Discover Biology
advertisement

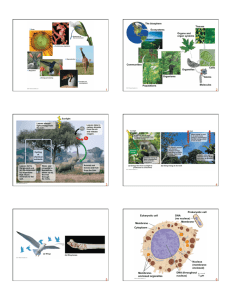
Discover Biology FIFTH EDITION CHAPTER 1 The Nature of Science and the Characteristics of Life Anu Singh-Cundy • Michael L. Cain © 2012 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Earthbound Extraterrestrial? Or Microbe in the Mud? • Bacterium discovered that uses arsenic instead of phosphorus in its DNA • All life created from set recipe of chemical building blocks? Not! Your assignment for next Wed is to read about this. Researches Wrangle over Bacteria • Previously, scientists agreed that all life on Earth required six major elements: – – – – – – Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Oxygen Sulfur Phosphorus • The bacteria that does not require phosphorus raises the question of whether any of the six major elements of life are actually required! Science Is a Body of Knowledge and a Process for Generating That Knowledge • The process is called the scientific method It can be applied to all areas of science • It begins with observation • Diet Beverages and depression (March 2013) After observation comes The Hypothesis “deductive reasoning” Diet Beverages and depression If….. Then…….. controls • What is the purpose of a control group? 2 ways we use the word control in science • Erbitux ($17,000 month!) 2 ways we use the word control in science WE CONTROL FOR Variables • What are variables? How many do we change at a time? (How do we “control” them?) Does sample size matter? U.S. 315,151,548 ~9 million depressed World 7,059,238,065 ~350 million depressed • What is sampling error? BLIND studies DOUBLE BLIND studies RESULTS When making a graph - what goes on x axis and what goes on y axis? DEPENDENT VARIABLE Effect (“then” this) GRAPH WHAT VARIES BASED ON WHAT YOU DID (DEPENDS) INDEPENDENT VARIABLE Cause (“if” this) WHAT YOU VARY OR CHANGE IN EXPERIMENT Then you will test higher for depression WHAT VARIES BASED ON WHAT YOU DID (DEPENDS) MOST HUMAN STUDIES ARE COORELATIONS GRAPH If you drink diet drinks WHAT YOU VARY OR CHANGE IN EXPERIMENT What can COORELATIONS really tell us? Are there too many variables in human studies? Proved? Not Proved? Right? Wrong? SUPPORTED NOT SUPPORTED What is a theory?? • A SCIENTIFIC theory is: – a proposed explanation for a natural phenomenon. – the body of interconnected concepts, supported by scientific reasoning and experimental evidence • solid ground of science Evolution is the core of biology • Species descend with modification • Natural selection (Darwin published first) CHANGE OVER TIME • does NOT mean we descended from apes!!!! • does mean things change over time life has been shaped by evolution Figure 1.9 Natural selection Large ground finch (seeds) Vegetarian finch (buds) Cactus ground finch (cactus fruits and flowers) Woodpecker finch (insects) Concept Quiz Observation: After a lengthy rainstorm, earthworms are on the surface of a sidewalk. Which of the following is an adequate hypothesis for the observation? a) The sidewalk is hard and flat. b) Lightning attracts earthworms. c) Saturated soil makes it difficult for the earthworms to “breathe” so they come out of the ground. How to study: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Read before class Ask yourself questions about the headings Read first sentence of each paragraph Preview figures Now read – and take notes (read out loud) Read again after 3-4 days Know key terms Use study aids Use other books 10.Take breaks 11.SLEEP What is common to LIFE? CELLULAR LEVEL Atoms •cells Molecule Macromolecule Organelle Cell Cells! • More than 10 trillion cells in human body Properties of life • • • • One or more cells Reproduction Energy utilization Response to environment • homeostasis • evolutionary adaptation (DNA information base) Emergent properties •Hierarchy (Figure 1.2) - molecule – organelle – cell – tissue – organ – organism Is the whole greater than its parts? Novel properties emerge Problem Reductionism –) Life depends on chemical and molecular reactions we must understand atoms and molecules ATOMS MOLECULES •ORGANIZATION OF LIFE Hierarchy -atoms - molecules Tissue Organ • organelles (little organs) – – – – – – – – – cells Tissue organ organism species population community ecosystem bioosphere Organ system Organism Organisms are open systems that interact with the environment • Ecosystems – cycling of nutrients – flow of energy – produce and consume • GENES INTERACT WITH ENVIRONMENT PKU •Energy conversion –plants solar energy to chemical energy Regulation • Homeostasis • Feedback • negative - temperature • positive – blood clots Cells are the basic unit of structure and function • Cell theory – living things are made of cells – cells come from other cells • all cells have membranes • all cells have DNA (at some stage) Microscopes • Hooke (1665) • Leeuwenhoek (1675) Diversity! • Estimates - 10 million - 200 million species!!!! – Currently 1.8 million species. • 280,000 plants • 50,000 vertebrates • 750,000 insects – Thousands more each year Continuity is heritable- based on DNA • Order requires instruction – four building blocks nucleotides – sequence - same to all life example: eyes Huntington's disease (CAG repeats) Structure is related to function Function is related to structure Human Human Cat Bat Porpoise Horse which comes first? Science, technology and society are interdependent • Example – scientific discovery needs tax dollars • • • • educate politicians bureaucrats corporate leaders voters Neuroscience in USA (Both Watson and Crick moved here) POLITICS • APPLIED SCIENCE • BASIC SCIENCE Concept Quiz Which of the following is a characteristic shared by all living organisms? A. Movement B. Reproduction C. Breathing Concept Quiz Which organism is the producer? A. Cactus B. Rattlesnake C. Hawk © 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e