Practice Test Ch 8 & 9 (pg 1 of 6)
advertisement
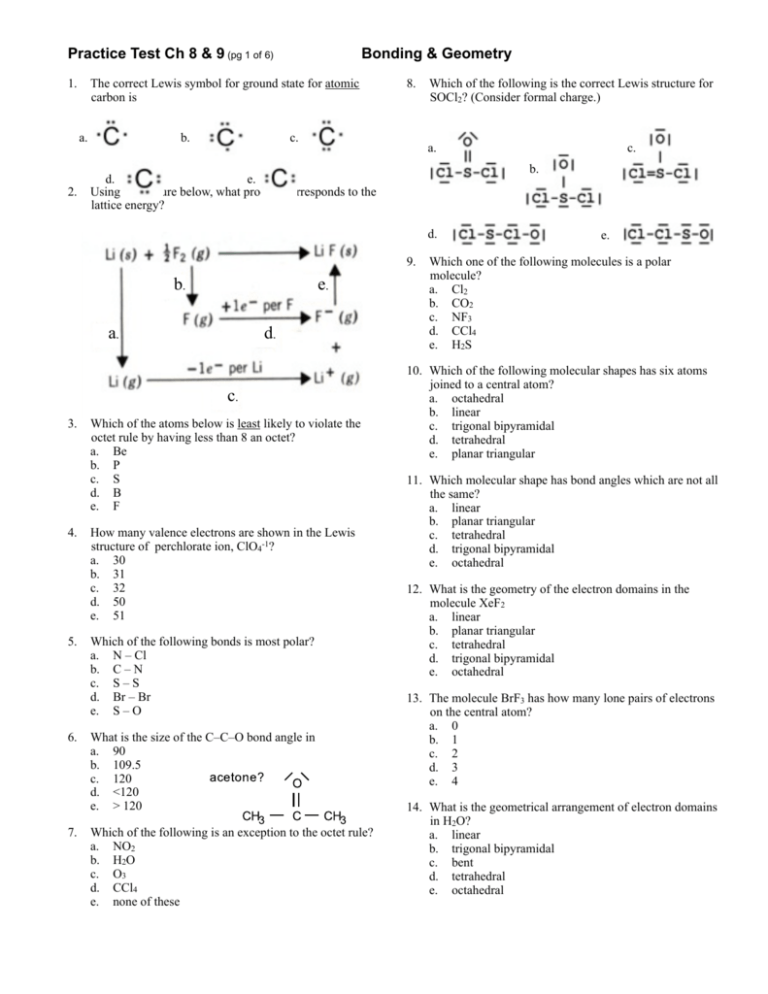
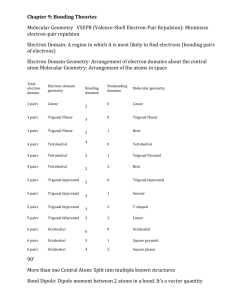
Practice Test Ch 8 & 9 (pg 1 of 6) 1. The correct Lewis symbol for ground state for atomic carbon is a. 2. Bonding & Geometry b. 8. c. Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for SOCl2? (Consider formal charge.) a. b. d. e. Using the picture below, what process corresponds to the lattice energy? d. 9. b. e. a. d. c. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Which of the atoms below is least likely to violate the octet rule by having less than 8 an octet? a. Be b. P c. S d. B e. F How many valence electrons are shown in the Lewis structure of perchlorate ion, ClO4-1? a. 30 b. 31 c. 32 d. 50 e. 51 Which of the following bonds is most polar? a. N – Cl b. C – N c. S – S d. Br – Br e. S – O What is the size of the C–C–O bond angle in a. 90 b. 109.5 c. 120 d. <120 e. > 120 Which of the following is an exception to the octet rule? a. NO2 b. H2O c. O3 d. CCl4 e. none of these c. e. Which one of the following molecules is a polar molecule? a. Cl2 b. CO2 c. NF3 d. CCl4 e. H2S 10. Which of the following molecular shapes has six atoms joined to a central atom? a. octahedral b. linear c. trigonal bipyramidal d. tetrahedral e. planar triangular 11. Which molecular shape has bond angles which are not all the same? a. linear b. planar triangular c. tetrahedral d. trigonal bipyramidal e. octahedral 12. What is the geometry of the electron domains in the molecule XeF2 a. linear b. planar triangular c. tetrahedral d. trigonal bipyramidal e. octahedral 13. The molecule BrF3 has how many lone pairs of electrons on the central atom? a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 e. 4 14. What is the geometrical arrangement of electron domains in H2O? a. linear b. trigonal bipyramidal c. bent d. tetrahedral e. octahedral Practice Test Ch 8 & 9 (pg 2 of 6) Bonding & Geometry 15. What is the shape of BrI3? a. square planar b. pyramidal c. T-shaped d. bent e. distorted tetrahedral 16. What type of hybridization is associated with a square planar molecular shape? a. sp b. sp2 c. sp3 d. sp3d e. sp3d2 17. What is the shape of the IF4-1 ion? a. square planar b. octahedral c. tetrahedral d. T-shaped e. square pyramidal 18. Which of the following is a polar species? a. CO2 b. PCl5 c. ICl2-1 d. TeCl4 e. CCl4 19. Among those listed below, which element will have the strongest tendency to form double bonds? a. Br b. B c. F d. O e. Mg 20. Which hybridization is associated with 3 domains? a. sp b. sp2 c. sp3 d. sp3d e. sp3d2 21. The molecule SF4 has how many electron domains on the central atom? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 e. 6 22. What is the hybridization of Br in BrF5? a. sp b. sp2 c. sp3 d. sp3d e. sp3d2 23. What shape for electron pairs is associated with sp3 hybridization? a. linear b. tetrahedral c. square planar d. octahedral e. trigonal planar 24. What hybridization is predicted for phosphorus in the PCl3 molecule? a. sp b. sp2 c. sp3 d. sp3d e. sp3d2 25. A double bond contains ___ sigma bond(s) and ___ pi bond(s). a. 0, 2 b. 1, 2 c. 2, 0 d. 1, 1 e. 0, 1 26. What angle exists between domains in an octahedral structure? a. 90.0° b. 120.0° c. 180.0° d. 78.5° e. 109.5° 27. Which of the following elements is most likely to display sp3d hybridization? a. oxygen b. carbon c. nitrogen d. boron e. phosphorus 28. How many sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are in a carbon dioxide molecule? a. four σ and zero π b. two σ and four π c. three σ and two π d. one σ and three π e. two σ and two π 29. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atoms in CH3OH and CO2, respectively? a. sp3, sp3 b. sp2, sp2 c. sp3, sp2 d. sp3, sp e. sp2, sp3 Practice Test Ch 8 & 9 (pg 3 of 6) Bonding & Geometry 30. All of the following species contain two π-bonds EXCEPT a. SCN-1 b. OCS c. CO d. NO -1 e. H2CCO 36. Of the following molecules, which has the largest dipole moment? a. NH3 b. CO2 c. OF2 d. H2O e. CF4 31. How many unshared pair of electrons on the central atom in the molecule, XeF2? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 37. The molecular geometry of SF4 is a. see-saw b. t-shape c. trigonal bipyramidal d. octahedral e. tetrahedron 32. Which of the following are true about BF3? i. trigonal planar ii. one unshared pair of electrons on B iii. polar molecule a. i only b. i and ii only c. i and iii only d. ii and iii only e. i, ii, and iii 33. Consider the chemical reaction below. BF3 + NH3 → BF3NH3 During this chemical reaction, the geometry around the boron atom changes from a. trigonal pyramid to tetrahedral b. trigonal planar to tetrahedral c. trigonal planar to octahedral d. trigonal pyramid to trigonal bipyramidal e. actually its geometry doesn’t change at all 34. The melting point of CaS is higher than that of KCl. Explanations for this observation include which of the following? I. II. III. IV. a. b. c. d. e. Ca+2 is more positively charged than K+1 S-2 is more negatively charged than Cl-1 The S-2 ion is smaller than the Cl-1 ion. The Ca+2 ion is smaller than the K+1 ion II only I, II, IV only III and IV only II and III only I, II, III, and IV 35. Types of hybridization exhibited by the three C atoms in propene, CH3CHCH2, include which of the following? I. sp a. b. c. d. e. I only III only I and II only II and III only I, II, and III II. sp2 III. sp3 38. In the molecule shown with the formula AF4 which element could be in position A a. S b. O c. Xe d. P e. It could be either a or b 39. In order to exhibit delocalized π bonding, a molecule must have a. at least two π bonds b. at least two resonance structures c. at least three σ bonds d. at least four atoms e. a and c are both true 40. In ozone, O3 the formal charge on the central atom is a. 0 b. +1 c. -1 d. +2 e. -2 41. The Lewis structure of HCN shows that ______ has _______ nonbonding electron pairs. a. C, 1 b. N, 1 c. H, 1 d. N, 2 e. C, 2 42. According to the VSEPR model, the progressive decrease in the bond angles in the series of molecules CH4, NH3 and H2O is best accounted for by the a. increasing strength of bonds b. decreasing size of the central atom c. increasing the electronegativity of the central atom d. increasing number of unshared pairs of electrons e. decreasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms 43. The hybridization of the carbon atom in methane, CH4 is a. sp b. sp2 c. sp3 d. sp4 e. sp3d Practice Test Ch 8 & 9 (pg 4 of 6) Bonding & Geometry For questions 44 - 51 refer to the following molecules. (You might find it useful to sketch a Lewis structure for each one.) More than one choice may be appropriate. a. CO2 b. H2O c. CH4 d. C2H4 e. PH3 f. None of the molecules above satisfy the statement. 44. The molecule whose central atom’s domains are tetrahedral. 45. The molecule(s) with only one double bond. 46. The molecule with the largest dipole moment. 47. The molecule(s) that has trigonal pyramidal geometry. 48. The molecule(s) with at least one bond angle greater than 109.5° 49. The molecule(s) that exhibits “legitimate” resonance. 50. The molecule(s) with more than one pi bond. 51. The molecule(s) with no non-bonded electron pairs. 52. The central iodine atom in ICl4-1 has _______ unshared electron pairs and ______ bonded electron pairs. a. 3, 2 b. 3, 1 c. 1, 3 d. 1, 4 e. 2, 4 53. What is the maximum number of double bonds that a single carbon atom can form? a. 4 b. 3 c. 2 d. 1 e. 0 54. How many single covalent bonds must a silicon atom form to have a complete octet of its valence electrons? a. 4 b. 3 c. 2 d. 1 e. 0 55. The bond angles around the atoms 1, 2, and 3 in the molecule below are approximately ______, _______, and _______ respectively. a. 90°, 90°, 90° b. 120°, 120°, 90° c. 120°, 120°, 109.5° d. 109.5°, 120°, 109.5° e. 109.5°, 90°, 120° 56. The hybridized orbitals around the C atom marked #2 in the structure above are a. sp b. sp2 c. sp3 d. sp3d e. sp3d2 57. Of the following, ________ can not accommodate more than an octet of electrons. a. P b. Xe c. N d. S e. I 58. A valid Lewis structure of _______ can not be drawn without violation the octet rule. a. PO4-3 b. SiF4 c. CF4 d. SeF4 e. NF3 59. The electron-domain geometry and molecular geometry of iodine trichloride are ______ and ______ respectively. a. trigonal planar, trigonal planar b. tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal c. trigonal bipyramidal, T-shaped d. octahedral, trigonal planar e. T-shaped, trigonal planar 60. If the electron domain geometry of some sulfur-centered compound is trigonal bipyramidal, then the hybridization of the central sulfur atom must be _______ a. sp b. sp2 c. sp3 d. sp3d e. sp3d2 61. There are _______ unhybridized p atomic orbitals on an sp hybridized carbon atom a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 e. 4 62. If the hybridization of orbitals on the central atom of a molecule is sp. The electron-domain geometry around this central atom must be ________ a. octahedral b. linear c. trigonal planar d. trigonal bipyramidal e. tetrahedral Practice Test Ch 8 & 9 (pg 5 of 6) Bonding & Geometry 63. The shortest F-Xe-F bond angle in the XeF4 molecule is about _______ a. 60° b. 90° c. 109.5° d. 120° e. 180° 64. When counting domains, a triple bond a. Should not be counted as a domain b. Depends on the geometry as to how many domains it should be counted as c. Should be counted as three domains d. Should be counted as two domains due to the 2 π bonds e. Should be counted as only one domain 66. The electron-domain geometry and the molecular geometry of a molecule of the general formula ABx will be the same if a. there are no unshared electron pairs on the central atom b. there is more than one central atom c. x is greater than 4 d. x is less than 4 e. the octet rule is obeyed 67. Of the molecules below, only ______ is nonpolar. a. BF3 b. NF3 c. IF3 d. PF3 e. BrF3 68. The molecular geometry of the H3O+1 ion is ______ a. linear b. tetrahedral c. bent d. trigonal pyramidal e. trigonal planar 65. A _______ covalent bond is the longest a. single b. double c. triple d. they are all the same length e. nonpolar 69. Draw the Lewis structure for carbonate: CO3-2. a. What is the shape of the electron domains around the central carbon? b. What is the shape of the carbonate ion? c. What are the bond angles in carbonate? d. Does the carbonate ion exhibit resonance? e. Does delocalization occur? What does this term mean? f. Comment on the bond lengths in carbonate. 70. Bond enthalpy values can be used to calculate and estimation for ∆Hrx when the ∆Hf° values are not available for all the compounds in the reaction. Use bond enthalpy values from the back of your ∆Hf tables to calculate the ∆Hrx for the reaction below. Do your work in the space below. Circle your final answer. Be sure and label it appropriately. H2CNH + H2O → CH2O + NH3 Practice Test Ch 8 & 9 (pg 6 of 6) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 69. 70. Bonding & Geometry ANSWERS a 18. d 35. d 52. e e 19. d 36. d 53. c e 20. b 37. a 54. a c 21. d 38. a 55. d a 22. e 39. b 56. b e 23. e 40. b 57. c a 24. c 41. b 58. d a 25. d 42. d 59. c c 26. a 43. c 60. d a 27. e 44. 61. c d 28. e 45. 62. b d 29. c 46. 63. b c 30. d 47. 64. e d 31. c 48. 65. a c 32. b 49. 66. a e 33. a 50. 67. a a 34. b 51. 68. d Carbonate ion a. trigonal planar b. trigonal planar c. 120º d. yes, the double bond can be in any of the three possible locations e. yes, the electrons are delocalizes across all three bonds. f. the bond lengths will all be the same, somewhere between single and double length (closer to single) ∆H = -40 kJ • Drawing the Lewis structures will show a bond inventory will show • Bonds breaking: 1*C=N (615), 2*O-H (463), 1*N-H(391), 2*C-H(413) • Bonds forming: 1*C=O (799), 3*N-H (391), 2*C-H(413) • Note that you can cancel out 1*N-H and 2*C-H from breaking and forming for the net result of -40