperson. B. level of compensation. C. number of years of service. D. number of client commendations received. E. career advancement. 84. The commission method of payment: A. includes some salary and some commission. B. offers the most security for the salesperson. C. offers the most incentive for the salesperson. D. is tied to results projected in the sales plan. E. increases the amount of sales supervision needed. 85. Which of the following statements by a sales manager suggests a problem? A. "Taking a successful sales rep out of a territory for sales training is like spending money to teach a fish to swim." B. "I was a sales rep before becoming manager, so I don't need a job description to help me look for new salespeople." C. "I select new salespeople all by myself, because I am the one responsible for the performance of the sales force." D. Each of the above indicates a problem. E. None of the above indicates a problem. 86. Regarding sales force compensation methods: A. combination plans provide some security and some incentive. B. straight commission avoids the need to consider a sales quota. C. straight salary provides the most incentive. D. sales quotas play no role in any of the methods. E. All of the above. 87. A customer service rep's job could include: A. understanding a customer's complaints. B. finding a remedy when something goes wrong with a firm's marketing mix after a purchase. C. resolving a billing problem. D. handling an exchange of a defective product. E. all of the above. 88. IBM's customers often need help installing its mini computer systems, so IBM should support the efforts of its order getters with: A. sales promotion specialists. B. selling aids. C. missionary salespeople. D. technical specialists. E. order takers. 16 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------89. Edward Seaton owns a firm that manufactures custom-made carpets. He has a regular sales force to call on smaller customers and an elite force to call on larger accounts. The elite sales force is called: A. customer service reps. B. major accounts sales force. C. technical specialists. D. supporting salespeople. E. missionary salespeople. 90. Which of the following statements about prospecting is FALSE? A. Prospecting focuses on identifying new customers. B. A sales rep needs to set priorities for all prospects—both old and new. C. A sales rep must qualify potential customers. D. CRM systems help with the process of prospecting. E. None of the above is false. 91. According to the text, to recruit, motivate, and keep good salespeople, a firm has to A. provide encouragement by giving trophies and certificates. B. give public recognition. C. develop an effective compensation plan. D. offer a promotion. E. reinvent its marketing strategies. 92. Order takers: A. are not necessary if the firm has good order getters. B. are the routine contact people in the sales force. C. usually don't call on customers. D. do not require any specialized training. E. All of the above are correct. 93. A lawn care firm selling by phone to people listed in the telephone directory should use which of the following sales presentations? A. consultative selling approach. B. selling formula approach. C. prepared sales presentation. D. target market presentation. E. None of the above. 94. An established merchant wholesaler of business supplies would rely mainly on: A. merchandisers. B. order takers. C. order getters. D. supporting salespeople. E. missionary salespeople. 17 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 15chprvw17edso Key 1. (p. 401-402) B 2. (p. 400) A 3. (p. 403-405) D 4. (p. 413) D 5. (p. 413) C 6. (p. 415) D 7. (p. 417-418) B 8. (p. 417-418) A 9. (p. 403-404) C 10. (p. 411) E 11. (p. 407) C 12. (p. 397) B 13. (p. 413-414) E 14. (p. 399) A 15. (p. 417) C 16. (p. 402) D 17. (p. 398) B 18. (p. 417) D 19. (p. 402) B 20. (p. 402) E 21. (p. 402) E 22. (p. 401) A 23. (p. 417) D 24. (p. 402) D 25. (p. 413-414) E 26. (p. 403) D 27. (p. 399) C 28. (p. 400) B 29. (p. 411-412) B 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30. (p. 415) B 31. (p. 413) B 32. (p. 413) A 33. (p. 400) A 34. (p. 400) B 35. (p. 404) B 36. (p. 413) E 37. (p. 402) A 38. (p. 417) A 39. (p. 411) D 40. (p. 398) C 41. (p. 418) B 42. (p. 413) A 43. (p. 406) E 44. (p. 404) A 45. (p. 400) A 46. (p. 399) E 47. (p. 402) B 48. (p. 402) C 49. (p. 413) B 50. (p. 415-416) E 51. (p. 402) D 52. (p. 417) B 53. (p. 418) D 54. (p. 401) A 55. (p. 413) D 56. (p. 404) A 57. (p. 397-398) C 58. (p. 418) A 59. (p. 417) D 60. (p. 402-404) E 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------61. (p. 417) C 62. (p. 411) A 63. (p. 418) A 64. (p. 413) C 65. (p. 400) E 66. (p. 402) C 67. (p. 405) C 68. (p. 411) D 69. (p. 417) B 70. (p. 418) B 71. (p. 400) D 72. (p. 407) B 73. (p. 402) B 74. (p. 417) E 75. (p. 400) D 76. (p. 417) D 77. (p. 402) D 78. (p. 400) B 79. (p. 399) D 80. (p. 400) A 81. (p. 412) A 82. (p. 400) D 83. (p. 413) B 84. (p. 413) C 85. (p. 411) D 86. (p. 413) A 87. (p. 404) E 88. (p. 402) D 89. (p. 406) B 90. (p. 415-416) E 91. (p. 412) C 3 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15 CH – MKG 300 PREVIEW QUESTIONS – PROFESSOR MOSER – PREVIEW Q’S – 15 CH --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------92. (p. 400) B 93. (p. 417) C 94. (p. 401) B 4