Ideal Gas Law Worksheet: Practice Problems & Concepts
advertisement

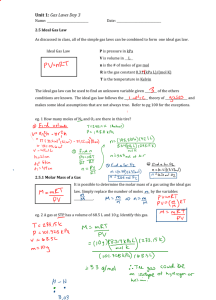
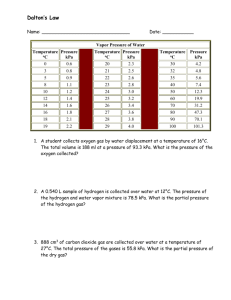
Ideal Gas Law Name ______________________________ Date __________________ Period _______ Given: Ideal Gas Law = then P= n= V= T= R= 1. What pressure is required to contain 0.023 moles of nitrogen gas in a 4.2 L container at a temperature of 20.C? 2. Oxygen gas is collected at a pressure of 123 kPa in a container which has a volume of 10.0 L. What temperature must be maintained on 0.500 moles of this gas in order to maintain this pressure? Express the temperature in degrees Celsius. 3. How many moles of chlorine gas would occupy a volume of 35.5 L at a pressure of 100.0 kPa and a temperature of 100. C? After determining the number of moles, calculate the number of grams of chlorine (Cl2) contained in this container? 4. What is the volume of a balloon if it contains 3.2 moles of helium at a temperature of 20. C and standard pressure? 5. Calculate the volume which 1.00 mole of a gas occupies at STP. 6. What volume would 20.0g of CO2 occupy at a temperature of 25 C and a pressure of 105 kPa? 7. A 23.6g sample of an unknown gas occupies a volume of 12.0 L at standard temperature and pressure. What is the molecular mass of this gas? 1 8. What mass of nitrous oxide gas (N2O) is contained in 20.0 L balloon at a pressure of 110.0 kPa and a temperature of 25 C? True and False: If the statement is true, write “true.” If it is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. Write your answer on the line provided. _____________________ 1. Real gases behave like ideal gases except at very high temperatures. _____________________ 2. The gas constant, R, is equal to 0.0821 when the pressure is expressed in kilopascals. _____________________ 3. As more gas particles are added to a container, there are fewer collisions because the particles don’t go as far. _____________________ 4. The number of moles of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume at STP. _____________________ 5. Real gases behave like ideal gases except at very high pressure. _____________________ 6. At a constant temperature, the pressure exerted by one mole of a gas decreases if the volume available is increased. _____________________ 7. The ideal gas equation will only give correct values if the temperature in expressed in degrees Celcius. _____________________ 8. One mole of oxygen at 760. mm Hg and 0 °C occupies a volume of one L. Matching: Match each variable listed on the left with the appropriate unit of measurement listed on the right. You may write one or more letters on each line. Circle the ones used in the Ideal Gas Equation. ___________________ 9. number of moles ___________________ 10. volume ___________________ 11. pressure ___________________ 12. temperature A. °C B. kg C. mol D. mm Hg E. K F. L G. atm H. Pa I. °F J. m3 K. cm3 L. kPa M lb/in2 2