Measuring Matter Lab 7th Grade PSI Teacher's Notes: Measuring
advertisement

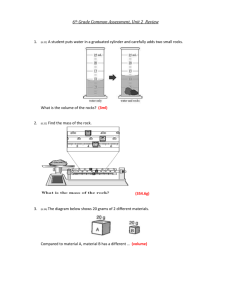
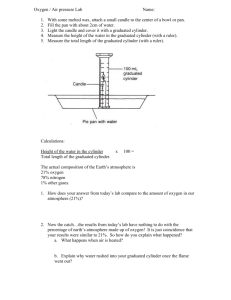
Measuring Matter Lab 7th Grade PSI Teacher’s Notes: Measuring Mass The objects chosen do not matter much as long as they are not too massive for your balances. It is suggested that you just choose 3 of the objects that will be used later in the lab. Volume of Regular Solids Choose 4 blocks of different sizes for this activity. Since density will not be touched upon yet, the blocks can even be made of the same substance. Sometimes, students have trouble figuring out which sides of the block to measure. If students are having difficulty differentiating between length, width and height, you could label the length, width and height of one of the boxes as an example. Volume of Liquids Again, since density is not to be discussed here, water can be used for all three substances. To differentiate between the three samples, you may use food coloring. You may also choose to use graduated cylinders of various sizes (10 mL, 50 mL, etc) Volume of Irregular Objects Choose any objects that will sink to complete this portion. Examples include screws, nails, bolts, washers, sinkers, masses, or any other small metal objects. You may wish to set a requirement for the initial water level (such as a 25 mL or 50 mL starting point) to be sure that students are putting enough water in the graduated cylinders. If the object is not completely submerged in the water, the full volume of the object will not be measured! You may also wish to just set up graduated cylinders on your own with a specific starting water volume to make the lab go smoother. Grading: Each row in the tables above counts as 1 point. Therefore, the measuring mass section is worth 3 points, volume of regular solids is 4 points, volume of liquids is 3 points and volume of irregular objects is 4 points. www.njctl.org 7th Grade PSI Matter and Its Properties Measuring Matter Lab Name __________________________ 7th Grade PSI Score: _________ / 14 points Purpose: Students will practice finding the mass and volume of various objects using common lab tools. Materials: triple beam balance digital balance graduated cylinder beakers rulers objects to measure Measuring Mass There are two common tools used to find the mass of objects. For centuries, scientists relied on the triple beam balance to find the mass of unknown objects. As technology improved, so did our scientific tools. Digital balances allow us to quickly find the mass of an object more precisely than ever before. Using a triple beam balance: 1. Place the object of unknown mass on the balance. 2. Use the three measuring beams (hence “triple” beam) to find the mass. Using a digital balance: 1. Turn the balance on and carefully place the object on. (Pretty simple!) Determine the mass of the three objects. Record your findings using the correct labels. Object Mass (grams, g) using triple Mass (grams, g) using digital beam balance balance 1. 2. 3. www.njctl.org 7th Grade PSI Matter and Its Properties Measuring Volume Scientists have a number of ways to measure the volume of substances. Some measuring tools are helpful when dealing with solids while some are useful when it comes to liquids. Volume of Regular Solids: For “regular” solids (typically those that have a box-like shape), we can use the formula for volume (Volume = Length x Width x Height). Use your ruler to find the lengths, widths and heights of the objects below (in cm). Use these numbers to find the volume of the 4 objects (in cm 3). Object Length (cm) Width (cm) Height (cm) Volume (cm3) 1. 2. 3. 4. Volume of Liquids: To find the volume of a liquid, we can use a graduated cylinder. Graduated cylinders come in a wide range of sizes. The smaller the graduated cylinder though, the more exact the measurement will be! When reading a graduated cylinder, you must read from the bottom of the meniscus. The meniscus is the slight curve you see at the top of the liquid. Reading from its lowest point will give you the most exact reading. Use the graduated cylinder to find the volume of the 3 liquids (in mL). Liquid Color Volume (mL) 1. 2. 3. www.njctl.org 7th Grade PSI Matter and Its Properties Volume of Irregular Objects: For some shapes, it is impossible to measure length, width and height. Other objects have strange shapes that would take a long time to measure. In order to quickly find the volume of these objects, we must use our graduated cylinders: 1. Pour water into a graduated cylinder and record the amount. 2. Drop the object into the graduated cylinder. Make sure the whole object is underwater! 3. Record the measurement of the new water level. 4. Subtract the original water level from the final level to get the volume. Find the volume of the 4 irregularly shaped objects. Object Initial water line (mL) Final water line (mL) Volume of object (mL) 1. 2. 3. 4. www.njctl.org 7th Grade PSI Matter and Its Properties