Counter Points, Chapter Summary cards
advertisement
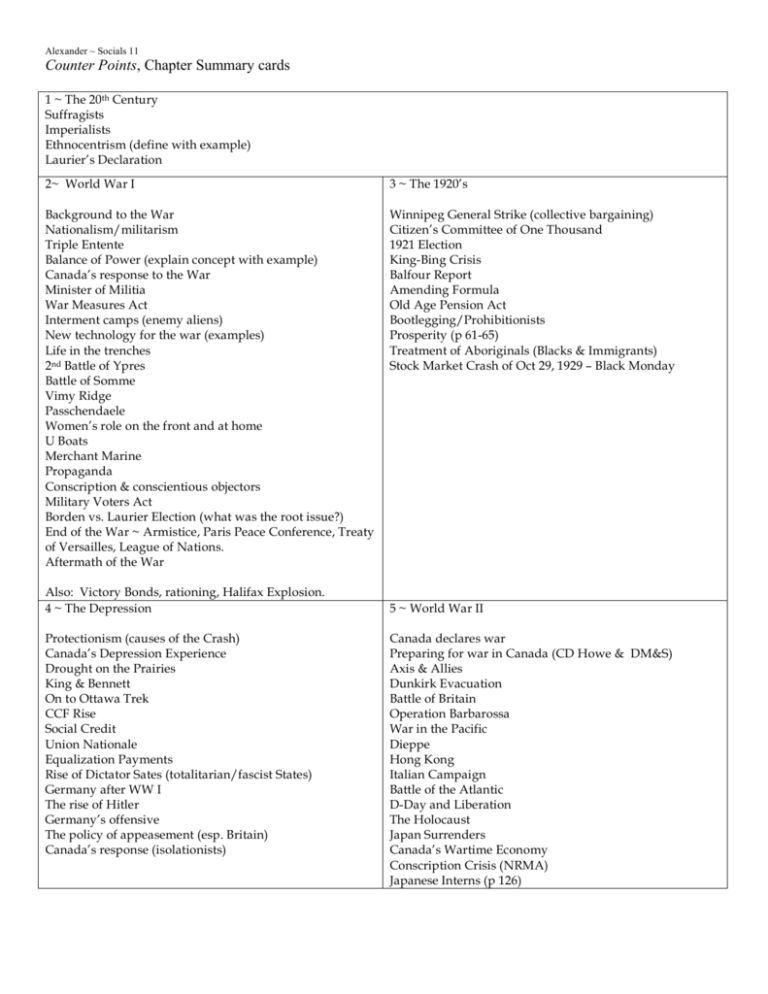
Alexander ~ Socials 11 Counter Points, Chapter Summary cards 1 ~ The 20th Century Suffragists Imperialists Ethnocentrism (define with example) Laurier’s Declaration 2~ World War I 3 ~ The 1920’s Background to the War Nationalism/militarism Triple Entente Balance of Power (explain concept with example) Canada’s response to the War Minister of Militia War Measures Act Interment camps (enemy aliens) New technology for the war (examples) Life in the trenches 2nd Battle of Ypres Battle of Somme Vimy Ridge Passchendaele Women’s role on the front and at home U Boats Merchant Marine Propaganda Conscription & conscientious objectors Military Voters Act Borden vs. Laurier Election (what was the root issue?) End of the War ~ Armistice, Paris Peace Conference, Treaty of Versailles, League of Nations. Aftermath of the War Winnipeg General Strike (collective bargaining) Citizen’s Committee of One Thousand 1921 Election King-Bing Crisis Balfour Report Amending Formula Old Age Pension Act Bootlegging/Prohibitionists Prosperity (p 61-65) Treatment of Aboriginals (Blacks & Immigrants) Stock Market Crash of Oct 29, 1929 – Black Monday Also: Victory Bonds, rationing, Halifax Explosion. 4 ~ The Depression Protectionism (causes of the Crash) Canada’s Depression Experience Drought on the Prairies King & Bennett On to Ottawa Trek CCF Rise Social Credit Union Nationale Equalization Payments Rise of Dictator Sates (totalitarian/fascist States) Germany after WW I The rise of Hitler Germany’s offensive The policy of appeasement (esp. Britain) Canada’s response (isolationists) 5 ~ World War II Canada declares war Preparing for war in Canada (CD Howe & DM&S) Axis & Allies Dunkirk Evacuation Battle of Britain Operation Barbarossa War in the Pacific Dieppe Hong Kong Italian Campaign Battle of the Atlantic D-Day and Liberation The Holocaust Japan Surrenders Canada’s Wartime Economy Conscription Crisis (NRMA) Japanese Interns (p 126) Alexander ~ Socials 11 6 Gouzenko Cold War (superpowers) NATO Warsaw Pact International Monetary Fund (IMF) Korean Conflict Suez Crisis Cuban Missile Crisis Vietnam War Trudeau’s Foreign Policy ________________________________________________ Know these key people, their political importance Gouzenko Mulroney McCarthy J.F. Kennedy U.N. Security Council Castro Lyndon Johnson 9 Representative Democracy Direct Democracy Representative Democracy Constitutional Monarchy Written Constitution Unwritten Constitution Federal System • residual powers • Legislative Branch • House of Commons • Caucus • Senate • Patronage Executive Branch Gov. General Prime Minister Cabinet *** How a Bill becomes Law *** Parliamentary System Executive Power Legislative Power Judicial Power 7 Referendum Social Welfare Youthquake St. Laurent Diefenbaker Pearson Trudeau _________________________________________________ 8 Quebec Separatism October Crisis Duplessis Lesage Levesque Laporte Parti Québécois (PQ) FLQ Bill 101 Sovereignty association Notwithstanding Clause Meech Lake & Charlottetown Accord Provincial/Territorial Gov’ts Responsibilities • Education • Environment • Health Care & Social Welfare • Negotiating with Federal Gov’t Order in Council Local Gov’t powers Aboriginal Self Gov’t (Nunavut & Nisga’a treaty) Be Able to: Explain the electoral system (candidates, parties, constituents, voting, election campaigns. Minority vs. Majority Gov’ts (benefits and challenges of). Free vote vs. Party discipline. Also: Constitution British North America (BNA) Act Bill of Rights Constitution Act (1982) Municipal government Formal assent Cabinet solidarity Private member’s bill Alexander ~ Socials 11 10 11 Elections Campaigns Public Opinion Polls Electoral System – 1st Past the Post; Proportional Representation Political Parties: Left Wing, Center, Right Wing B.C.’s major Political Parties – their philosophy and priorities NGO’s Lobbyists (pressure groups) Media Concentration Civil Disobedience Ridings (constituencies) Rule of Law Civil Law Criminal Law Common Law Be able to draw and label the wings of the Justice System Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms (know in depth) Draw out the Court structure Supreme Court of Canada Young Offenders Act (rights under the Act) Totalitarianism Democracy Liberalism Conservativism Socialism Fascism Communism 12 Human Rights Fundamental Freedoms Equality Rights Notwithstanding clause (how it is used) & the Amending Formula BC Human Rights Code Aboriginal Rights Gender Equity Children’s Rights Chapter 13 14 Demography Developed/Developing Countries Rule of Seventy Rates ~ Birth, Death, Emigration, Immigration Life Expectancy Demographic Transition Model Dependency Ratio Population Pyramids Population Distribution/Density Carrying Capacity Developed, Newly Industrialized, Developing Countries Poverty Trap Woman and Children in Poverty (explain the root causes) Epidemics ~ HIV/AIDS Foreign Aid (who provides it and where & how it is applied; 15 16 Urbanization Push/Pull factors Basic/Non-Basic Activities Multiplier Effect Sustainable Cities Economic Disparity Economic Activities (primary, secondary, tertiary) Traditional Economy Developed Economies Developing Economies Developmental Factors Sustainable Development Regional Disparities 17 Example: Wilfred Laurier (1841-1919) • Born into bicultural family (Quebec) • First became member of parliament in 1873 • In 1896 he became Canada’s seventh prime minister and Canada’s first Francophone prime minister • Went for 15 years, longest period (without breaks in between) being a prime minister in Canada yet • Went for the “sunny ways” approach (always looked for the compromise) • Urged Canadians to respect diversity of both English and French cultures KP: Excellent prime minister, 15 uninterrupted years. Helped Canadians accept the diversity of their country Know in more depth: Groundwater Aquifer Ogallala Aquifer Ozone Layer Global Warming Kyoto Protocol Stewardship Tied Aid.