Financial ratio analysis, exercise and worksheet - w3b
advertisement

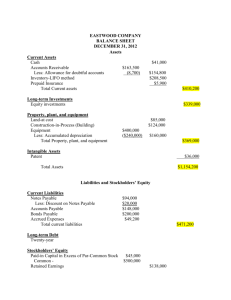
Financial ratio analysis, exercise and worksheet Financial ratio analysis Is the process of collecting, calculating, analysing and interpreting results from the accounts of companies and organisations. A financial ratio is a relationship between two or more financial values which can be expressed in a number of ways, e.g. percentage, times, number of weeks. It is important 1. To apply agreed rules regarding the specification of the various components of any ratio in a consistent manner. 2. To interpret changes in the resulting ratios against previous levels, industry averages or simple benchmarks. A basic analysis of financial ratios usually cover the following: Profitability: to assess the return on the capital employed by a company. Liquidity: to assess a company's ability to pay its way in the short-term; to meet its financial obligations. Gearing: measures the relationship between interest bearing debt and equity (or shareholder's fund). Using the analysis framework above, the following ratios can be calculated: Profitability: Profit as a percentage of Capital employed Profit as a percentage of Revenues Revenues divided by Capital employed Liquidity: Current assets divided by Current liabilities Liquid assets divided by Current liabilities Cost of sales divided by Inventories Trade receivables divided by average weekly revenues Gearing: Total Borrowings divided by Equity Interest Payable as a percentage of (Profit before Tax + Interest Payable) Financial ratio analysis – Example Income statement for the year ended: 2011 2010 £’000 £’000 5,500 2,850 1,800 600 140 110 -40 70 -20 50 4,700 3,000 900 600 150 50 -20 30 -20 10 £’000 £’000 400 300 950 500 50 1,500 (O) 1,100 600 100 1,800 425 675 0 0 1,100 600 660 20 20 1,300 NET WORKING CAPITAL 400 500 (E) TOTAL ASSETS LESS CURRENT LIABILITIES 800 800 (F) (G) EQUITY Issued share capital Retained earnings 130 550 680 130 500 630 (J) LONG-TERM LOAN 120 170 800 800 (D) (Q) (B) (A) REVENUES Cost of sales Distribution costs Administrative expenses Interest Payable PROFIT BEFORE TAXATION Taxation PROFIT ATTRIBUTABLE TO SHAREHOLDERS Dividend RETAINED PROFIT Balance Sheet as at 31st March NON-CURRENT ASSETS (P) CURRENT ASSETS Inventories Trade and other receivables Cash and cash equivalent (L) (I) CURRENT LIABILITIES Trade and other payables Bank overdraft Taxation Dividend (M) Financial ratio analysis worksheet - Profitability and Gearing Where to look PROFITABILITY (A) Profit before taxation IS (B) Interest payable IS (C) Profit before tax + interest payable (D) Revenues IS (E) Net capital employed (1) BS 1.1 PROFIT ÷ NET CAPITAL EMPLOYED % 1.2 PROFIT ÷ REVENUES % 1.3 REVENUES ÷ NET CAPITAL EMPLOYED A+B GEARING (F) Issued share capital BS (G) Retained earnings BS (H) Equity (or shareholders’ fund) F+G (I) Bank overdraft BS (J) Long-term loans BS (K) Total borrowings I+J 3.1 TOTAL BORROWINGS ÷ EQUITY 3.2 INTEREST PAYABLE ÷ PROFIT BEFORE TAX + INTEREST % (1) Net capital employed = Non-current assets + Current assets - Current liabilities Financial ratio analysis worksheet - Working capital Where to look WORKING CAPITAL (L) Current assets BS (M) Current liabilities BS (N) Liquid assets (1) BS 2.1 CURRENT ASSETS ÷ CURRENT LIABILITIES 2.2 LIQUID ASSETS ÷ CURRENT LIABILITIES (O) Inventories BS (P) Trade and other payables BS (Q) Cost of sales IS (R) Average weekly revenues (2) IS 2.3 COST OF SALES ÷ INVENTORIES 2.4 TRADE RECEIVABLES ÷ AVERAGE WEEKLY REVENUES (1) Liquid assets = Current assets - Inventories (2) Average weekly revenues = Revenues divided by number of weeks in period