(14) Heart Structure
advertisement

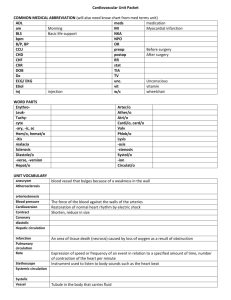
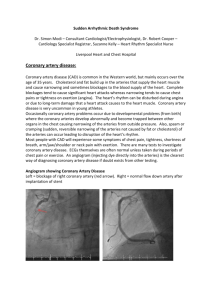
LAB 14 STRUCTURE OF THE HEART Objective: To identify the internal and external structures of the heart and to learn their function. To identify cardiac muscle and name the characteristic features of this muscle type. A. Microscopic Structure of the Heart Observe the prepared slide of cardiac muscle on high power. Draw what you see below and label the listed structures. Answer the following questions. a. b. c. d. branching cardiac fibers (cells) intercalated discs striations nuclei (number per cell?) QUESTIONS 1. Name three features of cardiac muscle that allow you to distinguish it from skeletal muscle. 2. What initiates contraction of cardiac muscle cells? 3. What controls the rate of contraction in cardiac muscle? B. Heart Model, Diagrams and Sheep Heart Use models and diagrams of the external heart and pericardial layers in your text to. Study the listed external features. Locate as many of these features as possible on your sheep heart prior to dissection. 1. Fibrous pericardium 2. Serous pericardium 7. Major vessels a. Aortic arch coronary vessels (cont.) 3. Right and left ventricles d. Superior and inferior vena cava (R) Marginal artery Anterior interventricular artery Posterior interventricular artery Circumflex artery 4. Right and left atria and auricles e. Coronary sinus Great cardiac vein 5. Atrioventricular sulcus f. Coronary vessels: Middle cardiac vein 6. Interventricular sulcus a. Parietal layer b. Pulmonary artery (trunk) b. Visceral layer (epicardium) c. Pulmonary veins (R) and (L) coronary arteries 56 QUESTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. Locate each structure listed below. For any heart chamber or blood vessel listed below, determine whether it contains blood high in oxygen or blood low in oxygen (just returned from the body) and designate which it contains by placing an ‘H’ (high) or an ‘L’ (low) next to each structure on the list. a. Right ventricle k. Inferior vena cava b. Left ventricle l. Coronary sinus c. Right atrium m. (R) coronary arteries d. Left atrium n. (L) coronary arteries e. Atrioventricular sulcus o. (R) marginal artery f. Interventricular sulcus p. Anterior interventricular artery g. Aortic arch q. Posterior interventricular artery h. Pulmonary artery (trunk) r. Circumflex artery i. Pulmonary veins s. Great cardiac vein j. Superior vena cava t. Middle cardiac vein Into what heart chamber do the following vessels dump their blood? a. Coronary sinus b. Inferior and superior vena cava c. Pulmonary veins Where do the following vessels take their blood? a. Pulmonary arteries b. Aorta c. Coronary arteries Which side of the heart is involved in systemic circulation? Which side of the heart is involved in pulmonary circulation? C. Dissection of Sheep Heart Use models, diagrams from your text and the sheep heart to locate and study the following structures of the heart. Cut your sheep heart as directed by your instructor. a. Endocardium, myocardium and epicardium b. Right atrium c. Right ventricle Tricuspid valve Pectinate muscles Trabeculae carnae SA and AV nodes Papillary muscles Coronary sinus orifice Chordae tendinae SVC and IVC orifice Moderator band (sheep) Fossa ovale (foramen prior to birth) Pulmonary trunk opening w/ pulmonary semilunar valve Auricle 57 d. e. Left atrium f. Other structures Pectinate muscles Interatrial septum Pulmonary vein orifices Interventricular septum Auricle Ligamentum arteriosum Left ventricle Bicuspid (mitral) valve Trabeculae carnae Chordae tendinae Opening to aorta w/ aorticsemilunar valve Apex (external feature) QUESTIONS 1. What is the function of the papillary muscles and the chordae tendinae? 2. Within what cavity is the heart located? (Be more specific than thoracic cavity!) 3. The fossa ovale is a remnant of what fetal structure? What is a patent foramen ovale and what is the problem caused by it? 4. Which coronary artery usually gives rise to nodal arteries that supply both the SA and and AV nodes? 5. Which heart chamber has the thickest myocardium? Why? 6. To what vessel do all of the coronary veins return blood? Where does this vessel empty the blood? 7. The ligamentum arteriosum is a remnant of what structure? Where do you find it? 8. Name the two valves that are open as the ventricles contract. 9. The endocardium is continuous with the walls of vessels as which tunic? 58 D. Label the indicated structures on the diagrams. 6 1 5 2 4 3 7 8 9 59 10 11 12 13 14 16 18 15 19 17 21 22 25 20 26 23 24 28 30 27 29 31 32 ANTERIOR VIEW 33 34 35 37 36 39 38 (flap) 40 42 41 43 44 46 45 47 48 50 49 POSTERIOR VIEW 60 51 53 52 54 56 55 58 57 62 59 63 60 61 65 64 66 67 68 70 69 71 INTERIOR VIEW 61