Ecological Relationship Notes
advertisement

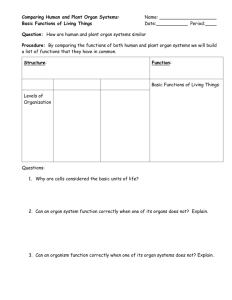
Ecological Relationship Notes Mutualism (Symbiosis) – Both species benefit o Ex. Bees and Flowers, Cows and cellulose digesting bacteria, clownfish and sea anemone Commensalism – One species benefits while the other is neither hurt nor helped o Ex. Birds and Army ants, sharks and little fish swimming below them, Predation – One organism feeds on the other o Ex. Any predator / prey relationship…. Killer whale / sea lion, Humans / cows Parasitism – One organism feeds off the other, but the other stays alive o Ex. Ticks, mosquitoes, some bacteria, fungi Parasitoid – One organism lays its eggs in the other. The infected organism then becomes a host that the larvae will use as a food source o Wasps and Caterpillars Competition – Organisms competing for the same mates, habitat, and / or food o Intraspecific competition –Competition within a species Ex. Male deer fighting for mates o Interspecific competition – 2 different species competing for food or habitats Ex. Scorpions and spiders Mimicry o Batesian mimicry - a form of mimicry typified by a situation where a harmless species has evolved to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species directed at a common predator. o Mullerian mimcry - natural phenomenon in which two or more poisonous species, that may or may not be closely related and share one or more common predators, have come to mimic each other's warning signals. Levels of Organization (Life’s Hierarchy) Least specific Biosphere – All environments on Earth that support life (Basically, the Earth and the sky above it that has living things occupying it.) Biomes – A group of ecosystems that have similar climates and communities Ecosystem – all living organisms in a particular area as well as the nonliving, physical components they interact with (ex. Sunlight, water, etc.) Community – All living things in an area Population – Single species living in a single area Organism – Single individual Organ System – group of organs working together for a certain function Organ – 1 part of an organ system Tissue – group of similar cells that do a particular function for an organ Cell – Smallest unit of life (All living things are made of up of one or more cells) Organelle – “organ” of a cell Molecule – cluster of atoms held together by chemical bonds Atom - basic unit of matter made of dense nucleus (protons and neutrons) with electron cloud around it Most specific Levels of Organization (Life’s Hierarchy) Least specific Biosphere – All environments on Earth that support life (Basically, the Earth and the sky above it that has living things occupying it.) Biomes – A group of ecosystems that have similar climates and communities Ecosystem – all living organisms in a particular area as well as the nonliving, physical components they interact with (ex. Sunlight, water, etc.) Community – All living things in an area Population – Single species living in a single area Organism – Single individual Organ System – group of organs working together for a certain function Organ – 1 part of an organ system Tissue – group of similar cells that do a particular function for an organ Cell – Smallest unit of life (All living things are made of up of one or more cells) Organelle – “organ” of a cell Molecule – cluster of atoms held together by chemical bonds Atom - basic unit of matter made of dense nucleus (protons and neutrons) with electron cloud around it Most specific