The Asch Phenomenon and Consumer Behavior
advertisement
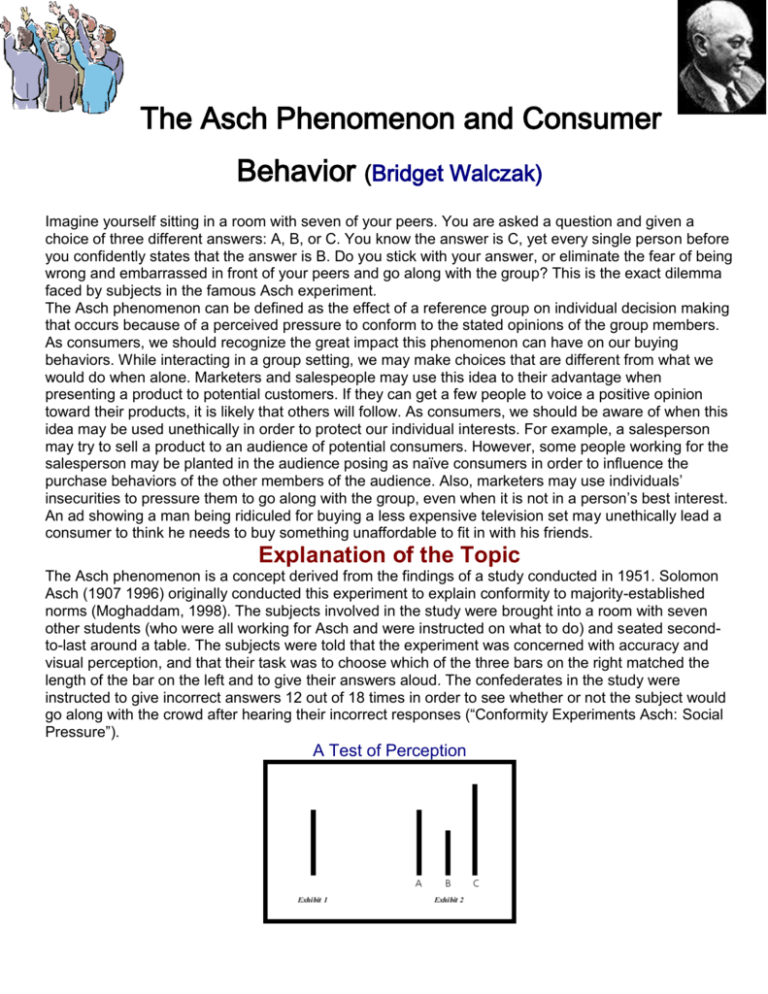
The Asch Phenomenon and Consumer Behavior (Bridget Walczak) Imagine yourself sitting in a room with seven of your peers. You are asked a question and given a choice of three different answers: A, B, or C. You know the answer is C, yet every single person before you confidently states that the answer is B. Do you stick with your answer, or eliminate the fear of being wrong and embarrassed in front of your peers and go along with the group? This is the exact dilemma faced by subjects in the famous Asch experiment. The Asch phenomenon can be defined as the effect of a reference group on individual decision making that occurs because of a perceived pressure to conform to the stated opinions of the group members. As consumers, we should recognize the great impact this phenomenon can have on our buying behaviors. While interacting in a group setting, we may make choices that are different from what we would do when alone. Marketers and salespeople may use this idea to their advantage when presenting a product to potential customers. If they can get a few people to voice a positive opinion toward their products, it is likely that others will follow. As consumers, we should be aware of when this idea may be used unethically in order to protect our individual interests. For example, a salesperson may try to sell a product to an audience of potential consumers. However, some people working for the salesperson may be planted in the audience posing as naïve consumers in order to influence the purchase behaviors of the other members of the audience. Also, marketers may use individuals’ insecurities to pressure them to go along with the group, even when it is not in a person’s best interest. An ad showing a man being ridiculed for buying a less expensive television set may unethically lead a consumer to think he needs to buy something unaffordable to fit in with his friends. Explanation of the Topic The Asch phenomenon is a concept derived from the findings of a study conducted in 1951. Solomon Asch (1907 1996) originally conducted this experiment to explain conformity to majority-established norms (Moghaddam, 1998). The subjects involved in the study were brought into a room with seven other students (who were all working for Asch and were instructed on what to do) and seated secondto-last around a table. The subjects were told that the experiment was concerned with accuracy and visual perception, and that their task was to choose which of the three bars on the right matched the length of the bar on the left and to give their answers aloud. The confederates in the study were instructed to give incorrect answers 12 out of 18 times in order to see whether or not the subject would go along with the crowd after hearing their incorrect responses (“Conformity Experiments Asch: Social Pressure”). A Test of Perception Which line in Exhibit 2 is the same length as the line in Exhibit 1? A series of experiments by Solomon Asch, testing the effects of social pressure on individual perceptions, showed that some people in some situations will go against the evidence of their own senses if the people around them seem to perceive something different. Thirty-seven of the fifty subjects conformed to the majority at least once, and fourteen of them conformed on more than half of the significant trials (“Conformity”). Overall, 35 percent of the subjects’ responses conformed to the group’s incorrect judgments. This is surprising because the control group achieved near perfect accuracy, showing that the task was not inherently difficult. In addition, when the experiment was duplicated allowing the subjects to write down their own judgments privately after hearing the incorrect responses of the group, conformity was drastically reduced (Baxter). The reasons why subjects gave in to group influence hold important ideas for salespeople and marketers. People conform for two main reasons: because they want to be liked by the group and because they believe the group is better informed than they are (“Conformity”). In this study, Asch reported that most of the participants yielded to group pressure because they assumed the majority was right and they were wrong, rather than because they wanted to be accepted by the majority (Levine, 1999). This difference is what separates the Asch phenomenon from the concept of peer pressure. Peer pressure tends to operate more in primary groups in which normative and identification group influences are at work, rather than informational group influences. A brief example may explain the differences between these three types of influences. Informational influence is at work when a person thinks, “I should buy that brand of cereal because my health-conscious friends recommend it as part of a nutritious diet.” Normative influence is at work when a person thinks, “I should buy that brand of cereal so that my friends think that I am also health-conscious, or so they won’t make fun of me for eating badly.” Finally, a person reacting to identification influence would think, “I should buy that brand of cereal because I am a member of Weight Watchers, and all of us value that brand.” Asch’s findings support more of an informational influence, particularly because the conforming subjects did not even know the other members of the group. They just assumed that the group must know something that they did not know, or decided it was easier and safer to go along with the group. The Asch phenomenon occurs even when there is only a perceived pressure to conform. That is, if members go against the group they will not experience any negative consequences. However, when dealing with peer pressure, often individuals who do not conform are ridiculed, humiliated, or excluded by his/her peers. Looking at the Asch study, you can see that while a significant proportion of people conformed, the majority did not. This suggests that some people may be more susceptible to the phenomenon than others, and that certain situations may create this pressure to conform more than others. There are five determinants of reference group influence. If there is visible usage, high relevance of a product to the group, low individual purchase confidence, strong individual commitment to the group, and it is a nonnecessary item, people are much more likely to be influenced by the opinions of the group members (Hawkins, 2004). Imagine shopping by yourself as opposed to shopping with a group of your fashionconscious friends. You notice a red shirt on the rack, but don’t really care for it. One of your friends later picks up the shirt and says, “This shirt is absolutely fabulous.” The other members of the group agree, and soon you find yourself agreeing that you also love the shirt. You do this not only because you want to be accepted by the group, but because you assume the others know more about fashion than you do. In addition, if the shirt is a reasonable price and you are looking for something to wear to a party where everyone will be dressed fashionably, the opinions of the group members will affect your purchase decision even more. The Asch phenomenon has been demonstrated in a variety of settings. In one study, 58 percent of college students were persuaded to agree to the statement that “the right of freedom of speech should be suspended when the Government feels threatened,” even though not one of these subjects held this view privately (Baxter). In another study, students’ perceptions of the nutritional value of a new diet food were influenced by the opinions of other members of a group. When the other students of the group were seen as “experts,” meaning they claimed to be majoring in and had work experience with nutrition, members changed their initial responses to conform to the group even more (Lascu, 1995). Clearly, this phenomenon should not be ignored when advertising a new product or designing a sales campaign, when potential consumers’ opinions are more likely to be swayed. The technique would be useful when potential consumers see others as having greater expertise about the product than they do. However, a great deal of risk in purchasing may cause a consumer to seek out information himself rather than go off of what others say. Therefore, the Asch phenomenon may work ideally in low-expertise and lowinvolvement situations. Examples Examples of the Asch phenomenon can be found throughout the media. When members of a group voice their positive opinions about a product, people are more willing to go along with this stated opinion. For example, Ford Motor Company uses the Asch phenomenon to build greater brand loyalty by providing a section on their website dedicated to personal stories with Ford vehicles. By reading all of the positive stories about Ford cars and trucks, consumers may also feel pressure to think the same way about Fords. Another example of the influence group members may have on individual purchasing decisions comes from the use of infomercials in which a product is displayed to a group of potential customers. At first, the consumers are skeptical that a product could be so easy to use, so convenient, or so inexpensive. However, a consumer is instructed to use a product, is impressed by the product, and says, “Wow, I really can feel my legs and abs getting stronger” or “Wow, this vegetable chopper really does make it easy.” Soon after, other members of the group are going along with the stated opinions of the original users, and people at home begin to agree with the group too, possibly to the point of purchasing the product. Specific companies using this technique include Ronco, Body by Jake, and Tae-bo. Pampered Chef kitchen shows work in a similar way, and depend on stated opinions of kitchen experts and groups of friends. As the host displays and uses a variety of kitchen products, showing how helpful, easy, and fun to use they are, other members of the group may try them out and voice similar opinions. A person who may not have otherwise been excited by a cooking stone or apple corer/peeler/slicer soon finds these products as amazing as the other members of the group, and has ordered them without giving a second thought as to when she will actually use them. People often find it very difficult to go against the positive opinions of movie critics and reviewers. When showing commercials for films, the previews include such statements as “The funniest movie of the year,” “Absolutely phenomenal” or “The best drama since (fill in the blank).” Claims such as these, especially from credible critics and publications, are difficult to disagree with and tend to sway people to go see the movie. For example, a person sees a movie on opening day before it is heavily advertised. This person thinks the movie is ok, but does not recommend it to any friends or family to see. However, after watching several ads on television in which positive claims are made about the movie, the person may change his/her opinion to go along with these claims. Suddenly, the movie seems better, and the individual finds him/herself agreeing with the critics and recommending the movie to others. This may be because he/she does not want to be the only one who thinks differently, or because the critics have greater expertise on movies.








