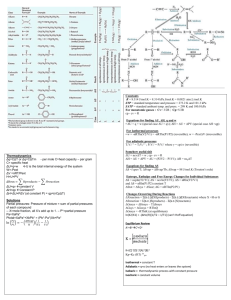
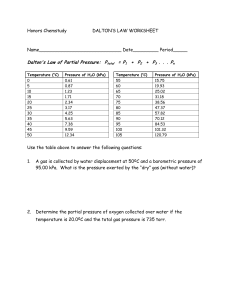
Ideal & General Gas Laws Worksheet: Chemistry Problems
advertisement
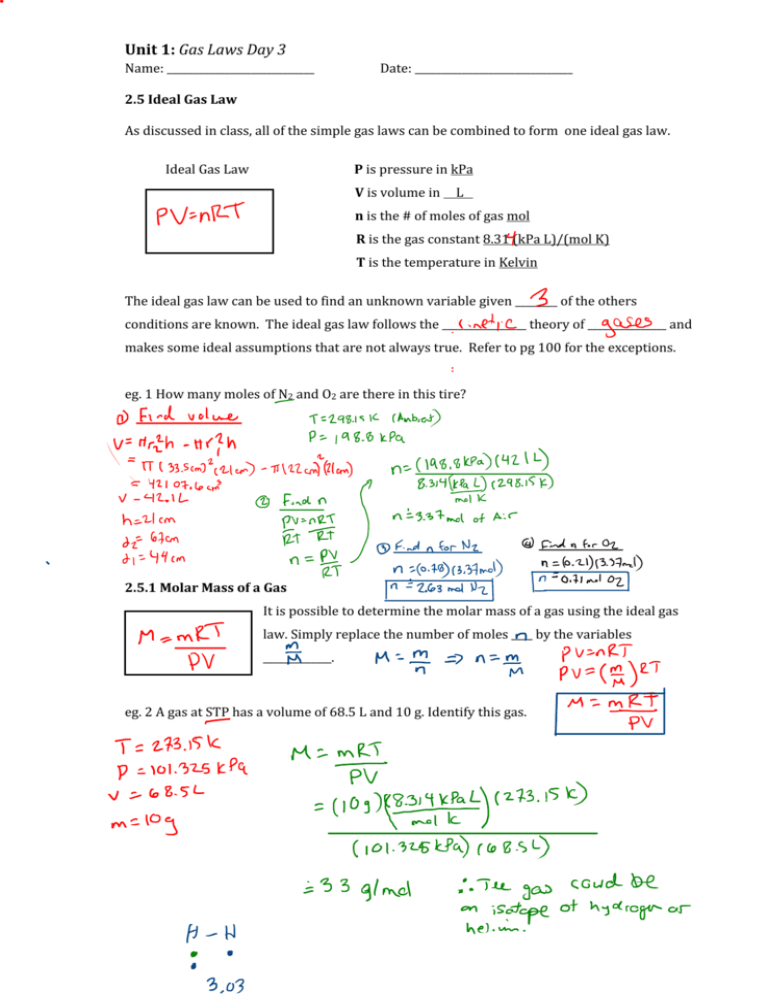
Unit 1: Gas Laws Day 3 Name: ____________________________ Date: ______________________________ 2.5 Ideal Gas Law As discussed in class, all of the simple gas laws can be combined to form one ideal gas law. Ideal Gas Law P is pressure in kPa V is volume in L n is the # of moles of gas mol R is the gas constant 8.31 (kPa L)/(mol K) T is the temperature in Kelvin The ideal gas law can be used to find an unknown variable given ________ of the others conditions are known. The ideal gas law follows the ________________ theory of _______________ and makes some ideal assumptions that are not always true. Refer to pg 100 for the exceptions. eg. 1 How many moles of N2 and O2 are there in this tire? 2.5.1 Molar Mass of a Gas It is possible to determine the molar mass of a gas using the ideal gas law. Simply replace the number of moles ____ by the variables _____________. eg. 2 A gas at STP has a volume of 68.5 L and 10 g. Identify this gas. Unit 1: Gas Laws Day 3 2.6 General Gas Law The general gas law is used to calculate the new conditions of a gas when at least two variables change. It is a combination of the all the simple gas laws. eg. 3 At SATP, 0.150 mol of water vapour occupies a volume of 55.0 mL. What is the new temperature in degrees Cesius (0C) if 0.030 mol of water vapour is removed while increase the pressure to 115.0 kPa and decreasing the volume to 40.0 mL. Homework Problems 1. If 3.7 moles of propane are at a temperature of 28oC and are under 154.2 kPa of pressure, what volume does the sample occupy? (60 L) 2. A sample of carbon monoxide at 57oC and under 0.67 atm of pressure takes up 85.3 L of space. What mass of carbon monoxide is present in the sample? (59 g CO) 3. At –45oC, 71 g of fluorine gas take up 6843 mL of space. What is the pressure of the gas, in kPa? (517.6 kPa) 4. At 971 mm Hg, 145 g of carbon dioxide have a volume of 34.13 dm3. What is the temperature of the sample, in oC? (‐112oC) 5. At 137oC and under a pressure of 3.11 atm, a 276 g sample of an unknown noble gas occupies 13.46 L of space. What is the gas? (Radon) 6. During a laboratory experiment, you put an unknown compound into some water. You observe a bubbling reaction. With the help of a syringe, you remove the gas produced. Consider the following data: Mass of the 140 mL syringe: 23.47 g Mass of the syringe with 140 mL of the gas: 23.72 g Temperature in the lab: 298.0 K Pressure in the room: 101.0 kPa Which of the following is most likely the identity of the gas produced and collected? (CO2)