mixed economic systems
advertisement
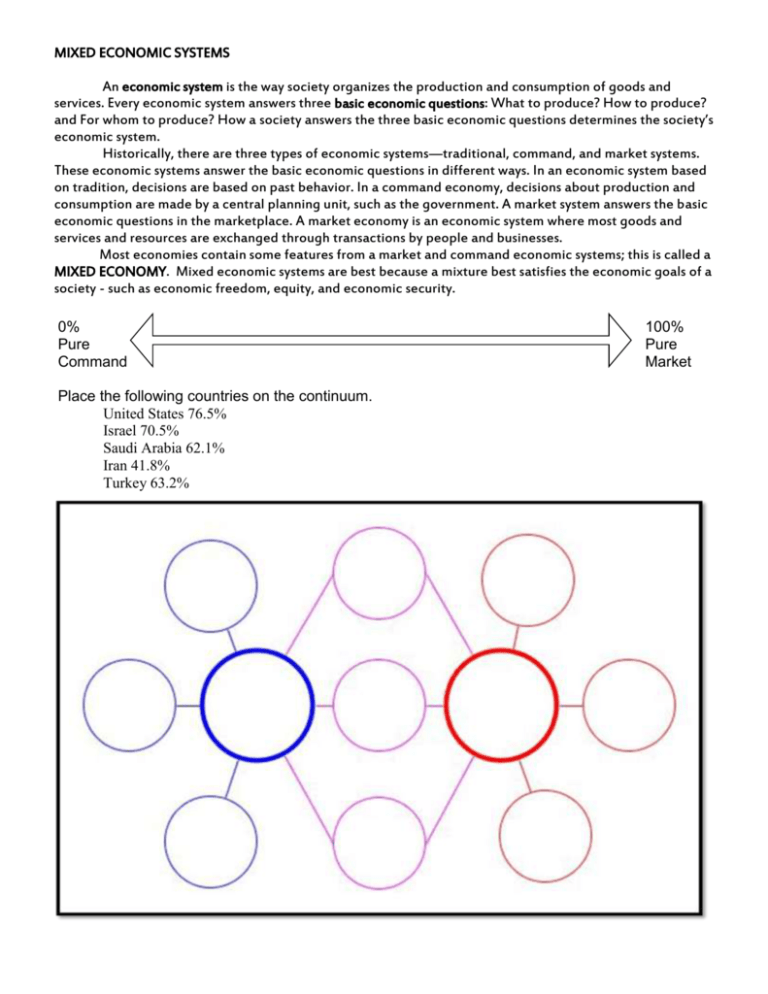
MIXED ECONOMIC SYSTEMS An economic system is the way society organizes the production and consumption of goods and services. Every economic system answers three basic economic questions: What to produce? How to produce? and For whom to produce? How a society answers the three basic economic questions determines the society’s economic system. Historically, there are three types of economic systems—traditional, command, and market systems. These economic systems answer the basic economic questions in different ways. In an economic system based on tradition, decisions are based on past behavior. In a command economy, decisions about production and consumption are made by a central planning unit, such as the government. A market system answers the basic economic questions in the marketplace. A market economy is an economic system where most goods and services and resources are exchanged through transactions by people and businesses. Most economies contain some features from a market and command economic systems; this is called a MIXED ECONOMY. Mixed economic systems are best because a mixture best satisfies the economic goals of a society - such as economic freedom, equity, and economic security. 0% Pure Command Place the following countries on the continuum. United States 76.5% Israel 70.5% Saudi Arabia 62.1% Iran 41.8% Turkey 63.2% 100% Pure Market MIXED ECONOMIC SYSTEMS An economic system is the way society organizes the production and consumption of goods and services. Every economic system answers three basic economic questions: What to produce? How to produce? and For whom to produce? How a society answers the three basic economic questions determines the society’s economic system. Historically, there are three types of economic systems—traditional, command, and market systems. These economic systems answer the basic economic questions in different ways. In an economic system based on tradition, decisions are based on past behavior. In a command economy, decisions about production and consumption are made by a central planning unit, such as the government. A market system answers the basic economic questions in the marketplace. A market economy is an economic system where most goods and services and resources are exchanged through transactions by people and businesses. Most economies contain some features from a market and command economic systems; this is called a MIXED ECONOMY. Mixed economic systems are best because a mixture best satisfies the economic goals of a society - such as economic freedom, equity, and economic security. 1% to 49% “more command than market” 0% pure command 100% pure market 51% to 99% “more market than command” “More Command than Market” What to produce? “More Market than Command” What to produce? Government decides what to produce, BUT private/individual ownership of small business is allowed in limited amounts How to produce? Business owners / leaders decide what to produce based on sales, BUT the government controls some of the decision making How to produce? Government controls most of the means of production (factories and tools), BUT small business owners /leaders make limited decisions on how to produce items Business owners / leaders decide how to produce, BUT the government sets minimum safety requirements, minimum wage, and age to start work (child labor laws). Government also sets guidelines for product safety For whom to produce? For whom to produce? Government determines who receives which goods and services BUT a few items available outside the governments control (black market) EXAMPLES North Korea, Iran Consumer’s incomes determine who gets which goods and services (whoever can buy it) BUT government provides welfare benefits for the needy EXAMPLES Israel, Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, South Africa, China, Japan, India











