Name the structures that make up the lumbo-pelvic
advertisement
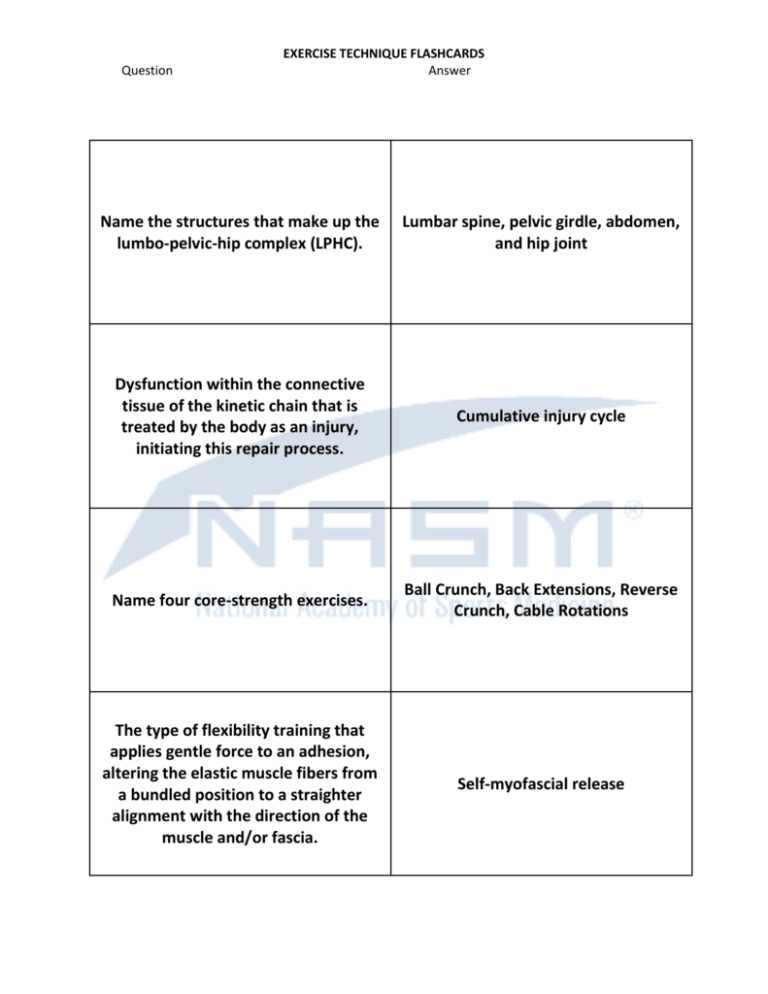
Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Name the structures that make up the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex (LPHC). Lumbar spine, pelvic girdle, abdomen, and hip joint Dysfunction within the connective tissue of the kinetic chain that is treated by the body as an injury, initiating this repair process. Cumulative injury cycle Name four core-strength exercises. Ball Crunch, Back Extensions, Reverse Crunch, Cable Rotations The type of flexibility training that applies gentle force to an adhesion, altering the elastic muscle fibers from a bundled position to a straighter alignment with the direction of the muscle and/or fascia. Self-myofascial release Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Exercises in the core-stabilization level are identified through these characteristics. They involve little motion through the spine and pelvis What are four common ways a stressor causes breakdown or injury? Stress fractures, muscle strains, joint pain, emotional fatigue Name four core-stabilization exercises. Marching, Floor Bridge, Floor Prone Cobra, Prone Iso-abs Law stating that soft tissue models along the lines of stress. Davis's law Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Referred to as a co-contraction of global muscles, such as the rectus abdominis, external obliques, and quadratus lumborum. Bracing It is critical that the core training program is designed to achieve these three functional outcomes in the right order. 1. Intervertebral stability, 2. Lumbopelvic stability, 3. Movement efficiency What are the proper backside mechanics during sprinting? Ankle plantar flexion, knee extension, hip extension, and neutral pelvis What are the proper frontside mechanics during sprinting? Ankle dorsiflexion, knee flexion, hip flexion, and neutral pelvis Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer The ability to accelerate, decelerate, stabilize, and change direction quickly, while maintaining proper posture. Agility The ability to react and change body position with maximum rate for force production, in all planes of motion and from all body positions, during functional activities. Quickness The ability to move the body in one intended direction as fast as possible. Speed Name four core-power exercises. Rotation Chest Pass, Ball Medicine Pullover Throw, Front Medicine Ball Oblique Throw, Soccer Throw Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer The ability of the body to produce high levels of force for prolonged periods of time. Muscular endurance What is a component of core-power exercises that make them easy to identify? Explosive movements with medicine balls Name five balance-stabilization exercises. Single-leg Balance, Single-leg Balance Reach, Single-leg Hip Internal and External Rotation, Single-leg Lift and Chop, Single-leg Throw and Catch Name five balance-strength exercises. Single-leg Squat, Single-leg Squat Touchdown, Single-leg Romanian Deadlift, Step-up to Balance, Multiplanar Lunge to Balance Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Name three balance-power exercises. Multiplanar Hop with Stabilization, Multiplanar Single-leg Box Hop-up with Stabilization, Multiplanar Single-leg Box Hop-down with Stabilization What are four plyometric-stabilization exercises? Squat Jump with Stabilization, Box Jump-up with Stabilization, Box Jumpdown with Stabilization, Multiplanar Jump with Stabilization Name four plyometric-strength exercises. Squat Jump, Tuck Jump, Butt Kick, Power Step-up Name three plyometric-power exercises. Ice Skater, Single-leg Power Step-up, Proprioceptive Plyometrics Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Exercises that use quick powerful movements involving an eccentric action immediately followed by an explosive concentric contraction. Plyometric training Body position progressions in balance training. Two-leg stable, single-leg stable, twolegs unstable, single-leg Give examples of chest exercises used in the Stabilization Level of the OPT model. Ball Dumbbell Chest Press, Push-up, Ball Push-up: hands on the ball, Standing Cable Chest Press What are the two techniques used in corrective flexibility according to the integrated flexibility continuum? SMR (self-myofascial release) and static stretching Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Give examples of total-body power exercises Two-arm Push Press, Barbell Clean, Dumbbell Snatch, Squat Thrust, Kettlebell Hang, Clean and Jerk What is the minimum amount of time static stretches should be held? 30 seconds Name two different leg-stabilization exercises. Ball Squat and Multiplanar Step-up to Balance What are three things that a client should have established prior to incorporating a dynamic stretching program? Good levels of tissue extensibility, core stability, and balance capabilities Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Name two strength level exercises for the legs. Leg Press and Barbell Squat Name two power level exercises for the legs. Squat Jump and Tuck Jump Give three examples of shoulderpower exercises. Front Medicine Ball Oblique Throw, Overhead Medicine Ball Throw, Speed Tubing Shoulder Press Give examples of total-body strength exercises. Lunge to Two-arm Dumbbell Press; Squat, Curl, to Two-arm Press; Step-up to Overhead Press: sagittal plane; Romanian Deadlift, Shrug to Calf Raise Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Based on the exercise selection continuum what exercises should be selected for the adaptation of stabilization? Total-body, multi-joint or single joint, controlled unstable Give four examples of corestabilization exercises. Marching, Floor Bridge, Floor Prone Cobra, Prone Iso-abs Give four examples of core-strength exercises. Ball Crunches, Back Extensions, Reverse Crunches, Cable Rotations Body position progressions used for balance training. 1. Two-leg stable 2. Single-leg stable 3. Two-legs unstable 4. Single-leg unstable Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Three types of core systems. Local stabilization system, Global stabilization system, Movement system What is the minimum duration pressure should be sustained on adhesions while performing selfmyofascial release? 30 seconds What are the seven methods for prescribing exercise intensity? Peak VO2, VO2 reserve, Peak metabolic equivalent (MET), Peak maximal heart rate, Heart rate reserve, Rating of perceived exertion, Talk test The cumulative sensory input to the central nervous system from all mechanoreceptors that sense position and limb movements. Proprioception Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer What are the acute variables for static stretching? 1-2 sets, hold each stretch for 30 seconds What is the mechanism of action that occurs in active-isolated stretching? Reciprocal inhibition When is the appropriate time to utilize dynamic stretching? After self-myofascial release when training in Phase 5 How long should the cardiorespiratory portion of the warm-up last? 5-10 minutes Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer What does F.I.T.T.E. stand for? Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type, Enjoyment Example of a Zone 1 cardiorespiratory activity and intensity level. Walking or jogging at 65-75% of maximal heart rate Example of a Zone 2 cardiorespiratory activity and intensity level. Group exercise classes or spinning at 76-85% of maximal heart rate Example of a Zone 3 cardiorespiratory activity and intensity level. Sprinting at 86-95% of maximal heart rate Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Type of training that has been found to be just as beneficial as traditional forms of cardiorespiratory training. Circuit training Name the structures that make up the core. Lumbo-pelvic-hip complex, pelvic girdle, abdomen, and hip joint Name the five muscles of the Local Stabilization System of the core. Transverse abdominis, internal oblique, lumbar multifidus, pelvic floor muscles, diaphragm Name the four muscles of the movement system of the core. Latissimus dorsi, hip flexors, hamstring complex, quadriceps Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer The normal extensibility of all soft tissues that allows the full range of motion of a joint. Flexibility The tendency of the body to seek the path of least resistance during functional movement patterns. Relative flexibility What are the benefits of a warm-up? Increased heart rate and respiratory rate, increased tissue temperature, and increased psychological preparation for bouts of exercise. The concept of muscle inhibition, caused by a tight agonist, which inhibits its functional antagonist. Altered reciprocal inhibition Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer The principle that states the body will adapt to the specific demands that are SAID Principle or Principle of Specificity placed on it. What does the acronym SAID in SAID Principle stand for? Specific Adaptation to Imposed Demands What kinetic chain deviations must a certified personal trainer watch for in the cardiorespiratory portion of the workout for clients who possess rounded shoulders? On steppers and treadmills watch for the grasping of the handles; on stationary bikes, treadmills and elliptical trainers watch for rounding of the shoulders. Feedback used after the completion of a movement to help inform clients about the outcome of their performance. Knowledge of results Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Feedback that provides information about the quality of the movement during exercise. Knowledge of performance The type of specificity that refers to the weight and movements placed on the body. Mechanical specificity The state where there is an elevation of the body's metabolism after exercise. Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) The three stages in the General Adaptation Syndrome. Alarm reaction, resistance development, exhaustion Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Four performance adaptive benefits from resistance training. Increased strength, increased power, increased endurance, increased neuromuscular control SAQ training can be used with what three nonathletic populations? Youth, weight-loss clients, seniors What is the drawing-in Maneuver? A maneuver that is used to recruit the local core stabilizers by drawing the naval towards the spine. Benefits of a cool-down include the following: Reduced heart rate and breathing rates, gradually cools body temperature, returns muscles to their optimal length-tension relationships, prevents venous pooling of blood in lower extremities, restores physiological systems close to baseline Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Give examples of total-body stabilization exercises. Single-leg Squat Touchdown, Curl, to Overhead Press; Single-leg Romanian Deadlift, Curl, to Overhead Press; Single-leg Squat to Row; Ball Squat, Curl, to Press; Multiplanar Step-up Balance, Curl, to Overhead Press Give examples of chest exercises used in the Strength Level of the OPT model. Incline Dumbbell Chest Press; Incline Barbell Bench Press; Flat Dumbbell Chest Press; Barbell Bench Press Give examples of chest exercises used in the Power Level of the OPT model. Two-arm Medicine Ball Chest Pass; Rotation Chest Pass; Speed Tubing Chest Press; Plyometric Push-up Give examples of back exercises used in the Stabilization Level of the OPT model. Single-leg Pull-down; Ball Cobra; Standing Cable Row; Ball Dumbbell Row Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Seated Cable Row; Seated Lat PullGive examples of back exercises used down; Straight-arm Pull-down; Pull-up; in the Strength Level of the OPT model. Supported Dumbbell Row Give examples of shoulder exercises used in the Stabilization Level of training. Single-leg Overhead Press; Single-leg Dumbbell Scaption; Seated Stability Ball Military Press The main goal of balance training is to continually increase the client's awareness of their limit of stability by creating______________. controlled instability Surface types for proprioceptive progressions during balance include. Floor, sport beam, half foam roll, foam pad, balance disk, wobble board, BOSU ball Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Exercises that use quick, powerful movements involving an eccentric action immediately followed by an explosive concentric contraction. Plyometric training Efficient movement requires eccentric force reduction, isometric stabilization, and concentric force production. Integrated performance paradigm The ability of the neuromuscular system to produce internal tension to overcome an external load. Strength What are six ways to progress plyometric exercises? Easy to hard, simple to complex, known to unknown, stable to unstable, body weight to loaded, activity-specific Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer Describe the five kinetic chain checkpoints? Feet: shoulder-width apart, pointing straight ahead; Knees: in line with the second and third toes; Hips: level with lumbar spine in a neutral position; Shoulders: depressed and slightly retracted; and Head: cervical spine in a neutral position What is dynamic balance? Dynamic balance is the ability to move and change directions under various conditions without falling What are the three phases of a plyometric exercise? Eccentric phase, amortization phase, concentric phase What is the proper progression for balance training when utilizing the proprioceptive continuum? Floor, balance beam, half foam roll, foam pad, balance disk Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer The ability of muscles to exert maximal force output in a minimal amount of time. Rate of force production The position of the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex during running movements. A slight forward lean with neutral spine What happens during the eccentric phase of a plyometric exercise Increase in muscle spindle activity by pre stretching the muscle before activation Research has demonstrated increased electromyogram activity and pelvic stabilization when this maneuver is performed. Drawing-in maneuver Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer What is delayed-onset muscle soreness? Pain or discomfort often felt 24 to 72 hours after intense exercise or unaccustomed physical activity. What is the proper way to progress an exercise in the stabilization level of training? Increase proprioceptive demand Give eight reasons for the incorporation of flexibility training. Correct muscle imbalances, increase joint range of motion, decrease excess tension of muscles, relieve joint stress, improve extensibility of musculotendinous junction, maintain normal functional length of muscles, improve neuromuscular efficiency, improve function Consistently repeating the same pattern of motion, which may place abnormal stresses on the body. Pattern overload Question EXERCISE TECHNIQUE FLASHCARDS Answer What are the three phases of the integrated flexibility continuum? Corrective flexibility, active flexibility, functional flexibility The type of flexibility designed to improve extensibility of soft tissue and increase neuromuscular efficiency by using reciprocal inhibition. Active flexibility During which phase of the general adaptation syndrome do stress fractures, muscle strains, joint pain and emotional fatigue occur? Exhaustion phase The stretching technique that focuses on the neural system and fascial system of the body by applying gentle force to an adhesion Self-myofascial release








