Titanium (Ti)
advertisement
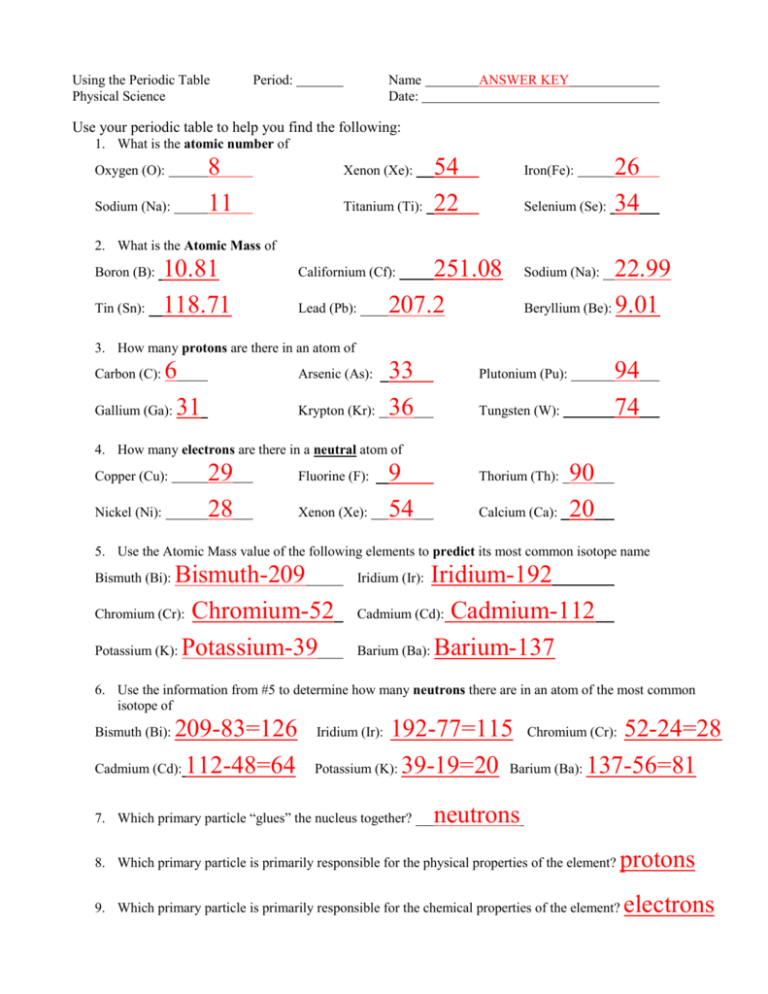
Using the Periodic Table Physical Science Period: Name Date: ANSWER KEY Use your periodic table to help you find the following: 1. What is the atomic number of Oxygen (O): Sodium (Na): 8 11 Xenon (Xe): Titanium (Ti): 54 22 Iron(Fe): Selenium (Se): 26 34 2. What is the Atomic Mass of Boron (B): Tin (Sn): 10.81 118.71 251.08 207.2 Californium (Cf): Lead (Pb): 22.99 Beryllium (Be): 9.01 Sodium (Na): 3. How many protons are there in an atom of 6 Gallium (Ga): 31 Carbon (C): Arsenic (As): Krypton (Kr): 33 36 94 74 Plutonium (Pu): Tungsten (W): 4. How many electrons are there in a neutral atom of Copper (Cu): Nickel (Ni): 29 28 Fluorine (F): Xenon (Xe): 9 54 Thorium (Th): Calcium (Ca): 90 20 5. Use the Atomic Mass value of the following elements to predict its most common isotope name Bismuth-209 Chromium (Cr): Chromium-52 Potassium (K): Potassium-39 Bismuth (Bi): Iridium-192 Cadmium (Cd): Cadmium-112 Barium (Ba): Barium-137 Iridium (Ir): 6. Use the information from #5 to determine how many neutrons there are in an atom of the most common isotope of 209-83=126 Cadmium (Cd): 112-48=64 Bismuth (Bi): 192-77=115 Chromium (Cr): 52-24=28 Potassium (K): 39-19=20 Barium (Ba): 137-56=81 Iridium (Ir): 7. Which primary particle “glues” the nucleus together? neutrons 8. Which primary particle is primarily responsible for the physical properties of the element? protons 9. Which primary particle is primarily responsible for the chemical properties of the element? electrons Silicon 28-14=14 10. What is the name of the atom that has 14 protons? have in the most common isotope? How many neutrons does it Gold 197-79=118 11. What is the name of the neutral atom that has 79 electrons? does it have in the most common isotope? How many neutrons 12. What name would be given to the isotope of an atom that has 70 protons and 105 neutrons? Ytterbium-175 What is the most common isotope of this element? Ytterbium-173 13. What name would be given to an isotope of an atom that has 80 protons and 122 neutrons? Mercury-202 What is the most common isotope of this element? 14. What is the name of the only atom that usually has no neutrons? Mercury-201 Hydrogen Use the diagram at the left to answer questions 15 – 19 15. What is the atomic number of the atom depicted here? How do you know? 5 Atomic number is the number of protons and there are 5 protons. 16. What is the mass number of the atom depicted here? 11 How do you know? Mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons in an atom, 5 + 6 = 11 Boron How do you know? Boron is the only atom with 5 protons 17. Which element does this diagram depict? Yes How do you know? The average atomic mass of Boron is 10.81 which rounds to 11, which is the mass number. 18. Is this the most common isotope of the element depicted above? 19. Does the diagram above show a neutral atom, a positive ion, or a negative ion? How do you know? Positive ion There are more protons (5) than electrons (4), so there is a net positive charge. 20. If somehow you removed an electron from a lead (Pb) atom, it would become a) a diff. isotope of Pb b) Thallium c) a cation of Pb d) an anion of Pb e) Bismuth g) an anion of Thallium h) a cation of bismuth i) an anion of bismuth f) a cation of Thallium j) none of these 21. If somehow you removed a proton and an electron from a lead (Pb) atom, it would become a) a diff. isotope of Pb b) Thallium c) a cation of Pb d) an anion of Pb e) Bismuth f) a cation of Thallium g) an anion of Thallium h) a cation of bismuth i) an anion of bismuth j) none of these 22. If somehow you removed just a proton from a lead (Pb) atom, it would become a) a diff. isotope of Pb b) Thallium c) a cation of Pb d) an anion of Pb e) Bismuth g) an anion of Thallium h) a cation of bismuth i) an anion of bismuth f) a cation of Thallium j) none of these 23. If you somehow removed a neutron from a lead (Pb) atom, it would become a) a diff. isotope of Pb b) Thallium c) a cation of Pb d) an anion of Pb e) Bismuth g) an anion of Thallium h) a cation of bismuth i) an anion of bismuth f) a cation of Thallium j) none of these 24. If you added an electron to a lead (Pb) atom, it would become a) a diff. isotope of Pb b) Thallium c) a cation of Pb d) an anion of Pb e) Bismuth g) an anion of Thallium h) a cation of bismuth i) an anion of bismuth f) a cation of Thallium j) none of these 25. If you added a proton and an electron to a lead (Pb) atom, it would become a) a diff. isotope of Pb b) Thallium c) a cation of Pb d) an anion of Pb e) Bismuth g) an anion of Thallium h) a cation of bismuth i) an anion of bismuth f) a cation of Thallium j) none of these 26. If you added just a proton to a lead (Pb) atom, it would become a) a diff. isotope of Pb b) Thallium c) a cation of Pb d) an anion of Pb e) Bismuth g) an anion of Thallium h) a cation of bismuth i) an anion of bismuth f) a cation of Thallium j) none of these 27. If you somehow added a neutron to a lead (Pb) atom, it would become a) a diff. isotope of Pb b) Thallium c) a cation of Pb d) an anion of Pb e) Bismuth g) an anion of Thallium h) a cation of bismuth i) an anion of bismuth f) a cation of Thallium j) none of these