Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Rate & Regioselectivity
advertisement

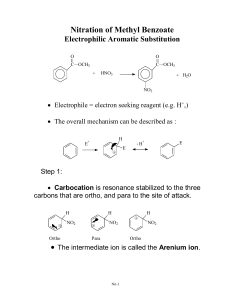
Effect on Rate Rate and Regioselectivity in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution A substituent already present on the ring affects both the rate and regioselectivity of electrophilic aromatic substitution. Activating substituents increase the rate compared to that of benzene. Deactivating substituents decrease the rate compared to benzene. Methyl Group CH3 Trifluoromethyl Group Toluene undergoes nitration 20-25 times faster than benzene. CF3 A methyl group is an activating substituent. substituent. A trifluoromethyl group is a deactivating substituent. substituent. Nitration of Toluene Effect on Regioselectivity CH3 CH3 Ortho-para directors direct an incoming electrophile to positions ortho and/or para to themselves. Meta directors direct an incoming electrophile to positions meta to themselves. (Trifluoromethyl)benzene Trifluoromethyl)benzene undergoes nitration 40,000 times more slowly than benzene . CH3 CH3 NO2 HNO3 + acetic anhydride + NO2 NO2 63% 3% 34% o - and p -nitrotoluene together comprise 97% of the product a methyl group is an ortho-para director Nitration of (Trifluoromethyl )benzene (Trifluoromethyl)benzene CF3 CF3 CF3 CF3 NO2 HNO3 + H2 SO4 + NO2 NO2 6% 91% Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Activating Substituents 3% m -nitro(trifluoromethyl)benzene comprises 91% of the product a trifluoromethyl group is a meta director Table Classification of Substituents in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions Very strongly activating Strongly activating Activating Standard of comparison is H Deactivating Strongly deactivating Very strongly deactivating Generalizations 1. All activating substituents are ortho-para directors. Electron-Releasing Groups (ERGs) are ortho-para directing and activating ERG 2. Halogen substituents are slightly deactivating but ortho-para directing. 3. Strongly deactivating substituents are meta directors. ERGs include —R, —Ar, and —C=C Electron-Releasing Groups (ERGs) Nitration of Phenol occurs about 1000 times faster than nitration of benzene are ortho-para directing and strongly activating ERG OH OH HNO3 + NO2 ERGs such as —OH, and —OR are strongly activating 44% Bromination of Anisole OCH3 Br2 acetic acid •• •• OCH3 H H + H Br 90% Electron-Releasing Groups (ERGs) or Electron “Donors” Donors” •• ERG ERGs with a lone pair on the atom directly attached to the ring are ortho-para directing and strongly activating 56% Oxygen Lone Pair Stabilizes Intermediate FeBr3 catalyst is not necessary OCH3 OH NO2 Br •• •• OCH3 H H H H + H Br •• + OCH3 H H H H H H H Br all atoms have octets A substituent can donate electrons into the ring by delocalizing its lone-pair electrons (resonance): Examples Lone Pair Stabilizes Intermediates for ortho and para Substitution O •• ERG = •• •• •• OH •• OR •• + ERG •• OCR O •• NH 2 •• NHR •• NHCR •• NR 2 + ERG H H H H X H H H H H All of these are ortho-para directing and strongly to very strongly activating X H comparable stabilization not possible for intermediate leading to meta substitution ERGs Stabilize Intermediates for ortho and para Substitution •• ERG Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Strongly Deactivating Substituents H •• ERG X + H H H H H EWG X + H H H H H + H H H H X —CF3 is a powerful EWG. It is strongly deactivating and meta directing X Many EWGs Have a Carbonyl Group Attached Directly to the Ring —EWG = EWG H H H Electron-withdrawing Groups (EWGs (EWGs)) Destabilize Intermediates for ortho and para Substitution H + H O O —CH —CR O O —COH —COR O —CCl All of these are meta directing and strongly deactivating Nitration of Benzaldehyde O2 N O HNO3 CH O O CH CCl H2 SO4 Cl O Cl2 CCl FeCl3 75-84% 62% Other EWGs Include: Electron withdrawing by resonance: —EWG = —NO2 —SO3 H —C N All of these are meta directing and strongly deactivating Disulfonation of Benzene C=O, CN, and NO2 also withdraw electrons by resonance Bromination of Nitrobenzene Br HO3S SO3 SO3H H2 SO4 90% NO2 Br2 Fe NO2 60-75% Nitration of Chlorobenzene Cl Cl Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Halogens Cl Cl NO2 HNO3 + + H2 SO4 NO2 NO2 F, Cl, Br, and I are ortho-para directing, but deactivating 30% 1% 69% The rate of nitration of chlorobenzene is about 30 times slower than that of benzene. Nitration of Toluene Effect on Regioselectivity CH3 CH3 Ortho-para directors direct an incoming electrophile to positions ortho and/or para to themselves. CH3 NO2 HNO3 + acetic anhydride Meta directors direct an incoming electrophile to positions meta to themselves. CH3 + NO2 NO2 63% 3% 34% o - and p -nitrotoluene together comprise 97% of the product a methyl group is an ortho-para director Nitration of (Trifluoromethyl )benzene (Trifluoromethyl)benzene CF3 CF3 CF3 NO2 HNO3 + H2 SO4 Question CF3 • Arrange the compounds below in order of decreasing rate of chlorination. + NO2 NO2 6% 91% m -nitro(trifluoromethyl )benzene comprises -nitro(trifluoromethyl)benzene 91% of the product a trifluoromethyl group is a meta director 3% • • • • A) B) C) D) 1>2>3 2>3>1 3>2>1 1>3>2 Question • Which compound will add a nitro group to the meta position? • A) B) • C) D) Rate and Regioselectivity in the Nitration of Toluene Carbocation Stability Controls Regioselectivity CH3 H NO2 + H H H CH3 H H + H H gives ortho CH3 H H H H CH3 H H H NO2 H + NO2 gives para Carbocation Stability Controls Regioselectivity H gives meta NO2 H + H CH3 H + H H H gives ortho NO2 gives para more stable CH3 H H H H H + H H NO2 gives meta less stable Nitration of Toluene: Interpretation Nitration of Toluene: Partial Rate Factors • The rate-determining intermediates for ortho and para nitration each have a resonance form that is a tertiary carbocation. carbocation. All of the resonance forms for the ratedetermining intermediate in meta nitration are secondary carbocations. carbocations. • Tertiary carbocations, carbocations, being more stable, are formed faster than secondary ones. Therefore, the intermediates for attack at the ortho and para positions are formed faster than the intermediate for attack at the meta position. This explains why the major products are o- and p-nitrotoluene. -nitrotoluene. • The experimentally determined reaction rate can be combined with the ortho/meta/para distribution to give partial rate factors for substitution at the various ring positions. • Expressed as a numerical value, a partial rate factor tells you by how much the rate of substitution at a particular position is faster (or slower) than at a single position of benzene. Nitration of Toluene: Partial Rate Factors Nitration of Toluene vs. vs. tert-Butylbenzene CH3 CH3 1 1 1 42 42 1 1 2.5 2.5 1 CH3 58 All of the available ring positions in toluene are more reactive than a single position of benzene. A methyl group activates all of the ring positions but the effect is greatest at the ortho and para positons. positons. Steric hindrance by the methyl group makes each ortho position slightly less reactive than para. para. Nitration of Toluene vs. vs. Chlorobenzene CH3 H3 C 42 42 4.5 2.5 2.5 3 CH3 4.5 3 75 58 tert-Butyl tert-Butyl is activating and orthoortho- para directing tert-Butyl tert-Butyl crowds the ortho positions and decreases the rate of attack at those positions. Nitration of (Trifluoromethyl )benzene: (Trifluoromethyl)benzene: Partial Rate Factors CF3 Cl 42 42 0.029 0.029 2.5 2.5 0.009 0.009 58 C 0.137 Question • Which is the most likely candidate for substituent X based on the partial rate factors for nitration given beside the structural formula? • A) -OCH3 • B) -CH=O • C) -SO3H • D) -Br 4.5 x 10-6 67 x 10-6 4.5 x 10-6 67 x 10-6 4.5 x 10-6 All of the available ring positions in (trifluoromethyl)benzene trifluoromethyl)benzene are much less reactive than a single position of benzene. A CF3 group deactivates all of the ring positions but the degree of deactivation is greatest at the ortho and para positons. positons. Question • Which reactants combine to • give the species shown at • the right as a reactive • intermediate? • • A) Benzene, isopropyl bromide, and HBr • B) Bromobenzene, isopropyl chloride, and AlCl3 • C) Isopropylbenzene, Br2, FeBr3 • D) Isopropylbenzene, light, and heat Question • Which of the following statements is false? • A) All activating groups are ortho, para directors. • B) Halogen substituents are slightly deactivating, but are ortho, para directing. • C) Strongly activating substances are meta directors. • D) Some of the most powerful activating substances are those with an oxygen directly attached to the ring. Question • Which step is incorrect in respect to its major organic product? Give the letter • corresponding to the first incorrect step. • • A) C) Step A Step C B) D) Step B Step D