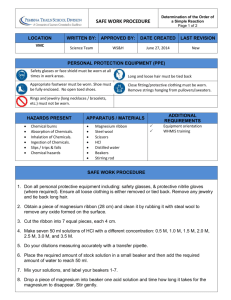
Chemistry Lab report 6
advertisement

Chemistry Lab report 7
DCP1=1,DCP2=1,DCP3=0
CE1=0,CE2=1,CE3=1
Effect of concentration on Rate of a
Chemical Reaction
Yumi Nakayama
2009 Mar 14
Subject Teacher: Helen Xu
1
Aim:
To use a simple reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid to discover concentration
which determines how fast chemical reactions occur.
Variables:
Independent Variable: Concentration of hydrochloric acid (%)
Dependent Variable: Time taken for magnesium ribbon to disappear (sec)
Controlled Variable: Length of magnesium ribbon (1cm)
Total volume of mixture of HCl and water (10ml)
Temperature of solution (room temperature, 20℃)
Materials:
Apparatus:
1. Test tube
2. Cylinder (10±0.1ml)
3. Stopwatch (±0.01sec)
4. Pipette
5. Ruler
6. Glass rod
Chemicals:
1. HCl
2. Mg ribbon
3. Distilled water
Procedure: referred to the first page of instruction paper
Data collection:
Qualitative Data:
When a 1cm magnesium ribbon is put into the mixture of HCl and water, it started to produce
small bubbles from its surface and gradually became smaller uniformly. It fizzled around the
surface of water, and dissolved into the solution. After the reaction has taken place, the test
tube became warmer.
2
Quantitative Data:
Table 1:
Individual student raw data showing the relationship between the concentration of HCl and the
time taken for 1cm of magnesium ribbon to disappear. The total volume of the solvent is 10ml
(±0.1ml), and the time is measured by stopwatch (±0.01sec).
Concentration of HCl (%) (±1%)
100
80
60
40
20
Volume of HCl (ml) (±0.1ml)
10
8
6
4
2
Volume of water (ml) (±0.1ml)
0
2
4
6
8
Time taken (sec) (±0.01sec)
28
58
75
138
1042
Data presentation:
Graph 1:
Graph showing the relationship between the concentration of HCl (%) and the time taken for
1cm magnesium ribbon to disappear (sec). The graph is based on Table 1.
Time taken for a magnesium to
disappeare (sec)
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
120%
C oncentration of H C l (%)
3
Equation of line calculated by computer program MS EXCEL:
y = 27.986x(-2.1253)
Balanced Equation of reaction between Mg and HCl:
Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
Conclusion:
From Data Collection and Data processing, it can be concluded that as the concentration of
HCl increases, the time taken for magnesium ribbon to disappear decreases. This is because
increase in HCl concentration allows more chances for magnesium to react with HCl. Because
water does not react with Mg, increase in volume of water increases the time taken for
magnesium to disappear, and thus slowers the rate of reaction.
The average rate of reaction can be calculated:
(28-1024) / (100-20) = -12.45
Because it is “how fast,” so the value should be positive 12.45
Calculation of uncertainty:
28-1024: 0.01+0.01=0.02sec
100-20:
1+1 = 2%
(28-1024) / (100-20): { (0.02 / 996) + (2 / 80) }x12.45 = 0.31
Thus, the average rate of reaction is 12.45±0.31
sec/ %
4
Evaluation:
Limitation of the experiment:
・The thickness of Mg ribbon is not controlled
The thickness of Mg ribbon, and thus the volume (for volume is calculated by area
multiplied by height), is not controlled in the experiment. Even though the length of the ribbon
is controlled, there is still a slight difference in thickness.
・Determination of when Mg has disappeared in the solution
Because whether Mg ribbon has disappeared is determined by merely watching it, the time
measured is not accurate regardless of small uncertainty of stopwatch. It is difficult to see
whether Mg ribbon is still left in the solution because of rapid bubbles.
Weakness of the experiment:
・Unreliability of data due to the small number of trials
Because experiment is only conducted once for each different concentration, the data are not
reliable. Because the slight change in volume of HCl affects the rate of reaction, the
experiment should be repeated
Improvement of the experiment:
・Control Mg ribbon by mass
Because length of ribbon is not controlled due to the difference in thickness, controlling by
mass will be much more accurate.
・Repeat the experiment
To increase the accuracy of the data, experiment should be repeated.
・Use watch glass instead of test tube
Because it was difficult to determine when Mg ribbon has disappeared in the test tubes, it is
better to use watch glass.
5