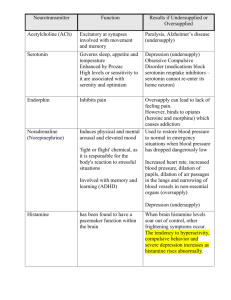
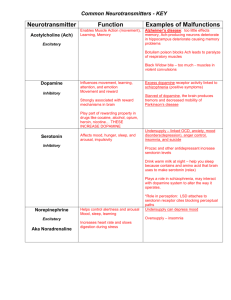
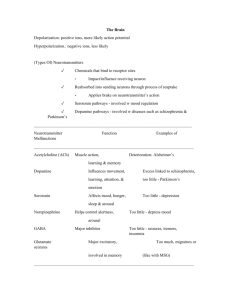
Name: _____________________________________ Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitter 1.Dopamine Function Influences movement, learning, attention, & emotion 2. Serotonin Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal 3.Norepinephrine Helps control alertness & arousal 4. GABA A major inhibitory neurotransmitter 5. Acetylcholine Major excitatory NT; causes contraction of skeletal muscles, helps regulate heart muscles, is involved in memory, transmits messages between the brain & spinal cord A NT similar to opiate morphine that relieves pain 6. Endorphins Surplus Excess dopamine receptor activity is linked to schizophrenia one hypothesis of its cause) Oversupply can lead to anxiety and insomnia Oversupply can stimulate brain, producing migraines or seizures (& the reason why people avoid MSG in food) Euphoria (“Runner’s high”) Deficit Undersupply produces the tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinson’s Disease Undersupply linked to depression Drugs/Therapy L-Dopa (given to patients with Parkinson’s disease) functions like a synthetic form of dopamine) Undersupply can depress mood MAOI’s act on norepinephrine and increase norepinephrine to reduce depression. MAOIs are used only if the SSRIs don’t work though, since diets have to be changed (e.g. no cheese) Undersupply linked to seizures and Huntington’s disease Benzodiazepine (Valium) and anticonvulsant drugs increase the activity of GABA) Botox works by blocking Ach release from the sending neuron, which paralyzes facial muscles, thereby smoothing wrinkles. Alzheimer’s disease Antidepressant drugs raise serotonin levels (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, SSRIs, e.g. Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil, et cetera.) Many painkillers (e.g. morphine) work by acting like endorphins and relieve pain. Name: _____________________________________ Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitter 1.Dopamine Function Influences movement, learning, attention, & emotion 2. Serotonin Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal 3.Norepinephrine Helps control alertness & arousal 4. GABA A major inhibitory neurotransmitter 5. Acetylcholine Major excitatory NT; causes contraction of skeletal muscles, helps regulate heart muscles, is involved in memory, transmits messages between the brain & spinal cord A NT similar to opiate morphine that relieves pain 6. Endorphins Surplus Excess dopamine receptor activity is linked to schizophrenia one hypothesis of its cause) Oversupply can lead to anxiety and insomnia Oversupply can stimulate brain, producing migraines or seizures (& the reason why people avoid MSG in food) Euphoria (“Runner’s high”) Deficit Undersupply produces the tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinson’s Disease Undersupply linked to depression Drugs/Therapy L-Dopa (given to patients with Parkinson’s disease) functions like a synthetic form of dopamine) Undersupply can depress mood MAOI’s act on norepinephrine and increase norepinephrine to reduce depression. MAOIs are used only if the SSRIs don’t work though, since diets have to be changed (e.g. no cheese) Undersupply linked to seizures and Huntington’s disease Benzodiazepine (Valium) and anticonvulsant drugs increase the activity of GABA) Botox works by blocking Ach release from the sending neuron, which paralyzes facial muscles, thereby smoothing wrinkles. Alzheimer’s disease Antidepressant drugs raise serotonin levels (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, SSRIs, e.g. Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil, et cetera.) Many painkillers (e.g. morphine) work by acting like endorphins and relieve pain.