Properties of Matter: Solids, Liquids, and Gases
advertisement

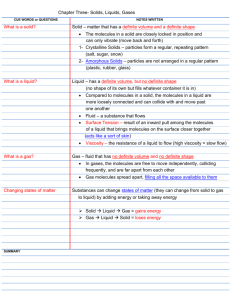
Properties of Matter Solids, Liquids, and Gases Promotion Benchmark 9 Lesson Review Student Copy Vocabulary Solid – A state or phase of matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume. Liquid – A state or phase of matter that has a definite volume but no definite shape. Gas – A state or phase of matter that has no definite shape or volume. Phase change – A change of matter from one phase to another. © County School Board of Fairfax County, VA 2005 IV – 128 Science 8 Review Review for Promotion Benchmark 9: Describes the properties of a solid, liquid and a gas; explains the effect of heating or cooling on the states of matter The matter around you is made up of moving molecules in the form of solids, liquids, and gases. The form that matter takes depends on its shape and volume. Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. The molecules in a solid are packed closely together. Although the molecules in a solid are moving, they are so close to one another that they don’t look like they are moving at all. They basically vibrate in their place. An ice cube, the table, the floor, and a metal bar are all examples of solids. A liquid has a definite volume but no definite shape. Liquid molecules are also packed closely together, but there is enough space between the molecules to allow them to slide past each other. This sliding action prevents the liquid from taking a shape of its own. As a result, liquids take the shape of the container that holds them. Some examples of liquids are water, milk, bleach, blood, and mercury (liquid metal). A gas has no definite shape and no definite volume. The molecules in a gas are spaced farther apart, and they move very rapidly. Gas molecules move to fill up the size of their container, like when you blow up a balloon. Some examples of gases are water vapor, air, carbon dioxide, ozone, and oxygen. © County School Board of Fairfax County, VA 2005 IV – 129 Science 8 Review Example: Water Molecule Solid Liquid Gas Closely packed; Barely Moving Loosely Packed; Sliding Past Free Floating; Moving Fast A phase change is a change in the state of matter from one form to another. There are four types of phase changes: melting, boiling or vaporizing, condensing, and freezing. An example of melting is when a solid changes to a liquid. When thermal energy is added to an ice cube, its molecules begin to move faster. This creates more space between the molecules and allows them to slip past each other changing the ice into water. If more thermal energy is added, the molecules in the water further increase their motion. This causes the water to boil or vaporize and turn into water vapor, a gas. Phase changes also result when thermal energy is removed from matter. When a gas such as water vapor is cooled, it condenses or changes into water, a liquid. The removal of thermal energy allows the molecules to slow their kinetic motion. As the molecules slow down, they pack more closely together and change the state of matter. Another phase change occurs when a liquid changes to a solid, or freezes. Freezing is the result © County School Board of Fairfax County, VA 2005 IV – 130 Science 8 Review of removing thermal energy from a liquid. As the molecules slow down, they pack closer together and form a solid, such as when water turns to ice. Usually, the addition or removal of thermal energy from a substance will result in a change in the average kinetic motion of the molecules, or temperature, of the substance. During a phase change, however, the thermal energy being used to change the state of matter will not cause a change in the temperature of the substance. The energy being added or removed from the system is being used to break or form the molecular bonds holding the molecules together. As a result, the temperature will remain steady, or reach a plateau, during a phase change. Solid Melting Boiling/Vaporizing Phase Change Phase Change Thermal energy added Tightly packed molecules, hardly moving Liquid Liquid Loosely packed molecules, sliding past Loosely packed molecules, sliding past Phase Change Free moving molecules, moving fast © Thermal energy taken away Gas Free moving molecules, moving fast Freezing Condensing Gas Thermal energy added Phase Change Liquid Liquid Loosely packed molecules, sliding past Loosely packed molecules, sliding past County School Board of Fairfax County, VA 2005 IV – 131 Thermal energy taken away Solid Tightly packed molecules, hardly moving Science 8 Review The Properties of Matter Solid Definition Molecules look like Liquid Definition Molecules look like (draw a picture) Phase Change © County School Board of Fairfax County, VA Gas Definition (draw a picture) Phase Change Molecules look like (draw a picture) Phase Change 2005 IV – 132 Science 8 Review Review for Promotion Benchmark 9 Directions: Match the word with the definition 1. ______ A change of matter from one phase to A. Solid 2. ______ Has no definite shape or volume B. Liquid 3. ______ A change from a liquid to a solid C. Gas 4. ______ Has a definite shape and volume D. Phase change 5. ______ A change from a solid to a liquid E. Freezing 6. ______ Has a definite volume and no definite F. Melting G. Boiling another shape 7. ______ A change from a liquid to a gas © County School Board of Fairfax County, VA 2005 IV – 133 Science 8 Review