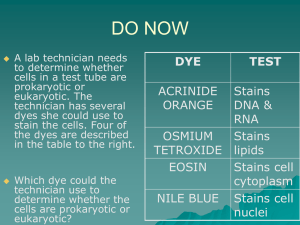
Unicellular Organisms - Avery County Schools
advertisement

Unicellular Organisms By Cindy Grigg You know that living things are made of cells. Some living things are made of only one cell. They are called unicellular. Uni- means one, as a unicycle has only one wheel. Most of us don't think about these unicellular creatures very much, but they are all around us. Most are invisible without a microscope, but a few can be seen with the naked eye. 1 The main groups of unicellular organisms are bacteria, protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi or yeasts. Each species is unique. They can be interesting to study because of their intricate and beautiful patterns. Some are sensitive to light. They may move toward it or away from it. They have novel ways of moving around. They also respond to touch. Some can live in very extreme environments. 2 Single-celled organisms have been on Earth for 3.8 billion years. They have had a long time in which to adapt. Scientists believe they were the first forms of life on Earth. 3 Although they are only one cell, they are complex. The more that we learn about them, the more marvelous we find them to be. Their shapes may be spheres, oblong, or spiral. A spherical shape helps keep them from drying out. That would be fatal to a cell. An oblong shape increases the cell's surface area for chemical processes. A spiral shape makes it easier for the organism to move. 4 Unicellular organisms have unusual ways of moving. The euglena have tiny hair-like structures called flagella. The flagella beat in the water and move the cell forward. The word flagellum means whip in Latin. Flagella (pronounced fla-jell-ah) is the plural form. Some have groups or rows of structures that move together like oars. These are called cilia (pronounced silly-ah). Cells with cilia move fast! One unicellular organism that moves with cilia is the paramecium. 5 Some unicellular organisms are able to change their shapes. Amoebas are "shape-shifters" that can extend parts of themselves into what are called pseudopodia and then flow in the direction in which they wish to go. Pseudopodia (pronounced sue-do-pode-ee-ah) means false feet. If they find something to eat, they can engulf, or surround, the particle with their pseudopodia. Then they pull themselves around it to digest it. 6 Just as the amoeba uses its pseudopodia for both movement and feeding, some unicellular organisms with 7 cilia also use the cilia to catch food. The stentor has cilia that beat rhythmically, which draws food into its mouth. This adaptation allows stentors to spend most of their lives attached to a surface. They can then save their energy for catching food. Some unicellular organisms live in extreme environments. They are called extremophiles. They have been found in such extreme habitats as Antarctic ice and in very hot deep-sea vents. The ability of organisms to adapt to extremely hot or cold environments gives scientists hope that signs of life will eventually be found on other planets. They believe that Mars and Europa, an icy moon of Jupiter, have conditions that could support some sort of living thing. 8 People use yeast, one kind of unicellular organism, to make bread and beer. Others help us by eating harmful bacteria and are food for fish and other animals. At least one kind of unicellular organism can cause illness in people. Amoebic dysentery, whose main symptom is bloody diarrhea, is transmitted by water containing one type of amoeba. It is well known as traveler's dysentery, or Montezuma's Revenge, particularly in Mexico. Liver infection and abscesses can occur also. It can be treated with antibiotic drugs. 9 Unicellular organisms are all around us. They have lived on Earth for many millions of years and have developed unique ways to survive. Although small, they are complex and beautiful. The next time you look at pond water, just think what you might discover there! 10 Copyright © 2012 edHelper Unicellular Organisms 1. 2. What are unicellular What does unicellular mean? organisms? One cell Plants with many cells Many cells Protozoa, algae, fungi, Unicycle or bacteria made of only one Multicellular cell Not alive Animals with many cells 3. 4. How long do scientists think What is the advantage of unicellular organisms have having a spherical shape? lived on Earth? Can get more food 3.8 trillion years Keeps it from drying out 3.8 million years Easier to move Millions of years More surface area for 3.8 billion years chemical processes 5. 6. What is the advantage of having a spiral shape? Can get more food More surface area for chemical processes Keeps it from drying out Easier to move Where have extremophiles been found? On Mars and Europa On the sun In Antarctica and the deep sea On the moon 7. 8. What is one kind of What does pseudopodia mean? unicellular organism that is False name helpful to people? Made-up name Yeast False feet Euglena Encyclopedia Amoeba Paramecium