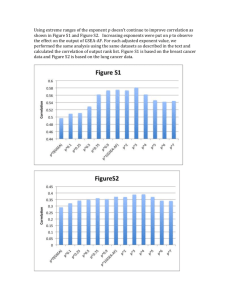
Power Exponent Rational Number Integer Base (of an exponential
advertisement
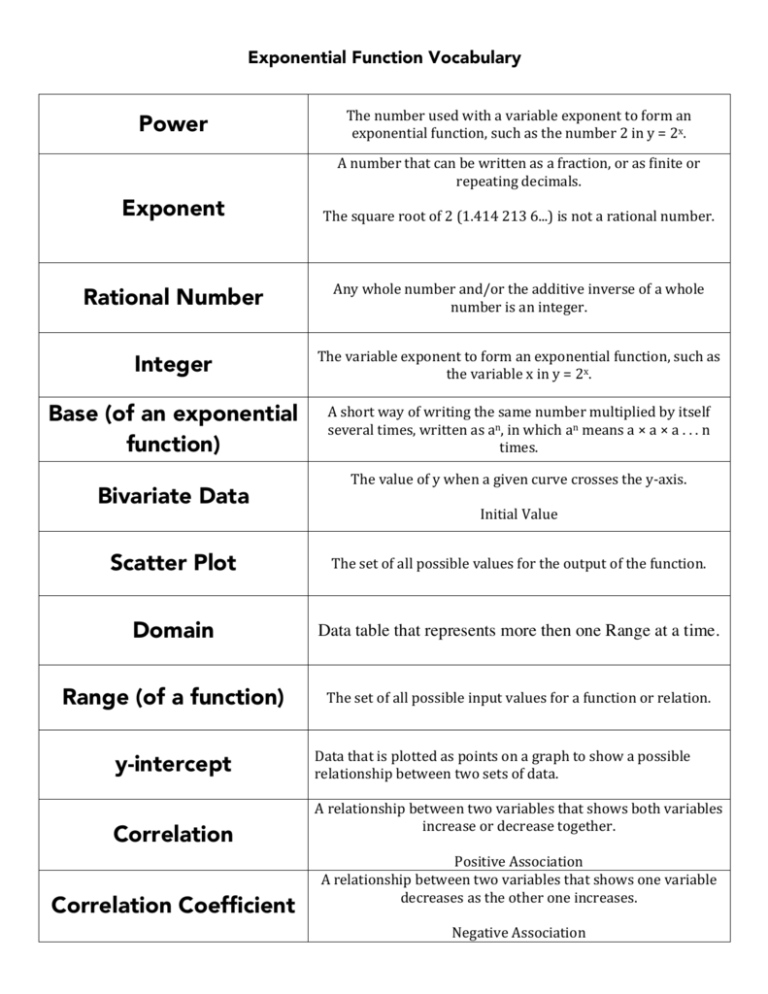
Exponential Function Vocabulary Power The number used with a variable exponent to form an exponential function, such as the number 2 in y = 2x. A number that can be written as a fraction, or as finite or repeating decimals. Exponent The square root of 2 (1.414 213 6...) is not a rational number. Rational Number Any whole number and/or the additive inverse of a whole number is an integer. Integer The variable exponent to form an exponential function, such as the variable x in y = 2x. Base (of an exponential function) A short way of writing the same number multiplied by itself several times, written as an, in which an means a × a × a . . . n times. Bivariate Data The value of y when a given curve crosses the y-­‐axis. Initial Value Scatter Plot The set of all possible values for the output of the function. Domain Data table that represents more then one Range at a time. Range (of a function) The set of all possible input values for a function or relation. y-intercept Correlation Correlation Coefficient Data that is plotted as points on a graph to show a possible relationship between two sets of data. A relationship between two variables that shows both variables increase or decrease together. Positive Association A relationship between two variables that shows one variable decreases as the other one increases. Negative Association Positive Correlation The rate becomes ever more rapid in proportion to the growing total number or size Negative Correlation A number between -­‐1 and 1 that represents how strong or weak the correlation of a scatter plot matches the line of best fit. Exponential Growth A relation between two variables that vary together. If one variable always increases as the other increases, the relationship is said to be positive or direct. Otherwise, the relationship is negative or inverse. The output number of a function. Its value depends on the given function and the chosen value(s) for the independent variable(s). Exponential Decay For example, in y = f(x) = 2x, x is the independent variable, and y is the dependent variable. You are free to choose any value for x as long as it is in the domain of the function. However, the value of y has to change as x changes. When x = 1, y = 2x = 2. Independent Variable Percent change is the extent to which something gains or loses value. Dependent Variable Intuitively, a straight line drawn through as near as possible to the various points on a scatter diagram so as to best represent the trend. A function whose exponent involves at least one variable. Line of Best Fit For example, f(x) = 2x+1. Percent Rate of Change Exponential Function A decrease that follows an exponential function. A variable that can change its value freely and first without being affected by any other variable(s) for its value. Usually, an independent variable is the input to a function and is normally denoted by the symbol x while y is often reserved for the dependent variable. For example, in y = f(x) = x2, x is the independent variable and y is the dependent variable. The variable x is allowed to change freely while the value of y has to change as x changes. http://www.mathematicsdictionary.com/math-­‐vocabulary.htm