X - Estrella Mountain Community College
advertisement

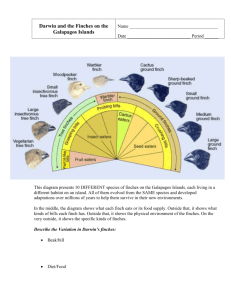
The biosphere Tissues Ecosystems Order Organs and organ systems Response to the environment Evolutionary adaptation Reproduction Communities Cells Organelles Regulation Organisms Energy processing Atoms Growth and development Molecules Populations 1 2 Sunlight Leaves absorb light energy from the sun. CO2 Leaves take in carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen. Sunlight O2 When energy is used to do work, some energy is converted to thermal energy, which is lost as heat. An animal’s muscle cells convert chemical energy from food to kinetic energy, the energy of motion. Chemical energy Cycling of chemical nutrients Leaves fall to the ground and are decomposed by organisms that return minerals to the soil. Heat Producers absorb light energy and transform it into chemical energy. Chemical energy in food is transferred from plants to consumers. Animals eat leaves and fruit from the tree. Water and minerals in the soil are taken up by the tree through its roots. (a) Energy flow from sunlight to producers to consumers A plant’s cells use chemical energy to do work such as growing new leaves. (b) Using energy to do work 3 4 Eukaryotic cell Membrane Prokaryotic cell DNA (no nucleus) Membrane Cytoplasm (a) Wings (b) Wing bones Nucleus (membraneenclosed) Membraneenclosed organelles 5 DNA (throughout 1 µm nucleus) 6 Nucleus A C DNA Nucleotide T A Sperm cell T Cell A Nuclei containing DNA C C Egg cell G Fertilized egg with DNA from both parents Embryo’s cells with copies of inherited DNA T Offspring with traits inherited from both parents A G T A (a) DNA double helix (b) Single strand of DNA 7 Negative feedback 8 Species Genus Family A Order Class Phylum Kingdom Domain Ursus americanus (American black bear) Enzyme 1 B Excess D blocks a step. D D Ursus Enzyme 2 D C Ursidae Enzyme 3 D Carnivora (a) Negative feedback W Mammalia Enzyme 4 Positive feedback + Excess Z stimulates a step. Z Chordata X Enzyme 5 Animalia Y Z Z Enzyme 6 Z Eukarya (b) Positive feedback 9 (a) Domain Bacteria 10 (b) Domain Archaea 15 µm 2 µm 2 µm 5 µm (c) Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Cilia of Paramecium Cilia of windpipe cells 100 µm 0.1 µm Kingdom Plantae Cross section of a cilium, as viewed with an electron microscope Protists Kingdom Fungi 11 12 Insect-eaters Green warbler finch Certhidea olivacea Gray warbler finch Certhidea fusca Bud-eater Seed-eater Warbler finches COMMON ANCESTOR Sharp-beaked ground finch Geospiza difficilis Vegetarian finch Platyspiza crassirostris Mangrove finch Cactospiza heliobates Tree finches Insect-eaters Woodpecker finch Cactospiza pallida Medium tree finch Camarhynchus pauper Large tree finch Camarhynchus psittacula 2 Elimination of individuals with certain traits 3 Reproduction of survivors Seed-eaters Ground finches 4 Increasing frequency of traits that enhance survival and reproductive success Cactus-flowereaters 1 Population with varied inherited traits Small tree finch Camarhynchus parvulus Large cactus ground finch Geospiza conirostris Cactus ground finch Geospiza scandens Small ground finch Geospiza fuliginosa Medium ground finch Geospiza fortis Large ground finch Geospiza magnirostris 13 Observations Question Hypothesis #1: Dead batteries Hypothesis #2: Burnt-out bulb Prediction: Replacing batteries will fix problem Prediction: Replacing bulb will fix problem Test of prediction Test of prediction Test falsifies hypothesis Test does not falsify hypothesis 15 14