These are some of the people, places and things you need to know
advertisement

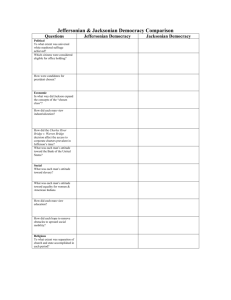
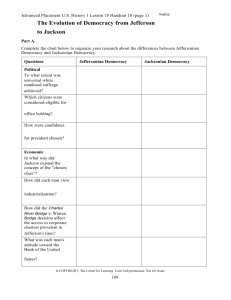
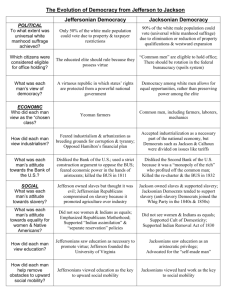
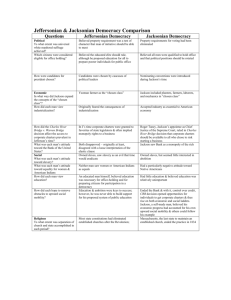
Unit Overview: Age of Jefferson, Era of Good Feelings, Age of Jackson Chapters 8, 9, 10, 11, & 12 These are some of the people, places and things you need to know by the end of the unit. Do not rely solely on the list below. Naturalization Act Alien & Sedition Acts Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions Doctrine of Nullification Age of Jefferson “Revolution of 1800” Twelfth Amendment Louisiana Purchase Lewis and Clark Expedition Wilkinson - Burr Conspiracy Barbary Pirates Chesapeake and Leopard incident Embargo Act of 1807 Non-Intercourse Act Macon’s Bill No. 2 (1810) War of 1812 Warhawks Henry Clay Tecumseh and Battle of Tippecanoe William Henry Harrison Battle of Lake Erie Burning of Washington Fort McHenry and Francis Scott Key Battle of New Orleans Andrew Jackson Era of Good Feeling Hartford Convention Judiciary Act of 1801 John Marshall Marbury v. Madison judicial review McCulloch v. Maryland Gibbons v. Ogden Fletcher v. Peck Dartmouth College v. Woodward Tallmadge Amendment Missouri Compromise Rush-Bagot Treaty Adams-Onis (Transcontinental) Treaty Second Bank of the U.S. Panic of 1819 Second Great Awakening Jacksonian Democracy Election of 1824 Corrupt Bargain Election of 1828 Extension of franchise Spoils System National Republicans Caucus System National Nominating Conventions Kitchen cabinet Peggy Eaton affair Whigs Maysville Road Veto Election of 1832 John C. Calhoun Tariff of Abominations Nullification Daniel Webster Webster-Hayne Debate SC Exposition and Protest Jefferson Day dinner Compromise Tariff of 1833 Force Bill Martin Van Buren Henry Clay Nicholas Biddle Second Bank of the U.S Bank Recharter Bill Veto Message Pet Banks Roger B. Taney Indian Removal Act of 1830 Black Hawk War Worcester v. Georgia Trail of Tears Log Cabin Campaign of 1840 Webster-Ashburton Treaty Nativism Know Nothing Party The Economic Revolution Samuel Slater Francis Cabot Lowell Waltham Plan Lowell, Massachusetts Eli Whitney Cotton Gin Interchangeable Parts National Trades Union Working Men’s Parties Commonwealth v. Hunt National Road Erie Canal Robert Fulton Transportation Revolution Samuel F.B. Morse Henry Clay’s American System Specie Circular Panic of 1837 Intellectual Movements Transcendentalism Romanticism Ralph Waldo Emerson Henry David Thoreau, “On Civil Disobedience” Margaret Fuller Louisa May Alcott James Fenimore Cooper, The Last of the Mohicans Herman Melville, Moby Dick Nathaniel Hawthorne, The Scarlet Letter Brook Farm Edgar Allan Poe Washington Irving Henry Wadsworth Longfellow Walt Whitman, Leaves of Grass Alexis de Tocqueville, Democracy in America Lyceum Movement Hudson River school of art Religious Movements Charles G. Finney The Second Great Awakening “The burned-over district” Mormons or Church of Latter-Day Saints Joseph Smith The Book of Mormon Brigham Young Utah Brook Farm New Harmony Robert Owen John Humphrey Noyes Oneida Community Mother Ann Lee Stanley Shakers Unitarian Church African Methodist Episcopal Church Unit Overview: Age of Jefferson, Era of Good Feelings, Age of Jackson Chapters 8, 9, 10, 11, & 12 Reform Movements Republican Mothers “Cult of Domesticity” Dorothea Dix Treatment of the Insane Horace Mann Noah Webster The McGuffey Reader American Temperance Movement Lucretia Mott Elizabeth Cady Stanton Seneca Falls Convention Declaration of Sentiments Susan B. Anthony Prison Reform Movement How did the division between the parties deepen during Adams’ presidency? How close did we come to war with France during Adams’ presidency? What was the meaning of the election of 1800? What is truly a ‘revolution’ as Jefferson said? How did Jefferson continue or alter Federalist policies? What was the impact of Jefferson’s decision to purchase the Louisiana Territory? What were foreign policy questions during Jefferson’s presidency? How did he work to avoid war? Was he effective? What were the issues that led us to war in 1812? What was the impact of the War of 1812? What led to the collapse of the Federalist Party? What were the foreign policy accomplishments of the Monroe administration? Was it truly an Era of Good Feelings? Were there underlying tensions? What divisions existed between the North and South in this time? How did society become more democratic in this period? The Jackson Presidency How was democracy broadened during this period? Who benefited and who didn’t? Was this truly the ‘Age of the Common Man?’ Why or why not? To what extent did Jacksonian Democracy reflect the social and economic developments in the nation? What were the crises during this period? How were each resolved? How did Jackson extend the power of the presidency? What signs are there of developing sectionalism during this period? What was the status of minorities during this period? Compare and contrast Jacksonian Democracy and Jeffersonian Democracy. What issues divided the Whigs and Democrats? Slavery and Abolition American Colonization Society Liberia Eli Whitney and Cotton Gin Gabriel Prosser Denmark Vesey Gag Rule John Quincy Adams William Lloyd Garrison The Liberator American Antislavery Society Angelina and Sarah Grimke Nat Turner’s Rebellion David Walker An Appeal to Colored Citizens of the World Sojourner Truth Box Brown Frederick Douglass Underground Railroad Economic Changes in the Jacksonian Era What elements contributed to the economic growth of the U.S. during this period? What were the reasons for increased urbanization during this period? What were the changes that resulted from that expansion? What was the impact of economic change and urbanization during the first half of the 19th century on the family and the role of women? What was the impact of increased immigration on American society and politics? What technological advances were made in this period and how did those advances alter American society? How and why did the life of the working class change in this period? What effect did the revolution in transportation have on American society, economics, and politics? Did the changes in transportation increase or decrease sectionalism? The Age of Reform How did the philosophy of the Transcendentalists encourage What is similar and different in the various religious movements people to reform their own society? of the time? What accounts for the increasing interest in To what extent did religious and reform movements of the religious experiences and expression? period extend democratic ideals? Compare and contrast the First and Second Great Awakenings. How did these early 19th century reform movements for What kinds of institutions and cultural developments established abolition and women’s rights illustrate strengths and a national identity? weaknesses of democracy in America? To what extent did a truly American culture develop in this period?