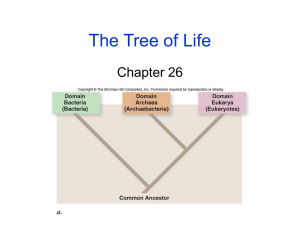
Linnaean Classification
advertisement
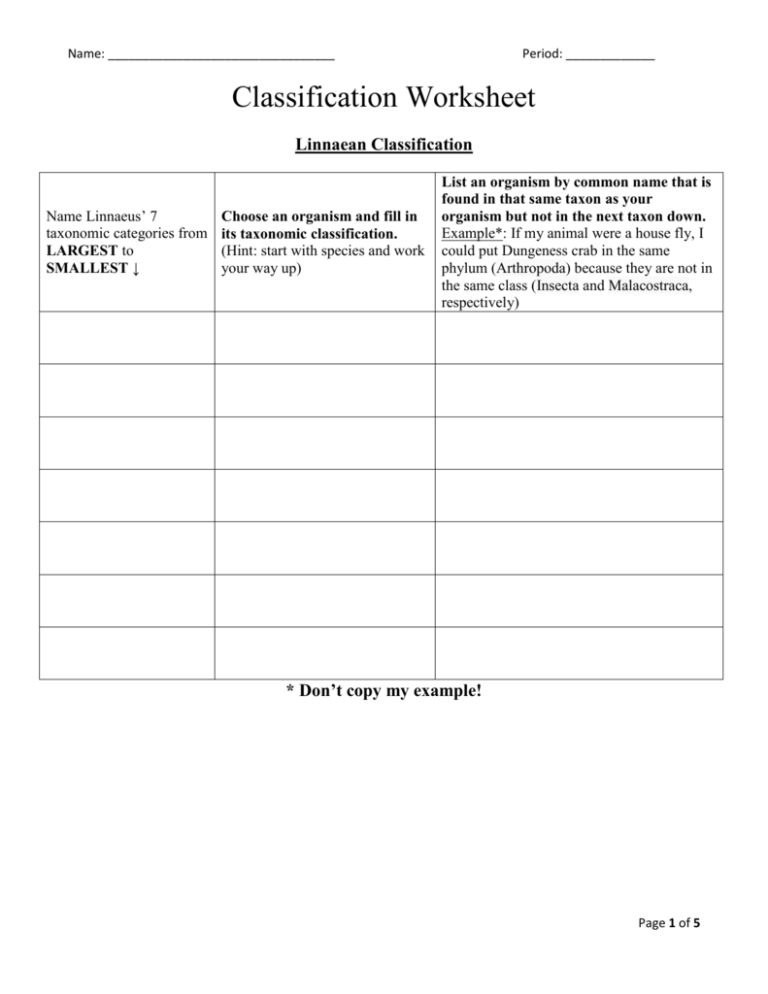
Name: _________________________________ Period: _____________ Classification Worksheet Linnaean Classification Name Linnaeus’ 7 taxonomic categories from LARGEST to SMALLEST ↓ Choose an organism and fill in its taxonomic classification. (Hint: start with species and work your way up) List an organism by common name that is found in that same taxon as your organism but not in the next taxon down. Example*: If my animal were a house fly, I could put Dungeness crab in the same phylum (Arthropoda) because they are not in the same class (Insecta and Malacostraca, respectively) * Don’t copy my example! Page 1 of 5 Name: _________________________________ Period: _____________ Three Domains All organisms belong to one of three domains, depending on their characteristics. A domain is the most inclusive taxonomic category. A single domain can contain one or more kingdoms. If you need, use your book to help fill in each of the domain names in the correct place in the table: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. DOMAIN CHARACTERISTICS EXAMPLES unicellular prokaryotes Bacillus, E. coli, peptidoglycan cell wall, cell membrane, ribosomes Streptococcus Cyanobacteria = “blueno membrane-bound organelles naked DNA, single circular chromosome, green algae” asexual reproduction = binary fission unicellular prokaryotes Methanococcus, cell wall (no peptidoglycans), cell membrane, ribosomes, Halobacterium, Thermoproteus no membrane-bound organelles DNA + histone proteins, single circular chromosome asexual reproduction = binary fission unicellular & multicellular eukaryotes animals, plants, protests, membrane-bound organelles: nucleus, mitochondria, fungi chloroplasts, Golgi complex, ER, lysosomes 1. Which domains are composed of unicellular organisms only? 2. To which domain do organisms whose cells contain nuclei belong? 3. Think of some of the words we use with temperature such as thermostat and thermometer. Now look at the names of the example organisms. Hypothesis which one can withstand high temperatures? Why is this your hypothesis? 4. Which domain(s) do the organisms use DNA? 5. The separation of Bacteria and Archaea first occurred in 1977. Long after they were first discovered. Using the information provided why do you think it took so long to separate these into separate domains? Page 2 of 5 Name: _________________________________ Period: _____________ Cladograms 6. Fill in the following table. Mark an ‘X’ if an organism has each trait. Hair/fur Legs Bipedal Eyes Human Fish Lizard Mouse 7. Fill in the cladogram below. a. Add each of these organisms to your cladogram below human, fish, lizard, mouse. b. Label each branch of your cladogram with the proper characteristic. 8. Using the cladogram that you just completed above in number 7, clearly circle two clades. Page 3 of 5 Name: _________________________________ Period: _____________ Identifying Kingdoms of Eukarya The domain Eukarya is made up of four kingdoms: Animalia, Fungi, Plantae, and Protista. Fill in the table using the kingdoms listed above. Kingdom Mode of Nutrition Multicellular or Unicellular Cell Wall Reproduction autotrophs multicellular (photosynthesis) Cell wall (cellulose) • sexual (spores & seeds) • asexual (cuttings, tubers, etc.) heterotrophs (by ingestion) None • sexual (gametes) • some have cell wall • some have only cell membrane • mostly asexual - binary fission - budding • sometimes sexual multicellular autotrophs (photosynthesis, unicellular or chemosynthesis) multicelluar heterotrophs (predators) heterotrophs (by absorption) multicellular or Cell wall unicellular (chitin) Example mosses ferns gymnosperm angiosperm invertebrate: sponges, worms, mollusks, arthropods vertebrates: fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals Euglena, Amoeba, Paramecium, kelp • mostly sexual mushrooms - + and - strains bread mold • asexual for unicellular yeast yeast 9. Autotrophs are organisms that produce their own food (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) from simple substances present in its surroundings. (“Auto” = self; “troph” = nourish) Which kingdoms contain autotrophs? 10. Which kingdoms contain unicellular organisms? 11. To which kingdom do grizzly bears belong? 12. What do fungi and plantae have in common? 13. What do fungi and animalia have in common? 14. Which kingdoms have photosynthesizers? Page 4 of 5 Name: _________________________________ Period: _____________ Vocabulary Match the description on the right to its vocabulary word on the left by putting the corresponding letter of the description next to the correct vocabulary word. Vocabulary Word Letter Description 1. Linnaeus A. domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cells walls that do not contain peptidoglycan 2. Taxa B. a tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items based on a series of choices between alternative characters 3. Species C. study of evolutionary relationships among organisms 4. Binomial nomenclature D. domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls containing peptidoglycan 5. Domain E. devised a system of naming organisms that is still in use today F. In ____________, an organism is given a 2‐part scientific name that give the organism’s genus and species G. the smallest taxon is the ________, which is made up of organisms that similar characteristics and can breed with one another. 6. Eukarya 7. Dichotomous Key 8. Scientific Name H. evolutionary branch of a cladogram that includes a single ancestor and all its descendants 9. Bacteria I. domain that includes all organisms that have a nucleus 10. Archaea J. another name for a binomial nomenclature 11. Clade K. organisms are placed in __________, or classification groups 12. Phylogeny L. a larger, more inclusive taxonomic category than a kingdom Other Vocabulary Words Genus Order Family Kingdom Class Phylum Page 5 of 5