Place Value Strategies
advertisement
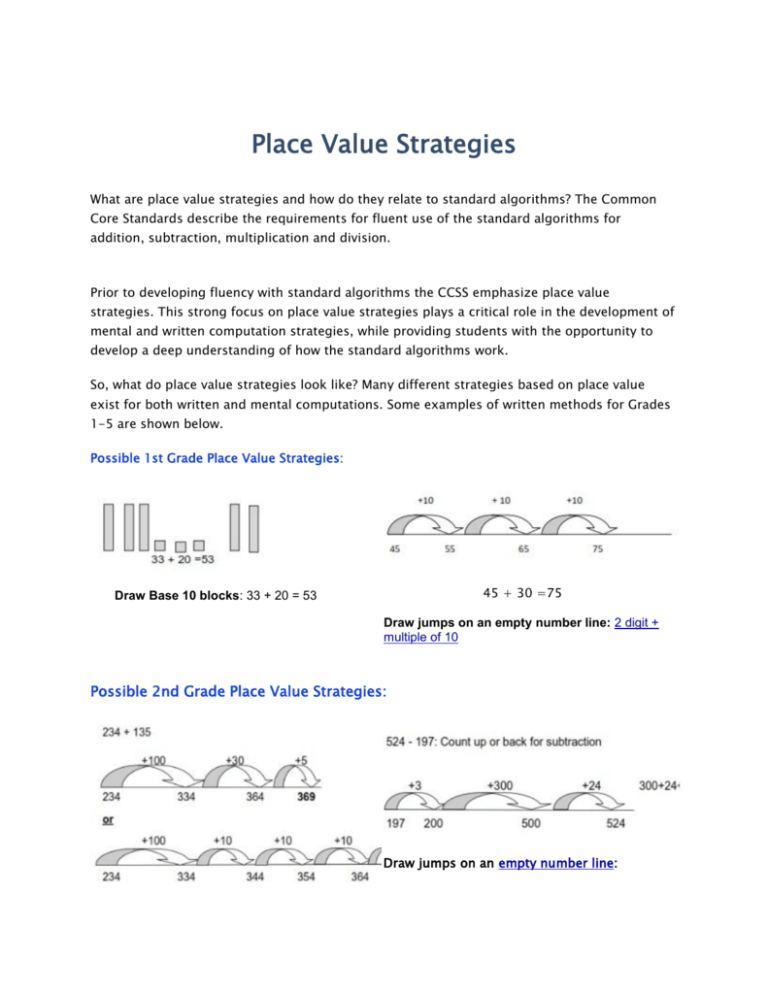
Place Value Strategies What are place value strategies and how do they relate to standard algorithms? The Common Core Standards describe the requirements for fluent use of the standard algorithms for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Prior to developing fluency with standard algorithms the CCSS emphasize place value strategies. This strong focus on place value strategies plays a critical role in the development of mental and written computation strategies, while providing students with the opportunity to develop a deep understanding of how the standard algorithms work. So, what do place value strategies look like? Many different strategies based on place value exist for both written and mental computations. Some examples of written methods for Grades 1-5 are shown below. Possible 1st Grade Place Value Strategies: 45 + 30 =75 Draw Base 10 blocks: 33 + 20 = 53 Draw jumps on an empty number line: 2 digit + multiple of 10 Possible 2nd Grade Place Value Strategies: Draw jumps on an empty number line: 207 Partial Sums (Expanded form layout): Each addend is represented using expanded notation. Like place values are added or subtracted. 123 + 234 = 238 + 473 = 100 + 20 + 3 200 + 30 + 8 + 200 + 30 + 4 + 400 + 70 + 3 300 + 50 + 7 = 357 600 + 100 + 11= 711 548 - 325 614 - 459 500 + 40 + 8 600 + 10 + 4 - 300 + 20 + 5 - 400 + 50 + 9 becomes 200 + 20 + 3 = 223 500 + 100 + 14 - 400 + 50 + 9 100 + 50 + 5= 155 Possible 3rd Grade Place Value Strategies: Partial Differences: Each number is Partial Sums: Expanded Form layout as above or vertical format. represented using expanded notation. Like place values are grouped and subtracted. Negative place values may result. 632+325= 632 + 325 900 752 - 436 523-259= 700 + 50 +2 500 + 20+ 3 - 400+30+6 300+ 20 - 4 = 316 - 200+ 50+9 300 - 30 - 6 = 264 50 7 957 Use multiplication facts and place value Use the distributive property to multiply within to multiply by multiples of ten: 9 x 80 = 100: 15 x 5 = 9 x80 = 9 x 8 tens = 72 tens = 720 9 x80 = 720 15 x 5 = (10 x 5) + (5x5) = 50 + 25 = 75 Possible 4th Grade Place Value Strategies: Partial Products: (2 digit x 2 digit) Area Model: (2 digit x 2 digit) 32 x 34 900 (30 x 30) 120 (30 x 4) 60 (2 x 30) 8 (2 x 4) 1,088 Area Model: (1 digit x 3 digit) 207 207 Partial Quotients: 7725/6 Partition the Dividend: Partition the dividend into multiples of the divisor. 1204 r 1 6) 7225 292/4 - 6000 ( 1000 x 6) 1225 - 1200 (200 x 6) 25 - 24 (4 x 6) 1 70 + 3 = 73 4) 280 + 12 Possible 5th Grade Place Value Strategies: Add decimals on an empty number line: 35.8 + 8.3 = Subtract decimals on an empty number line: (Count up to find the difference) 207 126.4 - 58.7 = Start at 58.7 and jump up 1.3 to 60, then jump 40 to 100, then jump 26.4 to 126.4. Add the jumps: 40 + 26.4 + 1.3 = 67.7 Draw Base-Ten Blocks: Division with decimals Area Model: Multiplying decimals 207 207 Regardless of which place value strategies are taught it is important that there is consistency across each grade level, and that a clear progression is maintained from one grade level to the next within a school. Time needs to be allocated to school wide discussions to ensure that place value strategies are being used or adopted. The following questions can be used to promote discussion and the selection of 1-2 focus strategies per grade for each operation: Which written methods for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division do we currently teach as a school? Do we have enough emphasis on place value strategies throughout the school? Are there written methods we don’t use at the moment? Do we need to adopt them? What mental calculation skills are needed in order for students to use written methods based on place value? Do our students have the necessary mental calculations skills needed? How can we develop whole school agreement on the written methods that we will teach for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division? How will consistency and progression be maintained?