Document
advertisement

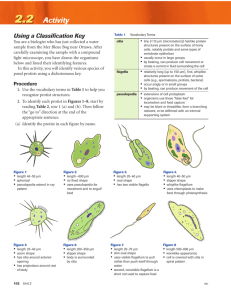
BIO 2 GO! 3213a Cellular Movement Cells that have the ability to move generally have an advantage over cells that cannot move. Cellular Movement 3.2.1.3a Upon successful completion of this unit, you should be able to do the following: 1. List and explain the 3 types of movement found in cells. 2. Use the following words correctly: Flagella Cilia Pseudopodia Unicellular Multicellular Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Cellular Movement 3.2.1.3a Some living organisms consist of only 1 cell. They are the simplest form of life. They can be plant or animal. However, even though they have only 1 cell, they still perform all of the life functions, like cellular respiration. Organisms that consist of only 1 cell are called unicellular. Most unicellular organisms live in water. Some unicellular organisms simply float along with water currents. Most unicellular organisms have the ability to move. These organisms usually are moving toward food or away from danger. There is a survival advantage in being able to move. This unit explains the movement of these unicellular organisms. There are 3 specialized 1. 2. 3. structures that allow unicellular organisms to move: flagella cilia pseudopodia 1. Flagella Flagella are whip-like structures that are attached to the cell and move it. They act like a rope or whip and wave back and forth to move the unicellular organism. Generally, the cell only has 1 flagella. It is not a very efficient way to travel. The unicellular organism, euglena, uses a flagella to move toward light. 2. Cilia Cilia are hair-like structures that often surround a cell. They work together much like oars or paddles on a boat. They are more efficient than flagella movement. Parameciums are unicellular organisms that use cilia to move toward food. 3. Pseudopodia Pseudopodia means “false foot”. A pseudopod is a blob-like extension of the cell membrane. It occurs when the cell tries to move in a direction. When this happens a blob of the cell moves forward and the rest of the cell follows. In order to move, the organism has to change its shape. It is usually slower than flagella movement. REMEMBER THIS!!! Flagella, cilia, and pseudopodia are the means by which unicellular organisms move. Interesting Scientific Fact: An amoeba is a unicellular organism that is so small that it is barely visible. When horror films were popular, the amoeba became popular as “The Blob”. The horror films made the amoeba large enough to eat a building or town. The films show the amoeba moving by pseudopodia. Question 1. What is the difference between a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism? Unicellular has only one cell and multicellular has many. Question 2. List and explain the 3 specialized structures for cell movement. Flagella, cilia, and pseudopodia Summary Cellular Movement 3.2.1.3a There are three main structures that can be used to help a single-celled organism move about. They are called flagella, cilia, and pseudopodia. A euglena is an example of a unicellular organism that has a flagellum. The flagellum is a single, long tail-like structure. It can be waved in a circular motion to create movement. A euglena must be able to move toward the light to be able to make its food. A paramecium is an example of a unicellular organism that has cilia. Cilia are much shorter than flagella. There are many of them surrounding a paramecium. Paramecia move their cilia together to create a wave of motion that helps them move. Paramecia must move in order to find food or to avoid predators. An amoeba is an example of a unicellular organism that has pseudopodia. Pseudopodia are extensions of the cytoplasm that allow the cell membrane to change shape and the amoeba to move. Amoeba cannot move as quickly as euglena or paramecium, but they can move. This helps them obtain food and avoid predators. Test Yourself Matching __C__1. paramecium a. has flagellum __A__ 2. euglena b. a long, single, tail-like structure __E__ 3. amoeba c. has cilia __B__ 4. flagellum d. many short hairs that move together __D__ 5. cilia e. has pseudopodia __F__ 6. pseudopodia f. extensions of cytoplasm True or False __F__ 1. Unicellular organisms cannot move. __T__ 2. Unicellular organisms have special structures to help them move. __T__ 3. A flagellum is a long, tail-like whip that can cause movement. __F__ 4. A flagellum is an extension of the cytoplasm that allows movement. __F__ 5. A flagellum is one of many short hairs that work together to create movement. __F__ 6. A cilium is an extension of the cytoplasm that allows movement. __T__ 7. A cilium is one of many short hairs that work together to create movement. __T__ 8. A pseudopodium is an extension of the cytoplasm that allows movement. __F__ 9. A pseudopodium is one of many short hairs that work together to create movement. __F__ 10. A euglena has a pseudopodium for movement. Fill in the Blank cilia euglena flagellum amoeba pseudopodia paramecium 1. The __AMOEBA_________ is an example of an organism with __PSEUDOPODIA_____, extensions of the cytoplasm that allow movement. 2. A __PARAMECIUM_______ has hundreds of __CILIA________, short hairs that surround its cell membrane, for movement. 3. A __EUGLENA______________ has a tail-like structure, called a __FLAGELLUM_____, for movement. Answer the Following 1. What is a flagellum? Name an organism that has one. Whip-like structures that help an organism to move. sperm 2. What are cilia? Name an organism that has them. Hair-like structures. Paramecium 3. What are pseudopodia? Name an organism that has them. A blob-like extension that helps it move. Amoeba