Organic Unit Review KEY
advertisement

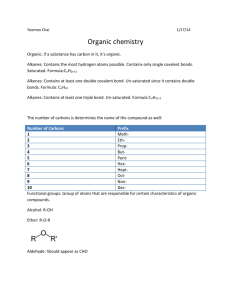
Mr. Storie Organic –Unit Review KEY 30S Chemistry Organic Unit Review KEY 1. Draw complete structural formulas for alkanes with two and six carbons. Name the structures. Ethane Hexane 2. Draw condensed structural formulas for pentane and heptane. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2 CH2CH2 CH2CH2CH3 3. Name the compounds that follow: a. 3,3-dimethylhexane b. 2,4-dimethylhexane c. 2,2,4,4-tetramethylpentane d. 3-ethylhexane e. 3-methylpentane Mr. Storie 30S Chemistry Organic –Unit Review KEY a. b. c. d. e. f. 4. Draw complete structural formulas for the following compounds: 3-ethyl-2,4-dimethyloctane 2,2,4-trimethylpentane 3-ethylhexane 3,5-diethyl-2,3-dimethyl-5-propyldecane propyne cyclopentane a. b. c. d. 5. Draw the structural formulas for the following alkenes. If a compound has geometric isomers, draw both the cis and trans forms. 1-pentene 2-hexene 2-methyl-2-hexene 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene Mr. Storie 30S Chemistry Organic –Unit Review KEY 6. Name the following compounds: propylbenzene 2-phenylpropane 2,5-dimethyl-3-phenylhexane 7. Why are the following names incorrect? a. 2-dimethylpentane – since it is “dimethyl” it should have either a second number placement (2,2) or only be a single methyl group (2-methyl). b. 1,3-dimethylpropane – with methyl groups off the first and third of a propane chain, it would actually be a 5-C long chain and thus better named pentane. c. 3-methylbutane – it would be better to number carbons from the other end, making this 2methylbutane. d. 3,4-dimethylbutane – two problems: a methyl group off the 4th and final carbon of a butane extends the long chain which means this is actually pentane. A re-numbering of the chain then leaves only 1 methyl group at the 3, giving 3-methylpentane. 8. Explain the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon compounds. Saturated is an alkane – all single bonds – all possible bonds filled with hydrogen Unsaturated is an alkene/yne – double or triple bonds – not completely full of possible hydrogen 9. Draw all the possible alkenes with the molecular formula C4H8. Name each compound. Mr. Storie Organic –Unit Review KEY 30S Chemistry 10. Explain why alkenes have cis/trans isomers and alkanes don’t. Double bonds can’t rotate. Single can – branches can be pointing up or down and move between. Double bonded branches are EITHER up or down pointing and can’t rotate. a. b. c. d. 11. Draw a structure for each compound. p – diethylbenzene 2-methyl-3-phenylpentane p-xylene toluene 12. Write a complete balanced equation for the combustion of pentane. C5H12 + 8 O 2 5 CO2 + 6 H2O 13. Name the following compounds: a. b. c. d. 2-methyl-2-butene 2-methypentene 2-butene cis 3-methyl-2-pentene Mr. Storie Organic –Unit Review KEY 30S Chemistry 14. Name the following compounds: a. b. c. d. e. d. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH a. b. c. d. e. f. 15. Give the structural formula for each of the following compounds: 2-chloropropane 1-iodo-2,2-dimethylpentane p-dibromobenzene. 2-methylphenol 1,2-dichlorocyclohexane 1,2-ethandiol bromobenzene chloroethane 3-chlorobutene Butanol 2-propanol Mr. Storie a. b. c. d. e. f. Organic –Unit Review KEY 30S Chemistry 16. Give the name for the following carboxylic acids and esters: HCOOH Methanoic acid CH3CH2COOH Propanoic acid CH3COOCH2CH3 Ethyl ethanoate CH3COOH Ethanoic acid CH3(CH2)4COOH Hexanoic acid CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3 Ethyl butanoate 17. Use the ester from question 16c to show a complete de-esterification reaction. CH3COOH ethanoic acid H2O + CH3COOCH2CH3 water ethyl ethanoate + HO-CH2CH3 ethanol 18. Use 2-butene to show a hydration reaction. CH3CH=CHCH3 + H2O 2-butene water CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3 2-butanol 19. Write the structure for the reactants and expected products from each reaction: a. propene + bromine gas CH2=CHCH3 propene + Br2 CH2(Br)CH(Br)CH3 bromine 2,3-dibromopropane b. 2-pentene + iodine gas CH3CH=CHCH2CH3 + I2 2-pentene iodine CH3CH(I)CH(I)CH2CH3 2,3-diiodopentane c. 3-octyne + hydrogen gas CH3CH2CΞCCH2CH2CH2CH3 + H2 3-octyne hydrogen CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH2CH2CH3 3-octene Or…if you used 2 moles of H2 the product would have been octane. d. trans 2-butene + hydrogen gas CH3 CH=CH CH3 trans 2-butene + H2 hydrogen CH3CH2CH2CH3 butane