Pre Lab Questions for Enzyme Lab This must be completed before
advertisement

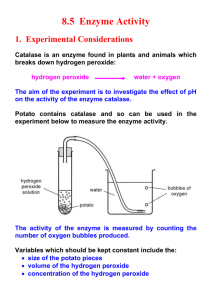
Pre Lab Questions for Enzyme Lab This must be completed before you are allowed to do your lab. 1. Define a catalyst. 2. What is the name of the biological catalyst? 3. Explain what would happen if you put the hydrogen peroxide in a clear tightly capped bottle. 4. Define substrate. 5. How are enzymes like a lock and key? 6. Based on what know about enzyme names, what is the name of the enzyme that breaks down a lipid? _____________________________________ 7. There will be a bottle labeled MnO2. What is in this bottle? 8. What is the independent variable in this lab? _________________________________________ 9. What is your dependent variable?_______________________________________________ 10. Create a question that you will test. 11. Write an if..then hypothesis. 12. On a sheet of paper, create the data table below. Substance Speed of Reaction Bubbles Test Tube Temp The list of substances are in the materials section and they are *. Make this neat and use a ruler since you will need it for your lab report. You are ready for the lab!! _____________________________________________________________________________________ Background: Enzymes are some of the most important kinds of molecules found in living cells. Cells could not function without enzymes. They speed up chemical reactions of the cells. In other words, enzymes act as catalysts. All enzymes are made of proteins; therefore they are often called protein catalysts. To understand how enzymes work, you will be observing some simple chemical reactions with hydrogen peroxide. You may have hydrogen peroxide in your medicine cabinet at home. It is commonly used as a bleaching disinfecting agent. Hydrogen peroxide is the chemical formula, H2O2. Notice the similarity between the formula and the formula for water, H2O. Hydrogen peroxide is unstable, which turns into water by the following reaction: 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 Hydrogen peroxide is stored in a brown bottle to keep out light because light speeds up this reaction. Certain chemicals can drastically increase the speed at which this reaction takes place. In this lab, you will work with some of them. HOW ENZYMES WORK: For each type of chemical reaction that occurs in the cell there is specific enzyme. This relationship is just like a key only works with one lock. An enzyme only works with one substrate. The chemical upon which the enzyme acts in the reaction is called a substrate. The product is made by the reaction of the substrates. General Equation for a catalyzed reaction: Enzyme names Biologists usually give an enzyme a name that ends in –ase. The first part of the enzyme name occurs from the substrate upon which the enzyme acts. For example, the enzyme that breaks down the substrate sucrose is called sucrase. The naming system is useful to remember, but it does not always hold true. The enzyme in living organisms that acts upon the substrate hydrogen peroxide may properly be called hydrogen peroxidase, but it is usually called catalase. Hydrogen peroxide formation and breakdown Hydrogen peroxide in plants and animals occurs as a waste product of cellular respiration, the process by which cells obtain energy from food. Water is usually formed at the end of this process. However, hydrogen peroxide is sometimes formed instead. When this happens, catalase immediately breaks down the hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water. Purpose: What effect will each substance have on the breaking down of hydrogen peroxide? Materials *Potato *Raw Liver Hydrogen Peroxide *Spinach Leaf *Chalk *Cooked Liver *Manganese Dioxide Test Tubes *Raw liver soaked in bleach *Test tube with hydrogen peroxide only Procedure: 1. Place each substance in a test tube. You will have one test tube that does not have a substance. 2. Add about 3 ml of hydrogen peroxide each of the8 test tubes. 3. Record your observations in the table. 4. For cleanup, all solid materials need to be put in the garbage. Wash out the test tubes and place them upside down in the test tube rack. Lab Report requirements I. Title II. Introduction Discuss the concepts of enzymes, lock and key, substrates, and factors that affect enzymes. Last statement is the purpose. You should not summarize your lab. III. Hypothesis IV. Identification of variables (See your lab report format for these. You will need to list all of the components. You need to list 4 controlled variables.) IV. Procedure-copy the materials and procedure V. Data Table VI. Analysis Questions VII. Conclusion ANALYSIS QUESTIONS FOR LAB REPORT-write in complete sentences. 1. What was the most vigorous reaction? What was the least vigorous reaction? 2. Did the reaction that was the most vigorous (look at #1) have more or less enzymes than the reactions that were slower? Explain your reasoning. Make sure to discuss how you can tell the reaction is less. 3. What was the difference between raw liver, liver in bleach, and cooked liver? Explain why you saw this. 4. What are the 2 products that hydrogen peroxide breaks down into? Which one caused the bubbling? 5. Which enzyme acts on the hydrogen peroxide in living organisms? 6. Would this enzyme work on another chemical other than hydrogen peroxide? Why or why not? 7. What was the substrate in this lab? 8. Is manganese dioxide an enzyme, substrate, or a catalyst? Explain your answer. 9. For the raw liver and manganese dioxide reactions, think back to the reaction and your observations. What type of reaction did you see? Explain your reasoning. Look back to your notes about the 2 TYPES of reactions. 10. What is a similarity between an enzyme and catalyst? What is the difference between an enzyme and catalyst? Conclusion a. What was your problem and hypothesis? Did you prove or disprove it? Explain your data. b. How does this lab connect to the information about enzymes? In your explanation, discuss what was the enzyme in the lab, what was the substrate, and how different factors affect how enzymes work. Your explanation should address each substance and why you saw the reaction for each substance. The lock and key model should be discussed in this section. c. Name another experiment you would like to do with enzymes. Tell me why you would do this. d. Name two things you learned in the lab. e. Name 3 ways to improve the lab. Make sure to explain your improvements in order to get full credit.