American Imperialism
advertisement
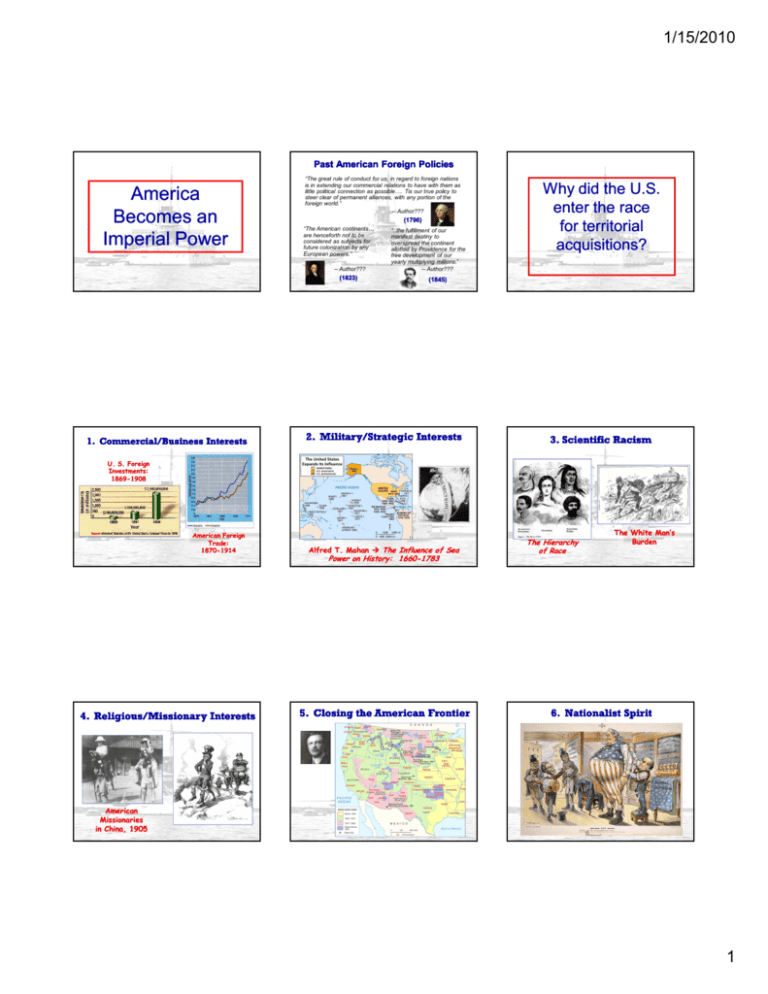
1/15/2010 Past American Foreign Policies America Becomes an Imperial Power “The great rule of conduct for us, in regard to foreign nations is in extending our commercial relations to have with them as little political connection as possible…. Tis our true policy to steer clear of permanent alliances, with any portion of the foreign world.” -- Author??? (1796) “The American continents… are henceforth not to be considered as subjects for future colonization by any European powers.” -- Author??? (1823) 1. Commercial/Business Interests “..the fulfillment of our manifest destiny to overspread the continent allotted by Providence for the free development of our yearly multiplying millions.” -- Author??? Why did the U.S. enter the race for territorial acquisitions? (1845) 2. Military/Strategic Interests 3. Scientific Racism U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of Sea Power on History: 1660-1783 4. Religious/Missionary Interests 5. Closing the American Frontier The Hierarchy of Race The White Man’s Burden 6. Nationalist Spirit American Missionaries in China, 1905 1 1/15/2010 Commodore Matthew Perry Opens Up Japan: 1853 Treaty of Kanagawa: 1854 “unequal treaty” under Tokugawa Seeking whaling rights; “Gunboat diplomacy” The Japanese View of Commodore Perry U. S. Missionaries in Hawaii Hawaii becomes a U. S. Protectorate in 1849 by virtue of economic treaties. Imiola Church – first built in the late 1820s Hawaiian Queen Liliuokalani U. S. View of Hawaiians U. S. Business Interests In Hawaii 1875 – Reciprocity Treaty 1890 – McKinley Tariff 1893 – American businessmen backed an uprising against Queen Liliuokalani To The Victor Belongs the Spoils Hawaiian Annexation Ceremony, 1898 Sanford Dole proclaims the Republic of Hawaii in 1894 “Hawaii for the Hawaiians!” 2 1/15/2010 Spanish Misrule in Cuba De Lôme Letter Remember the Maine and to Hell with Spain! Valeriano Weyler’s “Reconcentration” Policy “Yellow Journalism” & Jingoism Enrique Dupuy de Lôme, (Spanish Ambassador to the U.S.) Criticized President McKinley as “weak and a bidder for the admiration of the crowd, besides being a wouldwould-be politician who tries to leave a door open behind himself while keeping on good terms with the jingoes of his party.” Joseph Pulitzer Hearst to Frederick Remington: Funeral for Maine victims in Havana William Randolph Hearst You furnish the pictures, and I’ll furnish the war! Hearst’s New York Journal Current Hearst Publications Newspapers •San Francisco Chronicle •Seattle P-I The “Rough Riders” Magazines •Cosmopolitan •Esquire •Good Housekeeping •O •Popular Mechanics •Redbook 3 1/15/2010 The SpanishSpanish-American War (1898): Dewey Captures Manila! • over a million Americans enlisted, though the call was only for 200,000 • U.S. assumed control; Cuban rebels left out of operations planning • U.S. soldiers had control of the island in about 6 weeks “That Splendid Little War” - John Hay (to TR) William H. Taft, 1st Gov.--General of the Philippines Gov. Filipino Rebellion (1899(1899-1902) U.S. flag was hoisted when Spain relinquished control of the Philippines rebels began to plot against U.S. America’s “Sphere of Influence” “Our little brown brothers” American soldiers began to call Filipinos “the Indians” and advocated killing them Filipinos recruited AfricanAfrican-American soldiers to their side (some successfully) U.S. generals censored reports U.S. banned all antianti-American ideas (pictures, writings, speech, etc.), even the P.I. flag U.S. created concentration camps casualties: 4,000 Americans 200,000 Filipinos (20,000 were soldiers) The Treaty of Paris: 1898 Cuba was freed from Spanish rule (became U.S. protectorate in 1903) Spain gave up Puerto Rico and Guam to U.S. The U. S. paid Spain $20 mil. indemnity for the Philippines (annexed that same year) The U. S. becomes an imperial power! Taft set up/improved: • • • • • provincial governments public schools public works communication transportation Independent nation since 1946 The American AntiAnti-Imperialist League Founded in 1899 Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, William James, and William Jennings Bryan among the leaders. Campaigned against the annexation of the Philippines and other acts of imperialism Cuban Independence? Senator Orville Platt Platt Amendment (1903) 1. Cuba was not to enter into any agreements with foreign powers that would endanger its independence 2. The U.S. could intervene in Cuban affairs if necessary to maintain an efficient, independent govt 3. Cuba must lease Guantanamo Bay to the U.S. for naval and coaling station 4. Cuba must not build up an excessive public debt 4 1/15/2010 Puerto Rico: 1898 Now that the U.S. was an imperial power, a dilemma arose: The Insular Cases (1901(1901-1903) Constitution does NOT follow flag Did the Constitution Imperialists ☺ follow the flag? Jones Act (1917): Puerto Rico becomes the first test • granted US citizenship to Puerto Ricans • reorganized the PR government (US Pres. kept veto power) Panama Canal Panama: The King’s Crown 5,609 deaths (disease, accidents) Clayton Clayton-Bulwer Treaty (1850) US/Britain agreed not to try to take exclusive control of future canal route Hay Hay-PaunceforteTreaty (1901) U.S.. authorized to build and manage a canal U.S without British involvement; guarantee neutrality of region and int’l access The Roosevelt Corollary (to the Monroe Doctrine) Venezuela and Dominican Republic owed $$$ to Germany and Britain “Venezuelan Crisis” (1902): Germany sank VZ ships in attempt to force to pay debts owed to Germany Philippe BunauBunau-Varilla vigorously campaigned for canal; persuaded Congress to fund construction through Panama Hay Hay-Bunau Bunau-Varilla Treaty (1903) widened the zone; paid Panama $10 mil The Roosevelt Corollary (to the Monroe Doctrine) To keep European powers out of the Western Hemisphere, the U.S. would intervene (take over customs houses, pay off the debts, etc) in future financial crises “preventive intervention” TR in Panama (construction from 1904-1914) U.S. becomes “Policeman of the Western Hemisphere” The Roosevelt Corollary (to the Monroe Doctrine) U.S U.S.. had moral obligation to intervene contrast with Monroe Doctrine ??? promoted “Bad Neighbor” policy later used to justify wholesale interventions and landings of U.S. marines used in.. Dominican Republic (1905): collect tariffs in Cuba (1906) after revolution 5 1/15/2010 Stereotypes of the Chinese Immigrant Chinese Exclusion Act (1882) The Open Door Policy The Boxer Rebellion: 1900 The Society of Harmonious Fists The Open Door Policy Sec. of State John Hay The Open Door Policy 1st Note: all nations equal share access to trade in China ECONOMIC 2nd Note: guaranteed that China would NOT be taken over by any one foreign power POLITICAL The Cares of a Growing Family Speak Softly, But Carry a Big Stick! Constable of the World 6 1/15/2010 Russo--Japanese War 1904 Russo 1904--05 • Russia and Japan went to war over ports in Manchuria and Korea • Japan destroyed much of Russian fleet West is shocked! • TR wanted to prevent both sides from dominance in Asia, Asia, so helped negotiate peace settlement Treaty of Portsmouth: 1905 Russia conceded defeat; Japan awarded southern half of Sakhalin, but no indemnity But neither side is pleased… Japan wanted all of Sakhalin and $$$ blamed U.S. mistrust grows…along with naval arms race U.S U.S..-Russia relations soured “TR robbed them of victory” And the Nobel Peace Prize for TR! Gentleman’s Agreement: 1908 San Francisco schools segregated for Asian children Japanese furious talk of war in yellow press! TR invited school board to WH forced them to repeal order agreed not to ban Japanese from public schools Japan promised to stop flow of laborers to U.S U.S.. Japan recognized the U.S. right to exclude Japanese immigrants holding passports issued by other countries Lodge Corollary (to the Monroe Doctrine) Senate resolution (passed in 1912) NonNon-European powers, like Japan, would be excluded from owning territory in the Western Hemisphere Root--Takahira Agreement, 1908 Root The Great White Fleet: 1907 U.S. U.S. Japan pledged to respect each other’s territorial possessions in the Pacific uphold the Open Door in China To make sure Japan didn’t perceive U.S. weakness, TR sent… America as a Pacific Power What the U. S. Has Fought For Senator Henry Cabot Lodge 7