BUSINESS ENGLISH II
Course code
Course title
Type of course
Stage of study
Year of study
Semester
ECTS credits
Coordinating lecturer
Study form
Course prerequisites
Language of tuition
HUM 103
Business English II
Main
First/Bachelor
st
1
Spring
6;
60 class work hours, 100 individual work hours;
2 consultation hours
PhD student Jolita Butkienė
Full time
English
Annotation
Speaking a language that is understood by decision makers is critical for success in business and business studies. The
primary goal of the Business English II course is to provide instruction and practice in oral and written English using
business-related topics as its content base. The course also aims at developing students speaking, listening, reading and
writing skills for academic purposes. The course is designed to develop students’ self-study skills and learner
independence.
Subject Learning Outcomes
Subject Learning Outcomes
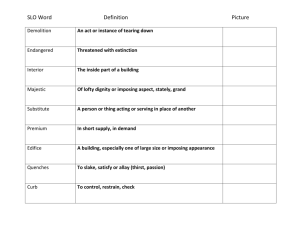
SLO1. Students will be able to read/listen to and
understand authentic texts related to their
studies for general idea and for detail.
SLO2. Students will be able to derive vocabulary
meaning from context; develop vocabulary
building skills and acquire sufficient vocabulary
in the topic areas defined in the course outline.
SLO3.
Students
will
develop
business
communication skills in key performance areas
such as exchanging information, discussing and
presenting business issues.
SLO4. Students will be able to write and
structure business reports, write summaries
SLO5. The learners will be able to give
presentations,
participate
in
meetings,
discussions and negotiations
Teaching and learning methods
Class assignments, individual
work (articles from business
journals and newspapers, and
texts written for second language
learners).
Class assignments, homework
exercises (articles from business
journals and newspapers, and
texts and exercises for second
language learners).
Class assignments, role-plays and
simulations of meetings.
Evaluation methods
Progress test, examination.
Class assignments and individual
homework.
Individual
and
group
presentations,
role-plays,
simulations.
Class and homework written
assignments, examination.
Assessed individual and group
presentations,
role-plays,
news updates.
Progress test, examination.
Case study, role-plays, class
and
homework
group
assignments.
Quality assurance
Reflective teaching; applying critical thinking skills; regular group and individual feedback provided to the students;
students’ feedback on the course quality.
Cheating prevention
Individual oral and written assignments and presentations; individual tasks. Tests administered with the assistance of
doctoral students.
1
Course outline:
Time
Week 1
Week 2
Topic
Week 4
Week 5
Week 6
Assignments (class and
homework)
Course introduction.
Overview of tasks and assignments.
Course requirements.
Venture capital (Unit
15)
Maze (discussion, small-group
decision making).
HW: Language exercises
Financial institutions.
Banking. (Unit 14)
.
Getting a loan.
Banking vocabulary.
Ways of raising finance for new
businesses.
The language of negotiations. What
are “good” negotiations and
successful negotiators?
Report writing conventions: structure,
style, layout.
Participating in negotiations:
preparation, participation, discussion,
reaching agreement.
Financial terms. Discussing different
investment possibilities.
News update.
Financial terms.
Stock market idioms.
Numbers.
News update.
Case study: investment
HW: Tasks from hand-outs
Negotiating skills
Week 3
Language skills, vocabulary
Report writing (1)
Negotiations (2)
Investment. Bonds
(Unit 16)
Stocks and shares
(Unit 17)
Hour
s
BBC &CNN news reports
4
4
Role-play: investing in start-ups.
HW: Language exercises
News update.
Role–play: negotiating a contract.
4
HW: Language exercises
News update.
Assessed role-play: negotiations
HW: Report on negotiations.
News update.
HW: Tasks from hand-outs
4
4
4
Progress test.
Week 7
TED talks
Week 8
Prices and
commodities
Week 9
Describing graphs
and figures.
Report writing (2)
Analysis of talks:
( J. Bezos On the next web
innovation; K. Robinson Changing
education paradigm)
Words and phrases in the context of
price and money
2
News update.
HW: Summary of two TED talks
News update.
Case study: Sumitomo bank
The language to describe changes.
Cause and effect. Tenses review.
TED:The beauty of data visualization
Different types of visuals.
Financial terms.
Interpreting financial documents.
News update.
Presentations
Student TED conference
Individual oral presentation.
Mergers and
Acquisitions. (Unit
21)
Discussing advantages and
disadvantages of takeovers and
mergers.
News update.
Case study: making new
acquisitions
HW: Tasks from handouts
Expressions of bankruptcy, debt and
credit.
Group presentations, analysis,
discussions.
News update.
Week 14
Finance and Credit
Business ethics
Case study:
Amazon.com
Week 15
Course review
Portfolio presentation and evaluation
News update.
Week 10
Week 11
Week 12
Week 13
Accounting and
financial statements.
(Unit 19)
2
4
4
Report on statistics/visuals.
HW: Language exercises
News update.
HW: Tasks from handouts
4
4
4
4
4
4
Total
60
2
Self-study and assessment
Assignment
Progress test
Case study (Group presentations and discussion)
News update
Course oral assignments (negotiations, presentations, roleplays)
TED talk
Course written assignments (summaries and reports)
Portfolio
Examination test
Consultation
Total
Number of self-study
hours
20
10
10
10
10
10
10
20
2
100 hours
Percentage of the total grade
20 %
10 %
10 %
10 %
10 %
10 %
10 %
20 %
100 %
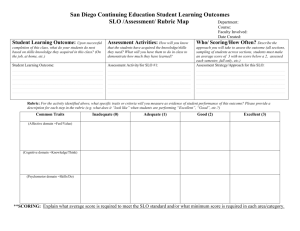
Assessment
1. Test. It consists of topics covered during weeks1-6 of the term. The test covers all four language skills (reading,
listening, writing and speaking) and contains vocabulary and language use items.
2. Course oral assignments include:
Presentations. Speaking is assessed through group/peer and individual presentations. Structure, vocabulary,
signposting, use of target vocabulary and grammar accuracy are assessed.
Meetings and negotiations. Role-plays are assessed for the use of language of meetings and negotiations,
active participation, clear and successful communication, task achievement.
Active participation means appropriate preparation for classes, active involvement in discussions and
meaningful contributions to any other class tasks.
3. Course written assignments include:
Summaries and reports. They are assessed for keeping appropriate format, style and register, task
achievement, and accuracy. They might be assigned as homework or written in class.
Any marks for “surprise” language tests will be included in this part of the assessment.
4. News update. This is a weekly assignment delivered by two students each week. The update should include
summary of the main news of the previous/current week, based on BBC and CNN or any reliable written sources. The
length is 10 min.-15 min.
5. Portfolio. The Portfolio of student’s work is an individual file which includes evidence of student’s work during the
term. It should include summaries of weekly news updates delivered by colleagues every week, written summaries of
three articles taken from “The Economist” or any other reliable magazine or newspaper, related to the topics covered
during the term or other current issues, language development exercises assigned for individual study.
6. Case study. This is a whole term group assignment which includes looking for and analysing information about on-line
and traditional selling models (Amazon.com vs Barnes and Noble). It weighs 10% of the final mark. Students work in
groups, find and read information for the topic, prepare vocabulary notes and are able to answer general comprehension
questions on the case content. After analysing the information they will prepare group PP presentations. For the case
discussion, they should be ready to provide arguments and reasons for their opinions. Some students will act as
facilitators and will be responsible for organising and running the discussion.
7. Examination is given at the end of the semester. It accounts for 20 % of the final mark. It consists of listening,
grammar, vocabulary, reading and writing tasks, covering topics of the whole term.
8. Re-take examination is taken by the students who do not get a “pass” mark at the end of the course. It is a test on the
topics of the whole course and accounts for 40% of the mark, plus case study (10%), portfolio (10%), news update
(10%), written and oral assignments (30%).
9. General instructions
Write your name on all assignments
All the assignment must be completed in conformity with the General Format Requirement for Undergraduate
Student Paper
All the written assignment must be typed
Double space all assignments
If you send your assignment by email, send it as a Word attachment
If you use additional resources, cite and reference them according to General Format Requirement for
Undergraduate Student Paper
10. Note: students are not allowed to make up for any course assignments after the deadline.
It is student’s responsibility to find out what they have missed if they are absent from lectures. Being absent
does not excuse them from tests or tasks on the day they return.
3
Main course book:
1.
MacKenzie, I. (2010).English for Business Studies. Third edition. Student’s book. CUP
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Powell, M. (2004). New Business Matters. Thomson.
Powell, M.(1999). Presenting in English. LTP
Oxford Business English Dictionary. (2006). OUP
Cotton, D. (2002).Market Leader. Upper Intermediate. Longman
Dubicka I., O’Keeffe M. (2007). Market Leader. Advanced. Pearson. Longman
Emmerson, P. (2002).Business Grammar Builder. Macmillan Education
Emmerson P. (2009). Business Vocabulary Builder. Macmillan.
Emmerson P. (2007). Business English Handbook. Advanced. Macmillan.
Mascull, B. (2002). Business Vocabulary in Use. Intermediate. CUP
Mascull, B. (2004). Business Vocabulary in Use. Advanced. CUP
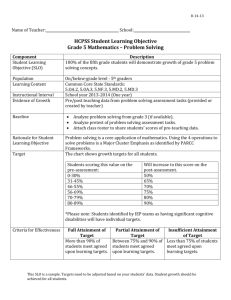
Role of the subject in reaching learning outcomes of Business Management and Analytics programme
Special learning outcomes
Subject Learning
Outcome
S1. To analyze a company or an organization as an integral unit, which strives for certain goals in a
market or social environment by effectively distributing their finite resources among objects and
business activities and obtains synergies from coordinated function planning, organization and
management;
S2. To forecast the influence of economic and financial decisions not only in a financial context, but
also in the wider context of business or organization management, to estimate the effect of
economic and financial decisions on the processes of a company or an organization, the motivation
of company’s human resources, product and service quality, customer satisfaction, brand strength,
corporate social responsibility;
S3. To select and to apply in practice organizational theories and models;
S4. To identify new possibilities in national and international markets, to foresee, to analyze and to
assess target markets, their potential, to adapt the old products and services and to develop the new
ones for these markets, to communicate effectively one’s proposals to the market;
S5. To describe and to analyze financial management and financial decision making processes in
companies and other organizations, to solve problems of different levels of complexity in financial
and management accounting ;
S6. To describe the main economic theories and theoretical models, to adapt them to the theoretical
and practical issues (for example, demand and supply elasticity theory, economic cycles, classical
economic theory, Keynesianism, monetarism, rational expectations theory, cost-benefit analysis);
S7. To analyze economic, legal, political and social environment of companies and other
organizations; to identify and to evaluate internal and external changes and to make necessary
decisions to keep the firm’s or organization’s economic and financial stability;
S8. To plan and to organize manufacturing, service provision and other company’s business
processes in short and long term, in national and international markets;
S9. To name the main principles of business law and to be able to analyze simple cases in business
law.
S10. To explain the corporate social responsibility and to be able to apply its principles in practice for
a company operating in a local as well as international markets.
S11. To select adequate research methods for the company’s internal and external analysis and to
conduct individually simple research of internal and external environment (to collect, to organize and
to interpret data, based on them to make managerial decisions).
S12. To name the main principles of strategic planning and management, to be able to analyze in
practice the strategic alternatives based on the company’s or organization’s competitive environment
and its resources, to create an outline of a strategic plan and to foresee tactical actions to implement
4
the strategy.
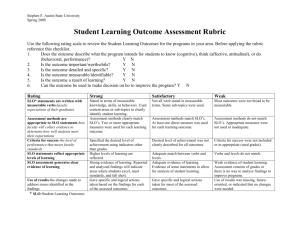
General learning outcomes
G1. To apply modern information technologies in the data gathering, analysis and communication;
SLO 1; SLO 2;
SLO 3; SLO 4;
SLO 5
G2. To apply calculations, modelling, optimisation and statistical analysis skills for analysis of
managerial and economical programmes
G3. To apply a systematic, critical and constructive thinking in problem identification and solving;
SLO 5
G4. To communicate well and express thoughts in writing and orally, both in English and native
language; to communicate with specialists and non-professional audiences;
G5. To prepare research papers according to proper language, writing style and general
bibliographic citation requirements;
SLO 3; SLO 4;
SLO 5
G6. To develop independent learning skills necessary to continue studies on a higher level;
SLO 1; SLO 2;
SLO 3
SLO 4; SLO 5
G7. To communicate and to work effectively in an intercultural and interdisciplinary group or team.
G8. To know and to apply in practice certain aspects of various social sciences (history, geography,
sociology, logics, philosophy, arts, etc.), to supplement effectively the education of business or
economics by general knowledge.
SLO 1; SLO 3;
SLO 5
5