Endocrine System
advertisement

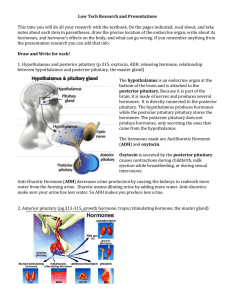
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 26 The Endocrine System • Specialized glands throughout the body • Help maintain homeostasis – Secrete hormones into blood • Slow acting • Long living • Act on target cells – Signaling molecules Controlling Secretion Negative Feedback Positive Feedback Categories of Hormones • Amino acid based – – – – Chains of AA’s Not membrane soluble (hydrophilic) e.g. oxytocin, insulin, and prolactin e.g. epinephrine, norepinephrine, and thyroxine – Derived from AA tryptophan and tyrosine • Steroids – Lipids made from cholesterol – Right through membrane (hydrophobic) – e.g. testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol Amino Acid Action • Dissolve in blood • Binds to plasma membrane (1) • Intracellular events (2) – Change permeability of ion channels – Change 2nd messenger system – Activate translation genes • Change physiology or behavior (3) – Rapid because all chemicals present Steroid Action • • • • Carriers in the blood Binds in cytoplasm or nucleus (2) Turns on genes (3) Synthesizes proteins (4) change physiology or behavior – Slower because chemicals need to be made Endocrine Glands • Pituitary gland – Posterior • Vasopressin (ADH) • Oxytocin – Anterior • Growth hormone (GH) • Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) • Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) • Lutenizing hormone (LH) • Prolactin (PRL) • Hypothalamus – Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) • Thyroid gland – Thyroid hormones • Adrenal glands – – – – Corticosteroids Glucocorticoids Sex steroids Epinephrine/norepineprine • Pancreas – Glucagon • Gonads – Sex steroids Pituitary Gland • Connected to hypothalamus • Bipartate structure – Posterior lobe • Neurosecretory cells signal exocytic release of hormones – Anterior • Hormone release to portal system Posterior Lobe • Hypothalamic storage • Neurohormone release – Oxytocin • Milk letdown • Childbirth contractions • Pair bonding/monogamy (voles) – Vasopressin • Water balance and loss • Alcohol and urination connection Anterior Lobe • Hypothalamic control • Blood portal system – Releasing or inhibiting hormones • Hormones released – Signal endocrine or nonendocrine glands Growth Hormone • Multiple target cells • Regulates body growth – Hypersecretion: gigantism or acromegaly – Hyposecretion: pituitary dwarfism • Artificial HGH can counter in youth • Artificially created in bacteria – Abused by athletes – Meat production and organic foods Thyroid Stimulating Hormone • Stimulates T3 and T4 from thyroid • Same effects, different targets • Most processes in body • Controls metabolism – Hyperthyroidism, Graves’ disease – Hypothyroidism, goiter • Growth and physical development – Cretinism • Metamorphosis in amphibians Grave’s Disease Adrenal Glands • Bipartite structure – Stress responses – Some level for glucose breakdown • Peaks in morning • Adrenal cortex – Long-term stress responses • Mineralcorticoids – Mineral and water balance • Glucocorticoids (cortisol) – Stress response • Sex steroids – Small amounts – Adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulates • Adrenal medulla – Short-term stress responses • Epinephrine • Norepinephrine – Hypothalamic neural signal Gonads • LH and FSH stimulate – Produce sex steroids – Cross BBB easily • Influence brain activation and organization • 3 hormone types in both sexes, but ratios vary – Estrogens (estradiol) • • • • Maintain female system Development of 2° sex characteristics Derived from androgens Masculinize male brain in early development – Progestins • Prepare and maintain uterus • Breast development • Can be converted to testosterone – Androgens (testosterone) • Maintain and stimulate development of male system • Development of 2° sex characteristics • 7th week level determines sex Pancreas • No hypothalamic or pituitary control • Produces insulin and glucagon – Manage energy supply by regulating blood glucose – Antagonistic hormones – Islets of Langerhans • Beta and alpha cells Diabetes Mellitus • Cells can’t absorb glucose from blood – Insufficient insulin or cells unresponsive • Cells burning fats and proteins • Excess absorbed by digestive system = [glucose] in urine is high • Treatments, but no cure – Genetic engineering produces synthetic insulin – W/o causes blindness, dehydration, kidney and cardiovascular disease • Type 1 (insulin dependent) – Autoimmune disease – WBC’s attack beta cells • Type 2 (non-insulin dependent) – Older onset – Obesity is common • Gestational diabetes – Can effect any pregnant woman Prolactin • Humans – Mammary gland growth – Milk production – Control egg release evolutionary adaptation? • Birds – Nest building behavior (male and female) – Regulates fat metabolism and reproduction • Amphibians – Movement to water to breed – Metamorphosis • Fish – Regulate salt and water balance when environments change